Dose-response relationships between individual nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NANSAIDs) and serious upper gastrointestinal bleeding: a meta-analysis based on individual patient data - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Dose-response relationships between individual nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NANSAIDs) and serious upper gastrointestinal bleeding: a meta-analysis based on individual patient data
S C Lewis et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Sep.
Abstract
Aims: To define by amalgamation of data obtained in contemporaneous case-control studies, the risks associated with individual nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NANSAIDs) according to doses used.
Methods: Meta-analysis of individual patient data from three retrospective case-control studies using similar data collection protocols was carried out in hospitals in Catalonia, England, Scotland and Sweden. 2472 cases of upper gastrointestinal bleeding and 5877 controls were studied. Main outcome measures were risks associated with individual NANSAIDs according to dose used and the period of time for which they were given.
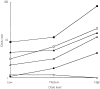
Results: Ibuprofen showed the lowest odds ratio (OR = 1.7; 95% confidence interval 1.1, 2.5), followed by diclofenac (4.9; 3.3, 7.1), indomethacin (6.0; 3.6, 10.0), naproxen (9.1; 6.0-13.7), piroxicam (13.1; 7.9-21.8) and ketoprofen (34.9; 12.7, 96.5). Striking dose-response relationships were seen with four to eight-fold increases in risk within conventionally used dose ranges for all except ketoprofen, where numbers were too few to allow dose analysis. Across the class, risk was highest during the first week of use (11.7; 6.5, 21.0), decreased thereafter with continuing use (5.6; 4.6, 7.0), and fell to 3.2 (2.1, 5.1) 1 week after discontinuing use. Concurrent use of more than one NANSAID substantially increased risk.
Conclusions: The risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding with NANSAIDs varies twenty-fold depending on the drug, and by three to seven-fold depending on the dose chosen. Risk is maximal during the first week and decreases thereafter. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is not associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding at any dose and should be the first-line analgesic wherever possible.
Figures
Figure 1
Dose–response relationships for the risks (odds ratios) of upper gastrointestinal bleeding with individual nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (▪, piroxicam, □ indomethacin, ▴ naproxen, ▵ diclofenac, • ibuprofen, ○ paracetamol).
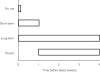
Figure 2
Schematic representation of long-term, short-term and recent use of nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs.
Similar articles
- Risk of serious upper gastrointestinal toxicity with over-the-counter nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Lewis JD, Kimmel SE, Localio AR, Metz DC, Farrar JT, Nessel L, Brensinger C, McGibney K, Strom BL. Lewis JD, et al. Gastroenterology. 2005 Dec;129(6):1865-74. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.08.051. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 16344055 - Variability in the risk of major gastrointestinal complications from nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Henry D, Dobson A, Turner C. Henry D, et al. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):1078-88. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90952-9. Gastroenterology. 1993. PMID: 8405852 - Which patients taking non-aspirin non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs bleed? A case-control study.
Hochain P, Berkelmans I, Czernichow P, Duhamel C, Tranvouez JL, Lerebours E, Colin R. Hochain P, et al. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995 May;7(5):419-26. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995. PMID: 7614104 - Gastrointestinal safety and tolerability of oral non-aspirin over-the-counter analgesics.
Moore N, Scheiman JM. Moore N, et al. Postgrad Med. 2018 Mar;130(2):188-199. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2018.1429793. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Postgrad Med. 2018. PMID: 29417856 Review. - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Lanas A. Lanas A. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;31 Suppl 1:S37-42. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10379468 Review.
Cited by
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and gastroprotection with proton pump inhibitors: a focus on ketoprofen/omeprazole.
Gigante A, Tagarro I. Gigante A, et al. Clin Drug Investig. 2012 Apr 1;32(4):221-33. doi: 10.2165/11596670-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2012. PMID: 22350497 Review. - Thailand Dyspepsia Guidelines: 2018.
Pittayanon R, Leelakusolvong S, Vilaichone RK, Rojborwonwitaya J, Treeprasertsuk S, Mairiang P, Chirnaksorn S, Chitapanarux T, Kaosombatwattana U, Sottisuporn J, Sansak I, Phisalprapa P, Bunchorntavakul C, Chuenrattanakul S, Chakkaphak S, Boonsirichan R, Wiwattanachang O, Maneerattanaporn M, Piyanirun W, Mahachai V. Pittayanon R, et al. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019 Jan 31;25(1):15-26. doi: 10.5056/jnm18081. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019. PMID: 30504528 Free PMC article. Review. - Treatment Satisfaction, Efficacy, and Tolerability of Low-Dose Diclofenac Epolamine Soft Capsules in Acute, Mild, or Moderate Musculoskeletal Pain: A Prospective Open-Label, Single-Arm Interventional Study.
Trevisan CLM, Carraro A, Baldari GLA; Study 18I-Fsg08 Investigators. Trevisan CLM, et al. Pain Ther. 2023 Oct;12(5):1149-1163. doi: 10.1007/s40122-023-00531-z. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Pain Ther. 2023. PMID: 37314686 Free PMC article. - Current evidence for the management of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic literature review for the ASAS/EULAR management recommendations in ankylosing spondylitis.
Zochling J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Braun J. Zochling J, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Apr;65(4):423-32. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.041129. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16126792 Free PMC article. Review. - Ankylosing spondylitis: recent breakthroughs in diagnosis and treatment.
Shaikh SA. Shaikh SA. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2007 Dec;51(4):249-60. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2007. PMID: 18060011 Free PMC article.
References
- Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Sheehan JE, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in relation to major upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993;53:485–494. - PubMed
- Langman MJS, Weil J, Wainright P, et al. Risks of bleeding peptic ulcer associated with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1994;343:1075–1078. - PubMed
- Laporte J-R, Carne X, Vidal X, Moreno V, Juan J. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in relation to previous use of analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet. 1991;337:85–89. - PubMed
- Meade EA, Smith WL, DeWitt DL. Differential inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) isozymes by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem. 1993;267:6610–6614. - PubMed
- Committee on Safety of Medicines. Relative safety of oral non-aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Current Problems Pharmacovigilance. 1994;20:9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical