PlasmoDB: the Plasmodium genome resource. A database integrating experimental and computational data - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2003 Jan 1;31(1):212-5.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg081.
Brian Brunk, Jonathan Crabtree, Martin J Fraunholz, Bindu Gajria, Gregory R Grant, Hagai Ginsburg, Dinesh Gupta, Jessica C Kissinger, Philip Labo, Li Li, Matthew D Mailman, Arthur J Milgram, David S Pearson, David S Roos, Jonathan Schug, Christian J Stoeckert Jr, Patricia Whetzel
Affiliations
- PMID: 12519984
- PMCID: PMC165528
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg081
PlasmoDB: the Plasmodium genome resource. A database integrating experimental and computational data
Amit Bahl et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003.
Abstract
PlasmoDB (http://PlasmoDB.org) is the official database of the Plasmodium falciparum genome sequencing consortium. This resource incorporates the recently completed P. falciparum genome sequence and annotation, as well as draft sequence and annotation emerging from other Plasmodium sequencing projects. PlasmoDB currently houses information from five parasite species and provides tools for intra- and inter-species comparisons. Sequence information is integrated with other genomic-scale data emerging from the Plasmodium research community, including gene expression analysis from EST, SAGE and microarray projects and proteomics studies. The relational schema used to build PlasmoDB, GUS (Genomics Unified Schema) employs a highly structured format to accommodate the diverse data types generated by sequence and expression projects. A variety of tools allow researchers to formulate complex, biologically-based, queries of the database. A stand-alone version of the database is also available on CD-ROM (P. falciparum GenePlot), facilitating access to the data in situations where internet access is difficult (e.g. by malaria researchers working in the field). The goal of PlasmoDB is to facilitate utilization of the vast quantities of genomic-scale data produced by the global malaria research community. The software used to develop PlasmoDB has been used to create a second Apicomplexan parasite genome database, ToxoDB (http://ToxoDB.org).
Figures
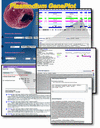
Figure 1
Composite of screen displays demonstrating features of the CD, Plasmodium GenePlot. The GenePlot home page provides access to three main tools. A graphical genome browser (A) highlights curated gene models (dark blue arrows), BLAST hits (shades of red reflect _P_-values), gene/coding potential predictions based on several different algorithms (PHAT, green arrows; GeneFinder, pink arrows; GlimmerM, light blue arrows; Hexamer, blue boxes), and tandem sequence repeats. Graphical views present chromosome data for individual genes and features via mouse-over; clicking on any one of these pulls up a page providing further information and evidence on all features associated with the gene. The search tool (B) performs complex searches of all genomic features and creates reports in a variety of different formats. Nucleotide sequences can be obtained from either the home page (C) or individual gene pages, using a multiple sequence retrieval tool. Some of the sequence manipulation tools available are shown in the background.
Similar articles
- PlasmoDB: the Plasmodium genome resource. An integrated database providing tools for accessing, analyzing and mapping expression and sequence data (both finished and unfinished).
Bahl A, Brunk B, Coppel RL, Crabtree J, Diskin SJ, Fraunholz MJ, Grant GR, Gupta D, Huestis RL, Kissinger JC, Labo P, Li L, McWeeney SK, Milgram AJ, Roos DS, Schug J, Stoeckert CJ Jr. Bahl A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):87-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.87. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752262 Free PMC article. - PlasmoDB: An integrative database of the Plasmodium falciparum genome. Tools for accessing and analyzing finished and unfinished sequence data. The Plasmodium Genome Database Collaborative.
The Plasmodium Genome Database Collaborative. The Plasmodium Genome Database Collaborative. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jan 1;29(1):66-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.66. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11125051 Free PMC article. - PlasmoDB: exploring genomics and post-genomics data of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.
Fraunholz MJ, Roos DS. Fraunholz MJ, et al. Redox Rep. 2003;8(5):317-20. doi: 10.1179/135100003225002961. Redox Rep. 2003. PMID: 14962373 Review. - Bioinformatics and the malaria genome: facilitating access and exploitation of sequence information.
Coppel RL. Coppel RL. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001 Dec;118(2):139-45. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(01)00365-6. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11738704 Review. - PlasmoDB: a functional genomic database for malaria parasites.
Aurrecoechea C, Brestelli J, Brunk BP, Dommer J, Fischer S, Gajria B, Gao X, Gingle A, Grant G, Harb OS, Heiges M, Innamorato F, Iodice J, Kissinger JC, Kraemer E, Li W, Miller JA, Nayak V, Pennington C, Pinney DF, Roos DS, Ross C, Stoeckert CJ Jr, Treatman C, Wang H. Aurrecoechea C, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D539-43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn814. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 18957442 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Expression of a type B RIFIN in Plasmodium falciparum merozoites and gametes.
Mwakalinga SB, Wang CW, Bengtsson DC, Turner L, Dinko B, Lusingu JP, Arnot DE, Sutherland CJ, Theander TG, Lavstsen T. Mwakalinga SB, et al. Malar J. 2012 Dec 21;11:429. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-429. Malar J. 2012. PMID: 23259643 Free PMC article. - Sequences conserved by selection across mouse and human malaria species.
Imamura H, Persampieri JH, Chuang JH. Imamura H, et al. BMC Genomics. 2007 Oct 15;8:372. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-372. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17937810 Free PMC article. - Decreased In Vitro Artemisinin Sensitivity of Plasmodium falciparum across India.
Chakrabarti R, White J, Babar PH, Kumar S, Mudeppa DG, Mascarenhas A, Pereira L, Dash R, Maki JN, Sharma A, Gogoi K, Sarma DK, Pal Bhowmick I, Manoharan SK, Gomes E, Mahanta J, Mohapatra PK, Chery L, Rathod PK. Chakrabarti R, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 23;63(10):e00101-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00101-19. Print 2019 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31332065 Free PMC article. - Comparative whole genome transcriptome analysis of three Plasmodium falciparum strains.
Llinás M, Bozdech Z, Wong ED, Adai AT, DeRisi JL. Llinás M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Feb 21;34(4):1166-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj517. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16493140 Free PMC article. - Unraveling the Plasmodium vivax sporozoite transcriptional journey from mosquito vector to human host.
Roth A, Adapa SR, Zhang M, Liao X, Saxena V, Goffe R, Li S, Ubalee R, Saggu GS, Pala ZR, Garg S, Davidson S, Jiang RHY, Adams JH. Roth A, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 15;8(1):12183. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30713-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30111801 Free PMC article.
References
- Kissinger J.C., Brunk,B.P., Crabtree,J., Fraunholz,M.J., Gajria,B., Milgram,A.J., Pearson,D.S., Schug,J., Bahl,A., Diskin,S.J. et al. (2002) PlasmoDB: The Plasmodium genome resource. Nature, 419, 490–492. - PubMed
- Florens L., Washburn,M.P., Raine,J.D., Anthony,R.M., Grainger,M., Haynes,J.D., Moch,J.K., Muster,N., Sacci,J.B., Tabb,D.L. et al. (2002) A proteomic view of Plasmodium falciparum life cycle. Nature, 419, 520–526. - PubMed
- Mu J., Duan,J., Makova,K.D., Joy,D.A., Huynh,C.Q., Branch,O.H., Li,W.H. and Su,X.Z. (2002) Chromosome-wide SNPs reveal an ancient origin for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature, 418, 323–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials