Interferon gamma is required for activation-induced death of T lymphocytes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Interferon gamma is required for activation-induced death of T lymphocytes
Yosef Refaeli et al. J Exp Med. 2002.
Erratum in
- J Exp Med. 2012 May 7;209(5):1049
Abstract
The effector cytokine interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) may play a role in T cell homeostasis. We have examined the requirement for IFN-gamma in one mechanism that regulates T cell expansion and survival, activation-induced cell death (AICD). CD4(+) T cells lacking IFN-gamma or the Stat1 transcription factor are resistant to AICD. IFN-gamma is required for the production of caspases, and retrovirus-mediated expression of caspase-8 restores the sensitivity of Stat1-deficient T cells to AICD. In vitro, IFN-gamma limits the expansion of T cells that are stimulated through their antigen receptors. Thus, IFN-gamma may function to control the expansion and persistence of T cells by promoting caspase-8-dependent apoptosis.
Figures
Figure 4.
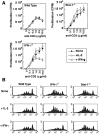
IFN-γ regulates the number of cells following antigenic stimulation by affecting apoptosis but not cell division and proliferation. CD4+ T cells were purified from pooled spleen and lymph node suspensions obtained from either C57BL/6 (wild type), IFN-γ−/− mice, or Stat-1−/− mice. (A) The cells were cultured with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for 4 d, rested in medium plus cytokines, as indicated, restimulated with soluble anti-CD3 antibodies at the indicated concentrations. These cultures were pulsed with [H3]thymidine for 12 h, 2 d after initial activation. (B) Freshly isolated cells were labeled with CFSE, activated with antibodies to CD3 and CD28, in the presence of exogenously added cytokines, as indicated. The activated T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry four days after activation.
Figure 1.
IL-2 and IFN-γ independently regulate AICD. CD4+ T cells were purified from pooled spleen and lymph node suspensions obtained from C57BL/6 (WT), IFN-γ−/−, or Stat1−/− mice (A–C), or from 3A9/+ (wild-type) and 3A9/IL-2−/− mice (D–F). These cells were activated in vitro with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, with the following cytokines added to the cultures: none (A and D), IL-2 (50 U/ml; B and E), or IFN-γ (10 U/ml; C and F). Activated cells were collected 3 d later, and incubated on anti-CD3 coated plates in the presence of IL-2. Apoptosis was determined by Propidium Iodide staining. The same cells were analyzed for the expression of FasL (G) and Fas (H) by staining and flow cytometry. The filled histograms in G represent resting cells and the empty histograms represent activated T cells. The filled histograms in H represent cells that were stained with an isotype-matched control antibody and the empty histograms represent cells that were stained with anti-Fas.
Figure 2.
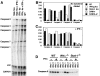
IFN-γ and Stat1 increase the levels of caspase transcripts. CD4+ T cells were purified from pooled lymph node and spleen suspensions obtained from C57BL6 (WT), IFN-γ−/−, Stat1−/−, 3A9/+, or 3A9/IL-2−/− mice. These cells were activated with antibodies to CD3 and CD28, with no added cytokine, or with added IFN-γ. Activated cells were collected after 3 d, and mRNA for caspases was assayed by RNase protection. The protected species were resolved on a TBE/Urea gel, and the bands quantified using a PhosphorImager, a representative example is shown in A. Levels of mRNA (B and C) were calculated by averaging the two bands for the housekeeping genes (L32 and GAPDH), and determining the percentage of the value for each of the caspase probes. The data were pooled from two independent experiments. (D) The levels of caspase-8 protein in CD4+ T cells from C57BL-6 (WT), IFN-γ−/−, and Stat1−/− mice activated for 1 or 3 d with no added cytokine or with IFN-γ (10 U/ml) were determined by Western blot analysis.
Figure 3.
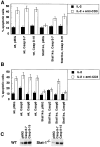
Retrovirally transduced caspase-8 is able to correct the AICD defect observed in Stat1−/− T cells. (A) CD4+ T cells were purified from pooled spleen and lymph node suspensions obtained from either C57BL-6 (wt), or Stat1−/− mice. These cells were activated and infected in vitro with bicistronic retroviral vectors encoding caspase-8 (two different clones, 8–7 and 8–15) or empty vector (pMIG). The infected cells were then incubated on anti-CD3 coated plates for 20 h to induce AICD, and apoptosis was assayed in GFP+ cells by flow cytometry. The data presented here were obtained from averaging the results of triplicate wells, from one experiment representative of three. (B) The specificity of the requirement for caspase-8 was determined by retrovirally transducing CD4+ T cells from either C57BL/6 (wt), or Stat1−/− mice with viruses encoding caspase-3 (Casp3), caspase-8 (Casp8), or caspase-9 (Casp9), and processed as in A. (C) The levels of caspase-8 expression in retrovirus-infected activated C57BL/6 (WT) and Stat1−/− cells were verified by Western blot analysis.
Similar articles
- Th17 cells undergo Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death independent of IFN-gamma.
Zhang Y, Xu G, Zhang L, Roberts AI, Shi Y. Zhang Y, et al. J Immunol. 2008 Jul 1;181(1):190-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.190. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18566384 - The immunity-related GTPase Irgm1 promotes the expansion of activated CD4+ T cell populations by preventing interferon-gamma-induced cell death.
Feng CG, Zheng L, Jankovic D, Báfica A, Cannons JL, Watford WT, Chaussabel D, Hieny S, Caspar P, Schwartzberg PL, Lenardo MJ, Sher A. Feng CG, et al. Nat Immunol. 2008 Nov;9(11):1279-87. doi: 10.1038/ni.1653. Epub 2008 Sep 21. Nat Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18806793 Free PMC article. - 'Activation-induced cell death': a special program able to preserve the homeostasis of the skin?
De Panfilis G. De Panfilis G. Exp Dermatol. 2002 Feb;11(1):1-11. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0625.2002.110101.x. Exp Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 11952823 Review. - Gamma delta T cells.
Lefranc MP, Bonneville M. Lefranc MP, et al. Res Immunol. 1990 Sep;141(7):579-81. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(90)90059-8. Res Immunol. 1990. PMID: 2095601 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Implications for Interleukin-33 in solid organ transplantation.
Liu Q, Turnquist HR. Liu Q, et al. Cytokine. 2013 May;62(2):183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.02.026. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 23541899 Free PMC article. Review. - Immune dysregulation and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in individuals with haploinsufficiency of SOCS1.
Lee PY, Platt CD, Weeks S, Grace RF, Maher G, Gauthier K, Devana S, Vitali S, Randolph AG, McDonald DR, Geha RS, Chou J. Lee PY, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Nov;146(5):1194-1200.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.033. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32853638 Free PMC article. - Neutralization of interleukin-16 protects nonobese diabetic mice from autoimmune type 1 diabetes by a CCL4-dependent mechanism.
Meagher C, Beilke J, Arreaza G, Mi QS, Chen W, Salojin K, Horst N, Cruikshank WW, Delovitch TL. Meagher C, et al. Diabetes. 2010 Nov;59(11):2862-71. doi: 10.2337/db09-0131. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20693344 Free PMC article. - The phenotype of type 1 and type 2 CD8+ T cells activated in vitro is affected by culture conditions and correlates with effector activity.
Kemp RA, Bäckström BT, Ronchese F. Kemp RA, et al. Immunology. 2005 Jul;115(3):315-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02168.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 15946249 Free PMC article. - IL-23 modulated myelin-specific T cells induce EAE via an IFNγ driven, IL-17 independent pathway.
Kroenke MA, Segal BM. Kroenke MA, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Jul;25(5):932-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 20951792 Free PMC article.
References
- Badovinac, V.P., A.R. Tvinnereim, and J.T. Harty. 2000. Regulation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell homeostasis by perforin and interferon-gamma. Science. 290:1354–1358. - PubMed
- Krakowski, M., and T. Owens. 1996. Interferon-gamma confers resistance to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 26:1641–1646. - PubMed
- Ferber, I.A., S. Brocke, C. Taylor-Edwards, W. Ridgway, C. Dinisco, L. Steinman, D. Dalton, and C.G. Fathman. 1996. Mice with a disrupted IFN-gamma gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J. Immunol. 156:5–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous