Rat-to-human transmission of Cowpox infection - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Rat-to-human transmission of Cowpox infection
Tom F W Wolfs et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002 Dec.
Abstract
We isolated Cowpox virus (CPXV) from the ulcerative eyelid lesions of a 14-year-old girl, who had cared for a clinically ill wild rat that later died. CPXV isolated from the rat (Rattus norvegicus) showed complete homology with the girl's virus. Our case is the first proven rat-to-human transmission of cowpox.
Figures
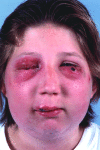
Figure 1
Cowpox lesions with ulcerated nodules on upper lip and left lower eyelid, several molluscum-like-lesions on the right eyelids, and oedema and erythema of the right side of the face.
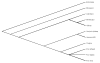
Figure 2
Phylogenetic tree of nucleotide sequences of 163-bp Orthopoxvirus fusion gene amplicons from the patient and rat (head and paw), Cowpox virus, Vaccinia virus (strain Ankara and WR), Camelpox virus, Monkeypox virus, Variola virus, and Ectromelia virus (Mousepox virus). The nucleotide sequences were aligned by using BioEdit software package (T. Hall, Dept. of Microbiology, Raleigh, NC). Phylogenetic relationships were determined by using the Lasergene software packages (DNASTAR Inc., Madison, WI).
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources