Does heterochromatin protein 1 always follow code? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2002 Dec 10;99 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):16462-9.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.162371699. Epub 2002 Jul 31.
Affiliations
- PMID: 12151603
- PMCID: PMC139909
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.162371699
Review
Does heterochromatin protein 1 always follow code?
Yuhong Li et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002.
Abstract
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is a conserved chromosomal protein that participates in chromatin packaging and gene silencing. A loss of HP1 leads to lethality in Drosophila and correlates with metastasis in human breast cancer cells. On Drosophila polytene chromosomes HP1 is localized to centric regions, telomeric regions, in a banded pattern along the fourth chromosome, and at many sites scattered throughout the euchromatic arms. Recently, one mechanism of HP1 chromosome association was revealed; the amino-terminal chromo domain of HP1 interacts with methylated lysine nine of histone H3, consistent with the histone code hypothesis. Compelling data support this mechanism of HP1 association at centric regions. Is this the only mechanism by which HP1 associates with chromosomes? Interest is now shifting toward the role of HP1 within euchromatic domains. Accumulating evidence in Drosophila and mammals suggests that HP1 associates with chromosomes through interactions with nonhistone chromosomal proteins at locations other than centric heterochromatin. Does HP1 play a similar role in chromatin packaging and gene regulation at these sites as it does in centric heterochromatin? Does HP1 associate with the same proteins at these sites as it does in centric heterochromatin? A first step toward answering these questions is the identification of sequences associated with HP1 within euchromatic domains. Such sequences are likely to include HP1 "target genes" whose discovery will aid in our understanding of HP1 lethality in Drosophila and metastasis of breast cancer cells.
Figures
Figure 1
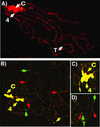
(A) Pattern of HP1 distribution on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. D. melanogaster larval polytene chromosomes were stained with mouse monoclonal C1A9 antibodies against HP1 (gift of Sarah C. R. Elgin) and a secondary antibody conjugated with rhodamine. The chromocenter (C), the fourth chromosome (indicated by 4), telomeres (T), and euchromatic sites associated with HP1. (B) The pattern of HP1 and methylated lysine nine of histone H3 on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. D. melanogaster larval polytene chromosomes were stained with mouse monoclonal C1A9 antibody against HP1 and a rabbit polyclonal antibody that recognizes methylated lysine nine of histone H3 (gift of C. David Allis, University of Virginia, Charlottesville). A Cy5-conjugated rabbit secondary antibody and a FITC-conjugated mouse secondary antibody were used for detection. The chromocenter (C) and the fourth chromosome (indicated by 4) show strong colocalization (yellow). Example locations enriched in HP1 are denoted by green arrows; example locations enriched in methylated lysine nine of histone H3 are indicated by red arrows. (C) Same as in B, showing a closer view of the chromocenter region. (D) Same as in B, showing a closer view of a telomeric region.
Figure 2
Diagram of HP1 proteins in Drosophila, mouse, human, and S. pombe. Total length of each protein is indicated and drawn to relative scale. Percent identity when compared with Drosophila HP1 over the full length (total), or the CD, CSD, or the hinge region was calculated according to ref. .
Figure 3
Models for HP1 association and nonassociation with chromosomes. (A) Interaction between the HP1 CD with the methylated lysine nine of histone H3. HP1 serves as a bridge for partner proteins. (B) HP1 interacts with histones in a nonmethylated-dependent fashion. (C) HP1 associates with chromosomes through interactions of the CSD and DNA binding proteins, such as zinc-finger proteins (ZNF). (D) HP1 does not associate with methylated histones that have additional modifications such as acetylation or phosphorylation.
Similar articles
- Effects of tethering HP1 to euchromatic regions of the Drosophila genome.
Li Y, Danzer JR, Alvarez P, Belmont AS, Wallrath LL. Li Y, et al. Development. 2003 May;130(9):1817-24. doi: 10.1242/dev.00405. Development. 2003. PMID: 12642487 - Role of Drosophila HP1 in euchromatic gene expression.
Cryderman DE, Grade SK, Li Y, Fanti L, Pimpinelli S, Wallrath LL. Cryderman DE, et al. Dev Dyn. 2005 Mar;232(3):767-74. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20310. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 15704177 - Chromosomal distribution of heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) in Drosophila: a cytological map of euchromatic HP1 binding sites.
Fanti L, Berloco M, Piacentini L, Pimpinelli S. Fanti L, et al. Genetica. 2003 Mar;117(2-3):135-47. doi: 10.1023/a:1022971407290. Genetica. 2003. PMID: 12723693 - Heterochromatin protein 1: don't judge the book by its cover!
Hediger F, Gasser SM. Hediger F, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006 Apr;16(2):143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.02.013. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006. PMID: 16503133 Review. - HP1: a functionally multifaceted protein.
Fanti L, Pimpinelli S. Fanti L, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008 Apr;18(2):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2008.01.009. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008. PMID: 18329871 Review.
Cited by
- Heterochromatin protein 1 promotes self-renewal and triggers regenerative proliferation in adult stem cells.
Zeng A, Li YQ, Wang C, Han XS, Li G, Wang JY, Li DS, Qin YW, Shi Y, Brewer G, Jing Q. Zeng A, et al. J Cell Biol. 2013 Apr 29;201(3):409-25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201207172. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23629965 Free PMC article. - HP1β carries an acidic linker domain and requires H3K9me3 for phase separation.
Qin W, Stengl A, Ugur E, Leidescher S, Ryan J, Cardoso MC, Leonhardt H. Qin W, et al. Nucleus. 2021 Dec;12(1):44-57. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2021.1889858. Nucleus. 2021. PMID: 33660589 Free PMC article. - Tethering of HP1 proteins to chromatin is relieved by phosphoacetylation of histone H3.
Mateescu B, England P, Halgand F, Yaniv M, Muchardt C. Mateescu B, et al. EMBO Rep. 2004 May;5(5):490-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400139. Epub 2004 Apr 23. EMBO Rep. 2004. PMID: 15105826 Free PMC article. - Functional cooperation between HP1 and DNMT1 mediates gene silencing.
Smallwood A, Estève PO, Pradhan S, Carey M. Smallwood A, et al. Genes Dev. 2007 May 15;21(10):1169-78. doi: 10.1101/gad.1536807. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17470536 Free PMC article. - Human genome replication proceeds through four chromatin states.
Julienne H, Zoufir A, Audit B, Arneodo A. Julienne H, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(10):e1003233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003233. Epub 2013 Oct 10. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 24130466 Free PMC article.
References
- Richards E J, Elgin S C. Cell. 2002;108:489–500. - PubMed
- Jeppesen P, Mitchell A, Turner B, Perry P. Chromosoma. 1992;101:322–332. - PubMed
- Turner B M, Birley A J, Lavender J. Cell. 1992;69:375–384. - PubMed
- Cheung P, Tanner K G, Cheung W L, Sassone-Corsi P, Denu J M, Allis C D. Mol Cell. 2000;5:905–915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials