Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expression in esophageal cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expression in esophageal cancer
Nan Wang et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Dec.
Abstract
Aim: Esophageal carcinoma is one of the most common malignant tumors in China. But the molecular mechanisms of esophageal carcinoma remains unclear. Gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor (GKLF) is a newly identified transcription factor which is expressed abandantly in the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and deregulation of GKLF was linked to several types of cancer. It is of interest to study the expression and role of GKLF in esophageal carcinoma.
Methods: Semi-quantitative RT-PCR was used to compare GKLF expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to normal mucosa of the same patients. The serum deprivation inducibility of GKLF was observed in an esophageal squamous cancer cell line by comparison to the primary culture of human fibroblast. The effect of antisense GKLF transfection on the proliferation and adhesion of esophageal squamous cancer cell line was also observed.
Results: The level of GKLF transcript is lower in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma compared to paired normal-appearing mucosa in 14 of 17 of the tumors analyzed. The serum deprivation inducibility of GKLF was greatly decreased in an esophageal squamous cancer cell line compared to the primary culture of human fibroblast. Decreased expression of GKLF in the esophageal cancer cell by antisense GKLF transfection increased its proliferation rate compared with that of vector transfected cell control (P<0.05). Transfection of antisense GKLF decreased its adhesion ability (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The findings of this study demonstrate the down-regulation of GKLF in esophageal squamous cancer, and suggest that deregulation of GKLF may play a role in initiation and/or progression as well as the metastasis of esophageal squamous cancer.
Figures
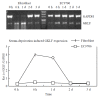
Figure 1
Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of GKLF in esophageal squamous cancer patients. RNA from specimens of normal appearing mucosa (N) and cancer (C) were extracted and GKLF as well as GAPDH were amplified. This figure showed the rep-resentative results from several individual patients.
Figure 2
Serum deprivation induced GKLF expression. Both human primary cultured fibroblast and an esophageal squa-mous cancer cell line EC9706 was underwent serum deprivation. GKLF expression was measured semi-quantitively by RT-PCR. The magnitude of GKLF expression was calcu-lated as ratio of GKLF to GAPDH.
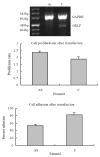
Figure 3
Cell growth and adhesion in GKLF transfected EC9706 cells. The cells were transiently transfected with antisense GKLF expression plasmid (AS) and pCDNA3.1 as control (C). The GKLF expression levels detected by RT-PCR were shown in the upper panel. The cell growth rates were shown in the middle panel; each data point represents mean ± S.E.M. of 7 repeats; there was a significant difference between AS and C (P < 0.05). The cell adhesions were shown in the lower panel; each data point represents mean ± S.E.M. of 4 repeats; AS had significant difference compared to C (P < 0.05).
Similar articles
- [Effect of expression of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor on esophageal squamous cancer cells].
Wang N, Liu ZH, Ding F, Wang XQ, Wu M. Wang N, et al. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2003 Jan;35(1):55-8. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2003. PMID: 12518228 Chinese. - Decreased expression of the gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor gene in intestinal adenomas of multiple intestinal neoplasia mice and in colonic adenomas of familial adenomatous polyposis patients.
Dang DT, Bachman KE, Mahatan CS, Dang LH, Giardiello FM, Yang VW. Dang DT, et al. FEBS Lett. 2000 Jul 7;476(3):203-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01727-0. FEBS Lett. 2000. PMID: 10913614 Free PMC article. - STAT1 is required for IFN-gamma-mediated gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor expression.
Chen ZY, Shie JL, Tseng CC. Chen ZY, et al. Exp Cell Res. 2002 Nov 15;281(1):19-27. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5633. Exp Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 12441126 - Role of gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor in colonic cell growth and differentiation.
Shie JL, Chen ZY, O'Brien MJ, Pestell RG, Lee ME, Tseng CC. Shie JL, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000 Oct;279(4):G806-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2000.279.4.G806. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11005769 - The Pathologic and Molecular Landscape of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis.
Businello G, Parente P, Mastracci L, Pennelli G, Traverso G, Milione M, Bellan E, Michelotto M, Kotsafti A, Grillo F, Fassan M. Businello G, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 4;12(8):2160. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082160. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32759723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Persistent Krüppel-like factor 4 expression predicts progression and poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Tai SK, Yang MH, Chang SY, Chang YC, Li WY, Tsai TL, Wang YF, Chu PY, Hsieh SL. Tai SK, et al. Cancer Sci. 2011 Apr;102(4):895-902. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01859.x. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21219537 Free PMC article. - Review: Experimental models for Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Garman KS, Orlando RC, Chen X. Garman KS, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):G1231-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00509.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22421618 Free PMC article. Review. - FT-IR spectroscopic analysis of normal and cancerous tissues of esophagus.
Wang JS, Shi JS, Xu YZ, Duan XY, Zhang L, Wang J, Yang LM, Weng SF, Wu JG. Wang JS, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;9(9):1897-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1897. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12970871 Free PMC article. - ΔNp63 in squamous cell carcinoma: defining the oncogenic routes affecting epigenetic landscape and tumour microenvironment.
Gatti V, Fierro C, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Melino G, Peschiaroli A. Gatti V, et al. Mol Oncol. 2019 May;13(5):981-1001. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12473. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30845357 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of Krüppel-like factor 4 and heat shock protein 27 in cancer of the larynx.
Karam J, Fadous-Khalifé MC, Tannous R, Fakhreddine S, Massoud M, Hadchity J, Aftimos G, Hadchity E. Karam J, et al. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017 Nov;7(5):808-814. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1412. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29181170 Free PMC article.
References
- Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B. A gene for a novel zinc-finger protein expressed in differentiated epithelial cells and transiently in certain mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:31384–31390. - PubMed
- Yet SF, McA'Nulty MM, Folta SC, Yen HW, Yoshizumi M, Hsieh CM, Layne MD, Chin MT, Wang H, Perrella MA, et al. Human EZF, a Krüppel-like zinc finger protein, is expressed in vascular endothelial cells and contains transcriptional activation and repression domains. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1026–1031. - PubMed
- Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet. 1999;22:356–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases