Identifying novel transcripts and novel genes in the human genome by using novel SAGE tags - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identifying novel transcripts and novel genes in the human genome by using novel SAGE tags
Jianjun Chen et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002.
Abstract
The number of genes in the human genome is still a controversial issue. Whereas most of the genes in the human genome are said to have been physically or computationally identified, many short cDNA sequences identified as tags by use of serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) do not match these genes. By performing experimental verification of more than 1,000 SAGE tags and analyzing 4,285,923 SAGE tags of human origin in the current SAGE database, we examined the nature of the unmatched SAGE tags. Our study shows that most of the unmatched SAGE tags are truly novel SAGE tags that originated from novel transcripts not yet identified in the human genome, including alternatively spliced transcripts from known genes and potential novel genes. Our study indicates that by using novel SAGE tags as probes, we should be able to identify efficiently many novel transcripts/novel genes in the human genome that are difficult to identify by conventional methods.
Figures
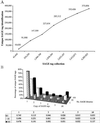
Fig 1.
Analyses of the SAGE tags collected from the 101 human SAGE libraries. (A) Relationship between SAGE tag collection and unique SAGE tag identification. The total SAGE tags and unique SAGE tags were extracted from 1, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 101 human SAGE libraries and used for comparison. (B) Changes in frequency of unique SAGE tags with increasing SAGE tag numbers. Unique SAGE tags from 1, 10, and 101 SAGE libraries were divided into groups based on copy number; the rate of unique SAGE tags in each group is illustrated in the bar graph.
Fig 2.
Genomic confirmation of novel full-length cDNAs converted from novel SAGE tags. Full-length cDNAs were generated from 3′ cDNAs converted from novel SAGE tags and matched to human genomic sequences. (A) The full-length cDNA originating from novel SAGE tag GTTCACACGG matches exactly the antisense strand of the β-2 microglobin (B2M) gene. (B) Match of a full-length cDNA originating from novel SAGE tag TTTTAGGTGG partially overlapping with predicted exons, but with no matches with known mRNA or EST.
Similar articles
- Pan-genome isolation of low abundance transcripts using SAGE tag.
Kim YC, Jung YC, Xuan Z, Dong H, Zhang MQ, Wang SM. Kim YC, et al. FEBS Lett. 2006 Dec 11;580(28-29):6721-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.11.013. Epub 2006 Nov 14. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 17113583 Free PMC article. - [Transcriptomes for serial analysis of gene expression].
Marti J, Piquemal D, Manchon L, Commes T. Marti J, et al. J Soc Biol. 2002;196(4):303-7. J Soc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12645300 Review. French. - Computational Analysis of Gene Identification with SAGE.
Clark T, Lee S, Ridgway Scott L, Wang SM. Clark T, et al. J Comput Biol. 2002;9(3):513-26. doi: 10.1089/106652702760138600. J Comput Biol. 2002. PMID: 12162890 - High-throughput GLGI procedure for converting a large number of serial analysis of gene expression tag sequences into 3' complementary DNAs.
Chen J, Lee S, Zhou G, Wang SM. Chen J, et al. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002 Mar;33(3):252-61. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10017. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11807982 - The new role of SAGE in gene discovery.
Boheler KR, Stern MD. Boheler KR, et al. Trends Biotechnol. 2003 Feb;21(2):55-7; discussion 57-8. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7799(02)00031-8. Trends Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12573851 Review.
Cited by
- Digital gene expression approach over multiple RNA-Seq data sets to detect neoblast transcriptional changes in Schmidtea mediterranea.
Rodríguez-Esteban G, González-Sastre A, Rojo-Laguna JI, Saló E, Abril JF. Rodríguez-Esteban G, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015 May 8;16(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1533-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25952370 Free PMC article. - Identification of novel androgen-responsive genes by sequencing of LongSAGE libraries.
Romanuik TL, Wang G, Holt RA, Jones SJ, Marra MA, Sadar MD. Romanuik TL, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Oct 15;10:476. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-476. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19832994 Free PMC article. - Pan-genome isolation of low abundance transcripts using SAGE tag.
Kim YC, Jung YC, Xuan Z, Dong H, Zhang MQ, Wang SM. Kim YC, et al. FEBS Lett. 2006 Dec 11;580(28-29):6721-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.11.013. Epub 2006 Nov 14. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 17113583 Free PMC article. - The gene expression patterns of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Li S, Jiang W, Huang R, Wang X, Liu W, Shen S. Li S, et al. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2007 Aug;27(4):367-71. doi: 10.1007/s11596-007-0405-6. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17828488 - The X chromosome is organized into a gene-rich outer rim and an internal core containing silenced nongenic sequences.
Clemson CM, Hall LL, Byron M, McNeil J, Lawrence JB. Clemson CM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 16;103(20):7688-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601069103. Epub 2006 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16682630 Free PMC article.
References
- Lander E. S., Linton, L. M., Birren, B., Nusbaum, C., Zody, M. C., Baldwin, J., Devon, K., Dewar, K., Doyle, M., FitzHugh, W., et al. (2001) Nature (London) 409, 860-921. - PubMed
- Venter J. C., Adams, M. D., Myers, E. W., Li, P. W., Mural, R. J., Sutton, G. G., Smith, H. O., Yandell, M., Evans, C. A., Holt, R. A., et al. (2001) Science 291, 1304-1351. - PubMed
- Hogenesch J. B., Ching, K. A., Batalov, S., Su, A. I., Walker, J. R., Zhou, Y., Kay, S. A., Schultz, P. G. & Cooke, M. P. (2001) Cell 106, 413-415. - PubMed
- Kapranov P., Cawley, , Simon, E., Drenkow, J., Bekiranov, S., Strausberg, R. L., Fodor, S. P. A. & Gingeras, T. R. (2002) Science 296, 916-919. - PubMed
- Adams M. D., Kelley, J. M., Gocayne, J. D., Dubnick, M., Polymeropoulos, M. H., Xiao, H., Merril, C. R., Wu, A., Olde, B., Moreno, R. F., et al. (1991) Science 252, 1651-1656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources