Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by heat shock - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by heat shock
Sonia Dorion et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002 Apr.
Abstract
In addition to inducing new transcriptional activities that lead within a few hours to the accumulation of heat shock proteins (Hsps), heat shock activates within minutes the major signaling transduction pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, stress-activated protein kinase 1 (SAPK1)-c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and SAPK2-p38. These kinases are involved in both survival and death pathways in response to other stresses and may, therefore, contribute significantly to the heat shock response. In the case of p38, the activation leads to the phosphorylation and activation of one of the Hsps, Hsp27. Phosphorylation occurs very early during stress, is tightly regulated, and results from the triggering of a highly specific heat shock-sensing pathway.
Figures
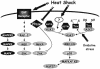
Fig. 1.
Proposed mechanisms for the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by heat shock. Whereas the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway appears to be activated after the agonist-independent phosphorylation and activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, as a result of the inactivation of a protein phosphatase of JNK (PPase), the p38 pathway is activated downstream of a specific heat shock sensor or sensing pathway (indicated by the question mark). See text for details
Similar articles
- A short lived protein involved in the heat shock sensing mechanism responsible for stress-activated protein kinase 2 (SAPK2/p38) activation.
Dorion S, Bérubé J, Huot J, Landry J. Dorion S, et al. J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 31;274(53):37591-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.53.37591. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10608813 - SAPK2/p38-dependent F-actin reorganization regulates early membrane blebbing during stress-induced apoptosis.
Huot J, Houle F, Rousseau S, Deschesnes RG, Shah GM, Landry J. Huot J, et al. J Cell Biol. 1998 Nov 30;143(5):1361-73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.5.1361. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9832563 Free PMC article. - Invited review: Interplay between molecular chaperones and signaling pathways in survival of heat shock.
Gabai VL, Sherman MY. Gabai VL, et al. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002 Apr;92(4):1743-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01101.2001. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002. PMID: 11896044 Review. - p38 MAP kinase activation by vascular endothelial growth factor mediates actin reorganization and cell migration in human endothelial cells.
Rousseau S, Houle F, Landry J, Huot J. Rousseau S, et al. Oncogene. 1997 Oct;15(18):2169-77. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201380. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9393975 - The heat shock response and cytoprotection of the intestinal epithelium.
Malago JJ, Koninkx JF, van Dijk JE. Malago JJ, et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002 Apr;7(2):191-9. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2002)007<0191:thsrac>2.0.co;2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002. PMID: 12380687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- HSP90 inhibitors in the context of heat shock and the unfolded protein response: effects on a primary canine pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell line.
Graner AN, Hellwinkel JE, Lencioni AM, Madsen HJ, Harland TA, Marchando P, Nguyen GJ, Wang M, Russell LM, Bemis LT, Anchordoquy TJ, Graner MW. Graner AN, et al. Int J Hyperthermia. 2017 May;33(3):303-317. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2016.1256503. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Int J Hyperthermia. 2017. PMID: 27829290 Free PMC article. - An investigation of methyl tert‑butyl ether‑induced cytotoxicity and protein profile in Chinese hamster ovary cells.
Xie G, Hong WX, Zhou L, Yang X, Huang H, Wu D, Huang X, Zhu W, Liu J. Xie G, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):8595-8604. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7761. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29039499 Free PMC article. - Bisphenol-A and Nonylphenol Induce Apoptosis in Reproductive Tract Cancer Cell Lines by the Activation of ADAM17.
Urriola-Muñoz P, Lagos-Cabré R, Patiño-García D, Reyes JG, Moreno RD. Urriola-Muñoz P, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 31;19(8):2238. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082238. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30065191 Free PMC article. - Drosophila heat shock response requires the JNK pathway and phosphorylation of mixed lineage kinase at a conserved serine-proline motif.
Gonda RL, Garlena RA, Stronach B. Gonda RL, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042369. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848763 Free PMC article. - IL-8 signaling is involved in resistance of lung carcinoma cells to erlotinib.
Fernando RI, Hamilton DH, Dominguez C, David JM, McCampbell KK, Palena C. Fernando RI, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42031-42044. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9662. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248176 Free PMC article.
References
- Adler V, Schaffer A, Kim J, Dolan L, Ronai Z. UV irradiation and heat shock mediate JNK activation via alternate pathways. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:26071–26077. - PubMed
- Ananthan J, Goldberg AL, Voellmy R. Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger the activation of heat shock genes. Science. 1986;232:522–524. - PubMed
- Arrigo AP, Landry J 1994 Expression and function of the low-molecular-weight heat shock proteins. In: The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones, ed Morimoto RI, Tissières A, Georgopoulos C. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 335–373.
- Beere HM, Green DR. Stress management. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:6–10. - PubMed
- Beere HM, Wolf BB, and Cain K. et al. 2000 Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous