Synthesis of stable-isotope enriched 5-methylpyrimidines and their use as probes of base reactivity in DNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Synthesis of stable-isotope enriched 5-methylpyrimidines and their use as probes of base reactivity in DNA
Artur Burdzy et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002.
Abstract
A specific and efficient method is presented for the conversion of 2'-deoxyuridine to thymidine via formation and reduction of the intermediate 5-hydroxymethyl derivative. The method has been used to generate both thymidine and 5-methyl-2'-deoxycytidine containing the stable isotopes 2H, 13C and 15N. Oligodeoxyribonucleotides have been constructed with these mass-tagged bases to investigate sequence-selectivity in hydroxyl radical reactions of pyrimidine methyl groups monitored by mass spectrometry. Studying the reactivity of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) is difficult as the reaction products can deaminate to the corresponding thymine derivatives, making the origin of the reaction products ambiguous. The method reported here can distinguish products derived from 5mC and thymine as well as investigate differences in reactivity for either base in different sequence contexts. The efficiency of formation of 5-hydroxymethyluracil from thymine is observed to be similar in magnitude in two different sequence contexts and when present in a mispair with guanine. The oxidation of 5mC proceeds slightly more efficiently than that of thymine and generates both 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-formylcytosine but not the deaminated products. Thymine glycol is generated by both thymine and 5mC, although with reduced efficiency for 5mC. The method presented here should be widely applicable, enabling the examination of the reactivity of selected bases in DNA.
Figures
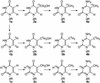
Figure 1
Synthesis of 5-substituted pyrimidine derivatives labeled with 13C, 15N and 2H atoms.
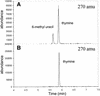
Figure 2
Methyl pyrimidine reaction products obtained from direct methylation of 2′-dU and via formation and reduction of 5-hydroxymethyl-2′-dU. Products were hydrolyzed in formic acid, converted to the TMS derivative and analyzed by GC/MS. The selective ion profile (270 amu) for products of the Bergstrom method (A) and for our products (B) are shown.
Figure 3
Sequences of self-complementary ODNs used for oxidation by Fenton-type reagent, where M = 5mC and T = 15N2-thymine (enriched). (A) Sequence 1: ODN containing enriched thymine at the inner positions (T:A base pair) and unenriched thymine (in a T:A base pair) at the outer position. (B) Sequence 2: ODN containing enriched thymine (inner positions, T:A base pair) and unenriched thymine at the outer position (T:G mispair). (C) Sequence 3: ODN containing enriched thymine (inner positions, T:A base pair) and unenriched 5mC (outer position, 5mC:G base pair).
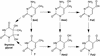
Figure 4
Reaction pathways for thymine and 5mC.
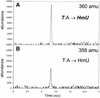
Figure 5
Formation of HmU in T:A base pairs. GC/MS trace at 360 amu (A) and 358 amu (B) of a silylated hydrolysate of duplex sequence 1 containing T:A base pair treated with Fe(III)NTA/H2O2/ascorbic acid.
Figure 6
Formation of HmU from a T:A base pair and formation of HmC and FoC from a 5mC:G base pair. GC/MS trace at 360 amu (A), 357 amu (B) and 268 amu (C) of a silylated hydrolysate of duplex sequence 3 (containing a 5mC:G base pair) treated with Fe(III)NTA/H2O2/ascorbic acid.
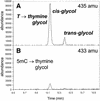
Figure 7
Formation of thymine glycol from T:A and 5mC:G base pairs. GC/MS trace at 435 amu (A) and 433 amu (B) of a silylated hydrolysate of duplex sequence 3 Fe(III)NTA/H2O2/ascorbic acid.
Similar articles
- Hydroxyl-radical-induced oxidation of 5-methylcytosine in isolated and cellular DNA.
Madugundu GS, Cadet J, Wagner JR. Madugundu GS, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(11):7450-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku334. Epub 2014 May 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24852253 Free PMC article. - One-electron oxidation of DNA: reaction at thymine.
Joseph J, Schuster GB. Joseph J, et al. Chem Commun (Camb). 2010 Nov 14;46(42):7872-8. doi: 10.1039/c0cc02118k. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Chem Commun (Camb). 2010. PMID: 20830420 - 5-methylcytosine attack by free radicals arising from bromotrichloromethane in a model system: structures of reaction products.
Castro GD, Stamato CJ, Castro JA. Castro GD, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 1994 Nov;17(5):419-28. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90168-6. Free Radic Biol Med. 1994. PMID: 7835748 - Enigmatic 5-hydroxymethyluracil: Oxidatively modified base, epigenetic mark or both?
Olinski R, Starczak M, Gackowski D. Olinski R, et al. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016 Jan-Mar;767:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016. PMID: 27036066 Review. - Thymidine glycol: the effect on DNA molecular structure and enzymatic processing.
Dolinnaya NG, Kubareva EA, Romanova EA, Trikin RM, Oretskaya TS. Dolinnaya NG, et al. Biochimie. 2013 Feb;95(2):134-47. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.09.008. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 23000318 Review.
Cited by
- Quantification of oxidative single-base and intrastrand cross-link lesions in unmethylated and CpG-methylated DNA induced by Fenton-type reagents.
Cao H, Wang Y. Cao H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(14):4833-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm497. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17626047 Free PMC article. - Strategies for discovery and validation of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA biomarkers.
Olkhov-Mitsel E, Bapat B. Olkhov-Mitsel E, et al. Cancer Med. 2012 Oct;1(2):237-60. doi: 10.1002/cam4.22. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Cancer Med. 2012. PMID: 23342273 Free PMC article. Review. - Oxidative damage to methyl-CpG sequences inhibits the binding of the methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) of methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2).
Valinluck V, Tsai HH, Rogstad DK, Burdzy A, Bird A, Sowers LC. Valinluck V, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Aug 9;32(14):4100-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh739. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15302911 Free PMC article. - Incorporation of 5-chlorocytosine into mammalian DNA results in heritable gene silencing and altered cytosine methylation patterns.
Lao VV, Herring JL, Kim CH, Darwanto A, Soto U, Sowers LC. Lao VV, et al. Carcinogenesis. 2009 May;30(5):886-93. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp060. Epub 2009 Mar 11. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19279184 Free PMC article. - Totipotency in the mouse.
Wu G, Lei L, Schöler HR. Wu G, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Jul;95(7):687-694. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1509-5. Epub 2017 Jan 19. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28102431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ehrlich M. and Wang,R.Y.-H. (1981) 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science, 212, 1350–1357. - PubMed
- Riggs A.D. and Jones,P.A. (1983) 5-Methylcytosine, gene regulation and cancer. Adv. Cancer Res., 40, 1–30. - PubMed
- Doerfler W. (1983) DNA Methylation and gene activity. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 52, 93–124. - PubMed
- Jones P.A. and Buckley,J.D. (1990) The role of DNA methylation in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res., 54, 1–23. - PubMed
- Jones P.A., Rideout,W.M.,III, Shen,J-C., Spruck,C.H. and Tsai,Y.C. (1992) Methylation, mutation and cancer. Bioessays, 14, 33–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources