Safety of a new extensively hydrolysed formula in children with cow's milk protein allergy: a double blind crossover study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Safety of a new extensively hydrolysed formula in children with cow's milk protein allergy: a double blind crossover study
Suzanne W J Terheggen-Lagro et al. BMC Pediatr. 2002.
Abstract
Background: Formulae for infants with cow's milk protein allergy (CMA) should be based on extensively hydrolysed protein. 'Extensively' however is not strictly defined. Differences in molecular weight and peptide chain length may affect its clinical outcome. We studied the safety of a new extensively hydrolysed casein based formula (Frisolac Allergycare: FAC) for children with IgE mediated CMA.
Methods: Thirty children, aged 1.5 - 14.8 years old (median 4.9 years) with persistent CMA were enrolled in this double-blind reference product (Nutramigen: NUT) controlled crossover study. All had positive skin prick tests (SPT) and IgE mediated allergy, showing immediate reactions after ingestion of small amounts of milk. Twenty-five children also had positive radio allergen sorbent tests (RAST) to cow's milk. Formulae provided consisted of 80% elementary formula in combination with 20% reference or test product. Crossover periods lasted for two weeks. From both products molecular weight (MALDI-TOF method and HPLC) and peptide chain length distribution (adapted Edman degradation) were determined.
Results: Maximum molecular weights of NUT and FAC are 2.1 and 2.56 kDa, respectively. The contribution of free amino acids and small peptides <0.5 kDa is 46% for FAC and 53% for NUT. About 50% of the protein fraction of both products consists of peptides longer than four amino acids. Three children did not complete the study. The other children all tolerated FAC very well; no adverse reactions were reported.
Conclusions: The new extensively hydrolysed casein-based formula (FAC) can safely be used in children with IgE mediated cow's milk allergy.
Figures
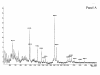
Figure 1
Molecular weight profile of the hydrolysate used in Frisolac Allergycare® (FAC). The molecular weight profile is determined with the MALDI-TOF method as described by Schols [19] and Kaufmann [15] and Soeryapranata [16].
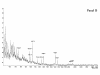
Figure 2
Molecular weight profile of Nutramigen® (NUT). The molecular weight profile is determined with the MALDI-TOF method as described by Schols [19] and Kaufmann [15] and Soeryapranata [16].
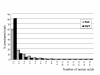
Figure 3
Peptide length profile of the hydrolysate used in Frisiolac Allergycare® (FAC) and Nutramigen® (NUT). The peptide length profile is determined with an adapted Edman degradation method as described by Siemensma et al. [17].
Similar articles
- Determination of allergenicity to three cow's milk hydrolysates and an amino acid-derived formula in children with cow's milk allergy.
Caffarelli C, Plebani A, Poiesi C, Petroccione T, Spattini A, Cavagni G. Caffarelli C, et al. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002 Jan;32(1):74-9. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-0477.2001.01262.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002. PMID: 12002741 - In vivo and in vitro studies on the residual allergenicity of partially hydrolysed infant formulae.
Niggemann B, Binder C, Klettke U, Wahn U. Niggemann B, et al. Acta Paediatr. 1999 Apr;88(4):394-8. doi: 10.1080/08035259950169756. Acta Paediatr. 1999. PMID: 10342536 - The effect of a partially hydrolysed formula based on rice protein in the treatment of infants with cow's milk protein allergy.
Reche M, Pascual C, Fiandor A, Polanco I, Rivero-Urgell M, Chifre R, Johnston S, Martín-Esteban M. Reche M, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010 Jun;21(4 Pt 1):577-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2010.00991.x. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20337976 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Formulas containing hydrolysed protein for prevention of allergy and food intolerance in infants.
Osborn DA, Sinn J. Osborn DA, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;(4):CD003664. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003664.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. PMID: 17054180 Updated. Review. - Hydrolysed Formulas in the Management of Cow's Milk Allergy: New Insights, Pitfalls and Tips.
D'Auria E, Salvatore S, Acunzo M, Peroni D, Pendezza E, Di Profio E, Fiore G, Zuccotti GV, Verduci E. D'Auria E, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Aug 12;13(8):2762. doi: 10.3390/nu13082762. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Milk processing as a tool to reduce cow's milk allergenicity: a mini-review.
Bu G, Luo Y, Chen F, Liu K, Zhu T. Bu G, et al. Dairy Sci Technol. 2013 May;93(3):211-223. doi: 10.1007/s13594-013-0113-x. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Dairy Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 23626868 Free PMC article. - In vitro pepsin resistance of proteins: Effect of non-reduced SDS-PAGE analysis on fragment observation.
Pickles J, Rafiq S, Cochrane SA, Lalljie A. Pickles J, et al. Toxicol Rep. 2014 Oct 16;1:858-870. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.10.008. eCollection 2014. Toxicol Rep. 2014. PMID: 28962297 Free PMC article. - Management of Cow's Milk Allergy from an Immunological Perspective: What Are the Options?
Knol EF, de Jong NW, Ulfman LH, Tiemessen MM. Knol EF, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Nov 11;11(11):2734. doi: 10.3390/nu11112734. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31718010 Free PMC article. Review. - Pediatric milk protein allergy causing hepatic portal venous gas: Case report.
Siddique Z, Thibodeau R, Jafroodifar A, Hanumaiah R. Siddique Z, et al. Radiol Case Rep. 2020 Nov 28;16(2):246-249. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.11.002. eCollection 2021 Feb. Radiol Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33304435 Free PMC article. - Approach to milk protein allergy in infants.
Brill H. Brill H. Can Fam Physician. 2008 Sep;54(9):1258-64. Can Fam Physician. 2008. PMID: 18791102 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Taylor SL. Immunologic and allergic properties of cow's milk proteins in humans. J Food Protect. 1986;49:239–250. - PubMed
- Exl B-M. A review of recent developments in the use of moderately hydrolyzed whey formulae in infant nutrition. Nutr Res. 2001;21:355–379. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5317(00)00259-1. - DOI
- Businco L, Dreborg S, Einarsson R, Giampietro PG, Høst A, Keller KM, Strobel S, Wahn U. Hydrolysed cow's mik formulae. Allergenicity and use in treatment and prevention. An ESPACI position paper. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1993;4:101–111. - PubMed
- Høst A, Koletzko B, Dreborg S, Muraro A, Wahn U, Aggett P, Bresson J-L, Hernell O, Lafeber H, Michaelsen KF, Michelli J-L, Rigo J, Weaver L, Heymans H, Strobel S, Vandenplas Y. Dietary products used in infants for treatment and prevention of food allergy. Joint statement of the European Society for Paediatric Allergology and Clinical Immunology (ESPACI) Committee on Hypoallergenic formulas and the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition. Arch Dis Child. 1999;81:80–84. - PMC - PubMed
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition: Hypoallergenic infant formulas. Pediatrics. 1989;83:1068–1069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical