Thymidine-dependent small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus exhibit gross morphological and ultrastructural changes consistent with impaired cell separation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Thymidine-dependent small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus exhibit gross morphological and ultrastructural changes consistent with impaired cell separation
Barbara C Kahl et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jan.
Abstract
Thymidine-dependent small-colony variants (SCV) of Staphylococcus aureus exhibited unusual colony morphology with "fried-egg" or pinpoint white colonies on agar plates and pleomorphic cocci as determined by Gram staining. Electron microscopy revealed enlarged cocci with incomplete or multiple cross walls consistent with impaired cell separation. Fried-egg SCV phenotypes could be reversed by thymidine supplementation.
Figures
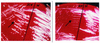
FIG. 1.
Growth of thymidine-dependent SCVs with fried-egg appearance and with pinpoint colonies on Columbia blood agar. (A) Fried-egg thymidine-dependent SCVs (left, arrow) in comparison to the isogenic normal S. aureus (right, N). (B) Pinpoint SCVs (left, arrow) in comparison to the isogenic normal S. aureus (right, N). All strains were grown overnight at 37°C.
FIG. 2.
Gram staining and SEM of fried-egg SCVs (panels I), pinpoint SCVs (panels II), and normal S. aureus (panels III). (A) Gram staining. Arrows indicate large cocci. (B and C) Low- and high-magnification SEM, respectively. Arrows indicate the enhanced intercellular substance present in SCVs compared to normal S. aureus.
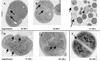
FIG. 3.
TEM of fried-egg SCVs (A, B, and C), pinpoint SCVs (D and E), and normal S. aureus (F). (A and B) Arrows indicate incomplete or multiple cross walls. (C) Incomplete cross wall (small arrows), cellular debris (intermediate arrow), and empty cells (large arrows) are seen. (D and E) Pinpoint SCVs with atypical unrounded cells and mesosome-like structures (arrow). (F) Normal S. aureus cells displaying regular cell separation by a cross wall (arrow) surrounding a highly contrasting splitting system.
Similar articles
- Evaluation of agar culture plates to efficiently identify small colony variants of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Watanabe Y, Oikawa N, Hariu M, Seki M. Watanabe Y, et al. Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Jun 21;12:1743-1748. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S207057. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31417291 Free PMC article. - Molecular analysis of the thymidine-auxotrophic small colony variant phenotype of Staphylococcus aureus.
Besier S, Ludwig A, Ohlsen K, Brade V, Wichelhaus TA. Besier S, et al. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007 Jul;297(4):217-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2007.02.003. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Int J Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17412637 - Enhanced post-stationary-phase survival of a clinical thymidine-dependent small-colony variant of Staphylococcus aureus results from lack of a functional tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Chatterjee I, Herrmann M, Proctor RA, Peters G, Kahl BC. Chatterjee I, et al. J Bacteriol. 2007 Apr;189(7):2936-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.01444-06. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17259321 Free PMC article. - [Analysis of bacterial small-colony variants isolated from clinical specimens].
Matsumoto T. Matsumoto T. Rinsho Byori. 2014 Jul;62(7):727-31. Rinsho Byori. 2014. PMID: 25669045 Review. Japanese. - Antibiotic activity against small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus: review of in vitro, animal and clinical data.
Garcia LG, Lemaire S, Kahl BC, Becker K, Proctor RA, Denis O, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F. Garcia LG, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Jul;68(7):1455-64. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt072. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23485724 Review.
Cited by
- Small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus--review.
Melter O, Radojevič B. Melter O, et al. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010 Nov;55(6):548-58. doi: 10.1007/s12223-010-0089-3. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010. PMID: 21253898 Review. - Characterization of small-colony-variant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolated from the sputum specimens of five patients with cystic fibrosis.
Anderson SW, Stapp JR, Burns JL, Qin X. Anderson SW, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;45(2):529-35. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01444-06. Epub 2006 Nov 29. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17135443 Free PMC article. - In Vitro Activity of the Bacteriophage Endolysin HY-133 against Staphylococcus aureus Small-Colony Variants and Their Corresponding Wild Types.
Schleimer N, Kaspar U, Knaack D, von Eiff C, Molinaro S, Grallert H, Idelevich EA, Becker K. Schleimer N, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 7;20(3):716. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030716. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30736446 Free PMC article. - Manuka honey as a non-antibiotic alternative against Staphylococcus spp. and their small colony variant (SCVs) phenotypes.
Onyango LA, Liang J. Onyango LA, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 28;14:1380289. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1380289. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38868298 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical Significance and Pathogenesis of Staphylococcal Small Colony Variants in Persistent Infections.
Kahl BC, Becker K, Löffler B. Kahl BC, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Apr;29(2):401-27. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00069-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26960941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Balwit, J. M., P. van Langefelde, J. M. Vann, and R. A. Proctor. 1994. Gentamicin-resistant menadione and hemin auxotrophic Staphylococcus aureus persist within cultured endothelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 170:1033-1037. - PubMed
- Kahl, B., M. Herrmann, A. Schulze Everding, H. G. Koch, K. Becker, E. Harms, R. A. Proctor, and G. Peters. 1998. Persistent infection with small colony variant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 177:1023-1029. - PubMed
- Lowy, F. D. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 339:520-532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources