Environmental enrichment reverses the effects of maternal separation on stress reactivity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Environmental enrichment reverses the effects of maternal separation on stress reactivity
Darlene D Francis et al. J Neurosci. 2002.
Abstract
Postnatal maternal separation increases hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) gene expression and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) and behavioral responses to stress. We report here that environmental enrichment during the peripubertal period completely reverses the effects of maternal separation on both HPA and behavioral responses to stress, with no effect on CRF mRNA expression. We conclude that environmental enrichment leads to a functional reversal of the effects of maternal separation through compensation for, rather than reversal of, the neural effects of early life adversity.
Figures
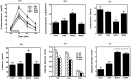
Fig. 1.
a, Mean ± SEM plasma level of corticosterone (in micrograms per deciliters;n = 8 per group) in response to a 20 min period of restraint stress (open bar) in H and MS animals reared under standard lab procedures (Ctl) or environmental enrichment (EE) during postnatal days 22–70 and tested on days 110–120. b, Mean ± SEM area-under-the-curve analysis for the corticosterone data displayed in_a_ calculated using the trapezoidal rule.c, Mean ± SEM time spent exploring the inner area of a 2 × 2 m novel open-field environment (n = 8–10 per group). d, Mean ± SEM latency to begin eating food presented to food-deprived animals in a novel environment (n = 8–9 per group).e, Mean ± SEM levels of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA in the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA1 and CA3 cell fields of the hippocampus, expressed as optical density units, on autoradiograms from in situ hybridization studies with a35S-labeled riboprobe for the rat glucocorticoid receptor (n = 3–5 per group). f, Mean ± SEM levels of CRF mRNA in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, expressed as optical density units, on autoradiograms from in situ hybridization studies with a35S-labeled oligonucleotide probe for the rat CRF (n = 3–5 per group).
Similar articles
- Differential neuroendocrine responses to chronic variable stress in adult Long Evans rats exposed to handling-maternal separation as neonates.
Ladd CO, Thrivikraman KV, Huot RL, Plotsky PM. Ladd CO, et al. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2005 Jul;30(6):520-33. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2004.12.004. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15808921 - Differential and age-dependent effects of maternal deprivation on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of brown norway rats from youth to senescence.
Workel JO, Oitzl MS, Fluttert M, Lesscher H, Karssen A, de Kloet ER. Workel JO, et al. J Neuroendocrinol. 2001 Jul;13(7):569-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2001.00668.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11442771 - Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress.
Liu D, Diorio J, Tannenbaum B, Caldji C, Francis D, Freedman A, Sharma S, Pearson D, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ. Liu D, et al. Science. 1997 Sep 12;277(5332):1659-62. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5332.1659. Science. 1997. PMID: 9287218 - Early environmental regulation of forebrain glucocorticoid receptor gene expression: implications for adrenocortical responses to stress.
Meaney MJ, Diorio J, Francis D, Widdowson J, LaPlante P, Caldji C, Sharma S, Seckl JR, Plotsky PM. Meaney MJ, et al. Dev Neurosci. 1996;18(1-2):49-72. doi: 10.1159/000111395. Dev Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8840086 Review. - Developmental plasticity of HPA and fear responses in rats: a critical review of the maternal mediation hypothesis.
Macrì S, Würbel H. Macrì S, et al. Horm Behav. 2006 Dec;50(5):667-80. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2006.06.015. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Horm Behav. 2006. PMID: 16890940 Review.
Cited by
- Enriched environment alleviates adolescent visceral pain, anxiety- and depression-like behaviors induced by neonatal maternal separation.
Ji NN, Xia M. Ji NN, et al. Transl Pediatr. 2022 Aug;11(8):1398-1407. doi: 10.21037/tp-22-410. Transl Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36072545 Free PMC article. - Effects of Maternal Deprivation and Complex Housing on Rat Social Behavior in Adolescence and Adulthood.
Kentrop J, Smid CR, Achterberg EJM, van IJzendoorn MH, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Joëls M, van der Veen R. Kentrop J, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Sep 11;12:193. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00193. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30254573 Free PMC article. - Early life stress and serotonin transporter gene variation interact to affect the transcription of the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors, and the co-chaperone FKBP5, in the adult rat brain.
van der Doelen RH, Calabrese F, Guidotti G, Geenen B, Riva MA, Kozicz T, Homberg JR. van der Doelen RH, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Oct 13;8:355. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00355. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25352794 Free PMC article. - Pre-reproductive maternal enrichment influences offspring developmental trajectories: motor behavior and neurotrophin expression.
Caporali P, Cutuli D, Gelfo F, Laricchiuta D, Foti F, De Bartolo P, Mancini L, Angelucci F, Petrosini L. Caporali P, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 May 30;8:195. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00195. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24910599 Free PMC article. - Why and how the early-life environment affects development of coping behaviours.
Langenhof MR, Komdeur J. Langenhof MR, et al. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 2018;72(3):34. doi: 10.1007/s00265-018-2452-3. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 2018. PMID: 29449757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bakshi VP, Shelton SE, Kalin NH. Neurobiological correlates of defensive behaviors. Prog Brain Res. 2000;122:105–115. - PubMed
- Blier P, de Montigny C. Serotonin and drug-induced therapeutic responses in major depression, obsessive-compulsive and panic disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:91S–98S. - PubMed
- Britton DR, Thatcher-Britton R. A sensitive-open-field measure of anxiolytic drug action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1981;15:577–580. - PubMed
- Caldji C, Francis D, Sharma S, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ. The effects of early rearing environment on the development of GABAA and central benzodiazepine receptor levels and novelty-induced fearfulness in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000;22:219–229. - PubMed
- Chapillon P, Manneche C, Belzung C, Caston J. Rearing environmental enrichment in two inbred strains of mice. I. Effects on emotional reactivity. Behav Genet. 1999;29:41–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources