Mitotic-specific methylation of histone H4 Lys 20 follows increased PR-Set7 expression and its localization to mitotic chromosomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mitotic-specific methylation of histone H4 Lys 20 follows increased PR-Set7 expression and its localization to mitotic chromosomes
Judd C Rice et al. Genes Dev. 2002.
Abstract
We describe distinct patterns of histone methylation during human cell cycle progression. Histone H4 methyltransferase activity was found to be cell cycle-regulated, consistent with increased H4 Lys 20 methylation at mitosis. This increase closely followed the cell cycle-regulated expression of the H4 Lys 20 methyltransferase, PR-Set7. Localization of PR-Set7 to mitotic chromosomes and subsequent increase in H4 Lys 20 methylation were inversely correlated to transient H4 Lys 16 acetylation in early S-phase. These data suggest that H4 Lys 20 methylation by PR-Set7 during mitosis acts to antagonize H4 Lys 16 acetylation and to establish a mechanism by which this mark is epigenetically transmitted.
Figures
Figure 1
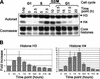
Increased histone H3 and H4 methyltransferase activity during human cell cycle progression. (A) In nucleo assay in synchronized HeLa cells. Cells were released from G1 arrest and analyzed every 2.5 h. The cell cycle phase was confirmed by FACS. Autoradiography indicates the HMT activity specific for histones H3 and H4 at distinct phases in the cell cycle (top panel). Coomassie-stained core histones represent the loading control (bottom panel). (B) Quantitative assessment of HMT activity during the cell cycle. The changes in HMT activity relative to G1 were determined (see text for details). The _X_-axis is the time in hours after release from G1 arrest, and the _Y_-axis represents the fold increase in HMT activity relative to G1 for both histone H3 (left) and H4 (right). This experiment was performed twice with similar results as shown by the error bars.
Figure 2
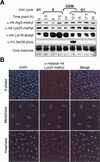
Histone H4 Lys 20 methylation decreases at mid-S-phase and increases during mitosis. (A) Analysis of histone H4 modifications in synchronized HeLa cells. Cells were released from G1 arrest and analyzed every 2.5 h. The cell cycle phase was confirmed by FACS. The relative protein levels of histone H4 arginine 3-methyl, H4 Lys 20-methyl, H4 Lys 16-acetyl, and the H3 serine 28-phos modifications were determined by Western blot. Ponceau-stained core histones represent the loading control (bottom panel). This experiment was performed ≥2 times for each antibody. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of histone H4 Lys 20 methylation (red) in Drosophila embryos. The cell cycle phase was determined by DAPI staining (blue).
Figure 3
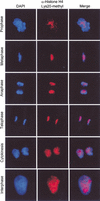
Histone H4 Lys 20 methylation occurs prior to or during metaphase. Immunofluorescence staining of histone H4 Lys 20 methylation (red) in mitotic and interphase HeLa cells. The cell cycle phase was determined by DAPI staining (blue).
Figure 4
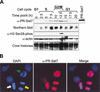
PR-Set7 localizes to mitotic chromosomes and is cell cycle regulated. (A) Analysis of PR-Set7 RNA and protein expression in synchronized HeLa cells. Cells were released from G1 arrest and analyzed every 2.5 h. The cell cycle phase was confirmed by FACS. Northern analysis was performed with a probe generated against the PR-Set7 open reading frame. The relative protein levels of PR-Set7, phosphorylated histone H3 serine 28, and actin (loading control) were determined by Western blot. The shift in molecular weight of the recombinant PR-Set7 protein is owing to its fusion product. This experiment was performed ≥2 times for each antibody. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of PR-Set7 (red) in HeLa cells. The cell cycle phase was determined by DAPI staining (blue). The green arrow indicates prometaphase, the white arrow indicates metaphase, and the yellow arrow indicates anaphase.
Similar articles
- PR-Set7-dependent methylation of histone H4 Lys 20 functions in repression of gene expression and is essential for mitosis.
Karachentsev D, Sarma K, Reinberg D, Steward R. Karachentsev D, et al. Genes Dev. 2005 Feb 15;19(4):431-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.1263005. Epub 2005 Jan 28. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15681608 Free PMC article. - PR-Set7 is a nucleosome-specific methyltransferase that modifies lysine 20 of histone H4 and is associated with silent chromatin.
Nishioka K, Rice JC, Sarma K, Erdjument-Bromage H, Werner J, Wang Y, Chuikov S, Valenzuela P, Tempst P, Steward R, Lis JT, Allis CD, Reinberg D. Nishioka K, et al. Mol Cell. 2002 Jun;9(6):1201-13. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00548-8. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12086618 - A switch in mitotic histone H4 lysine 20 methylation status is linked to M phase defects upon loss of HCF-1.
Julien E, Herr W. Julien E, et al. Mol Cell. 2004 Jun 18;14(6):713-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.008. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15200950 - Coupling mitosis to DNA replication: the emerging role of the histone H4-lysine 20 methyltransferase PR-Set7.
Brustel J, Tardat M, Kirsh O, Grimaud C, Julien E. Brustel J, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;21(8):452-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.04.006. Epub 2011 May 31. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21632252 Review. - PR-Set7 and H4K20me1: at the crossroads of genome integrity, cell cycle, chromosome condensation, and transcription.
Beck DB, Oda H, Shen SS, Reinberg D. Beck DB, et al. Genes Dev. 2012 Feb 15;26(4):325-37. doi: 10.1101/gad.177444.111. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22345514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Preferential dimethylation of histone H4 lysine 20 by Suv4-20.
Yang H, Pesavento JJ, Starnes TW, Cryderman DE, Wallrath LL, Kelleher NL, Mizzen CA. Yang H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2008 May 2;283(18):12085-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707974200. Epub 2008 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18296440 Free PMC article. - Comparative distributions of RSBN1 and methylated histone H4 Lysine 20 in the mouse spermatogenesis.
Wang Y, Iwamori T, Kaneko T, Iida H, Iwamori N. Wang Y, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Jun 29;16(6):e0253897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253897. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34185806 Free PMC article. - The retinoblastoma protein regulates pericentric heterochromatin.
Isaac CE, Francis SM, Martens AL, Julian LM, Seifried LA, Erdmann N, Binné UK, Harrington L, Sicinski P, Bérubé NG, Dyson NJ, Dick FA. Isaac CE, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2006 May;26(9):3659-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.9.3659-3671.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16612004 Free PMC article. - Histone H4K20 Trimethylation Is Decreased in Murine Models of Heart Disease.
Hickenlooper SM, Davis K, Szulik MW, Sheikh H, Miller M, Valdez S, Bia R, Franklin S. Hickenlooper SM, et al. ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 23;7(35):30710-30719. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00984. eCollection 2022 Sep 6. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36092581 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of the SET8 Pathway Ameliorates Lung Fibrosis Even Through Fibroblast Dedifferentiation.
Ugai K, Matsuda S, Mikami H, Shimada A, Misawa T, Nakamura H, Tatsumi K, Hatano M, Murayama T, Kasuya Y. Ugai K, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Aug 5;7:192. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00192. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32850975 Free PMC article.
References
- Aparicio OM, Gottschling DE. Overcoming telomeric silencing: A trans-activator competes to establish gene expression in a cell cycle-dependent way. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:1133–1146. - PubMed
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
- Fang J, Feng Q, Ketel CS, Wang H, Cao R, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Simon JA, Zhang Y. Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1086–1099. - PubMed
- Georgi AB, Stukenberg PT, Kirschner MW. Timing of events in mitosis. Curr Biol. 2002;12:105–114. - PubMed
- Goto H, Tomono Y, Ajiro K, Kosako H, Fujita M, Sakurai M, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Okigaki T, Takahashi T, et al. Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on histone H3 coupled with mitotic chromosome condensation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:25543–25549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM-53512/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM037120/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-64279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM064279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM053512/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM037120/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials