Activation of human eosinophils through leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor 7 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Activation of human eosinophils through leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor 7
Nicodemus Tedla et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003.
Abstract
Eosinophils are implicated prominently in allergic diseases and the host response to parasitic infections. Eosinophils may be activated in vitro by diverse classes of agonists such as immunoglobulins, lipid mediators, and cytokines. The leukocyte Ig-like receptors (LIRs) comprise a family of inhibitory and activating cell-surface receptors. Inhibitory LIRs down-regulate cellular responses through cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs. There are limited data on the action of the activating LIRs, which are thought to signal through the Fc receptor gamma chain, which contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif. We now demonstrate the expression of LIR1 (inhibitory), LIR2 (inhibitory), LIR3 (inhibitory), and LIR7 (activating) on eosinophils from 4, 4, 12, and 11, respectively, of 12 healthy donors. Cross-linking of LIR7 with plate-bound antibody elicited the dose- and time-dependent release of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and leukotriene C(4). Eosinophils activated with antibodies to LIR7 embedded in gel-phase EliCell preparations showed leukotriene C(4) generation at the nuclear envelope and the release of IL-12 but not IL-4 by vesicular transport. Thus, LIR7 is an activating receptor for eosinophils that elicited the release of cytotoxic granule proteins, de novo lipid mediator generation, and cytokine release through vesicular transport.
Figures
Figure 1
Flow-cytometric analysis of LIR expression. Cell-surface expression of LIRs on eosinophils, neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes, PMN), and monocytes was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. mAbs directed to CD9, CD16, and CD14 were used as markers for eosinophils, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and monocytes, respectively. Representative histograms are shown.
Figure 2
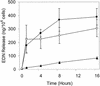
Time course of release of EDN. Purified eosinophils were stimulated with plate-bound mAb (5 μg/ml) to LIR7 (filled circles), to CD9 (open circles), or to MHC class I (filled triangles) as described in Materials and Methods (n = 3). Results are means ± SE.
Figure 3
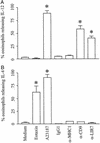
LTC4 generation by eosinophils. Agarose-embedded eosinophils were stimulated with recombinant eotaxin (12 nM), with A23187 (0.1 μM), with mAbs to CD9 (2.5 μg/ml), LIR7 (10 μg/ml), or MHC class I (10 μg/ml), or with irrelevant mouse IgG1 control (10 μg/ml) for 1 h. Cells were fixed and stained with Alexa 488-labeled anti-cysteinyl LT mAb. The data are expressed as the percentages of cells containing immunodetectable LTC4. *, P < 0.05 compared with medium alone or control IgG1 (n = 3).
Figure 4
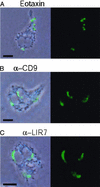
Intracellular localization of LTC4 biosynthesis. Agarose-embedded eosinophils were stimulated with 12 nM eotaxin (A), 2.5 μg/ml mAb to CD9 (B), or 10 μg/ml mAb to LIR7 (C) for 1 h. Cells then were fixed and stained with Alexa 488-labeled anti-cysteinyl LT mAb. To facilitate intracellular localization, anti-LTC4 immunoreactive sites (green staining) were overlaid on phase-contrast images. (Bar, 5 μm.) The figure is illustrative of three independent experiments.
Figure 5
IL-12 and IL-4 release by eosinophils. Agarose-embedded eosinophils were stimulated with eotaxin (6 nM), A23187 (0.5 μM), mAb to CD9 (2.5 μg/ml), mAb to LIR7 (10 μg/ml), mAb to MHC class I (10 μg/ml), or mouse IgG1 control (10 μg/ml). IL-12 and IL-4 release was determined by using the EliCell assay. The data are reported as the percentage of cells with detectable cytokine release. Shown is release of IL-12 (A) and IL-4 (B) in response to each stimulus at 1 h. The data are expressed as percentage of cells releasing each cytokine. *, P < 0.05 compared with medium alone or control IgG1 (n = 3–5).
Similar articles
- Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors: novel innate receptors for human basophil activation and inhibition.
Sloane DE, Tedla N, Awoniyi M, Macglashan DW Jr, Borges L, Austen KF, Arm JP. Sloane DE, et al. Blood. 2004 Nov 1;104(9):2832-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0268. Epub 2004 Jul 8. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15242876 - 2B4 (CD244) is expressed and functional on human eosinophils.
Munitz A, Bachelet I, Fraenkel S, Katz G, Mandelboim O, Simon HU, Moretta L, Colonna M, Levi-Schaffer F. Munitz A, et al. J Immunol. 2005 Jan 1;174(1):110-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.1.110. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15611233 - The co-expression of activating and inhibitory leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors in rheumatoid synovium.
Tedla N, Gibson K, McNeil HP, Cosman D, Borges L, Arm JP. Tedla N, et al. Am J Pathol. 2002 Feb;160(2):425-31. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64861-4. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 11839562 Free PMC article. - Intracellular signaling by the killer immunoglobulin-like receptors and Ly49.
McVicar DW, Burshtyn DN. McVicar DW, et al. Sci STKE. 2001 Mar 27;2001(75):re1. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.75.re1. Sci STKE. 2001. PMID: 11752646 Review. - [Eosinophilic granulocytes and their significance in allergic diseases].
Bruijnzeel PL, Rihs S, Betz S. Bruijnzeel PL, et al. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1992 Feb 8;122(6):173-80. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1992. PMID: 1535993 Review. German.
Cited by
- LILRB3 Supports Immunosuppressive Activity of Myeloid Cells and Tumor Development.
Huang R, Liu X, Kim J, Deng H, Deng M, Gui X, Chen H, Wu G, Xiong W, Xie J, Lewis C, Homsi J, Yang X, Zhang C, He Y, Lou Q, Smith C, John S, Zhang N, An Z, Zhang CC. Huang R, et al. Cancer Immunol Res. 2024 Mar 4;12(3):350-362. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0496. Cancer Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38113030 Free PMC article. - Human leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors in health and disease.
Redondo-García S, Barritt C, Papagregoriou C, Yeboah M, Frendeus B, Cragg MS, Roghanian A. Redondo-García S, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 13;14:1282874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1282874. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022598 Free PMC article. Review. - Distinct frequency patterns of LILRB3 and LILRA6 allelic variants in Europeans.
Bashirova AA, Kasprzak W, O'hUigin C, Carrington M. Bashirova AA, et al. Immunogenetics. 2023 Jun;75(3):263-267. doi: 10.1007/s00251-022-01286-1. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Immunogenetics. 2023. PMID: 36449053 Free PMC article. - Identification of hub genes and pathophysiological mechanism related to acute unilateral vestibulopathy by integrated bioinformatics analysis.
Cheng Y, Zheng J, Zhan Y, Liu C, Lu B, Hu J. Cheng Y, et al. Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 27;13:987076. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.987076. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36237611 Free PMC article. - LILRB3 supports acute myeloid leukemia development and regulates T-cell antitumor immune responses through the TRAF2-cFLIP-NF-κB signaling axis.
Wu G, Xu Y, Schultz RD, Chen H, Xie J, Deng M, Liu X, Gui X, John S, Lu Z, Arase H, Zhang N, An Z, Zhang CC. Wu G, et al. Nat Cancer. 2021 Nov;2(11):1170-1184. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00262-0. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Nat Cancer. 2021. PMID: 35122056 Free PMC article.
References
- Gleich G. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:651–663. - PubMed
- Popken-Harris P, Thomas L, Oxvig C, Sottrup-Jensen L, Kubo H, Klein J S, Gleich G J. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994;94:1282–1289. - PubMed
- Lacy P, Moqbel R. Chem Immunol. 2000;76:134–155. - PubMed
- Six A D, Dennis E A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1488:1–19. - PubMed
- Owen W F, Jr, Soberman R J, Yoshimoto T, Sheffer A L, Lewis R A, Austen K F. J Immunol. 1987;138:532–538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL07718/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI22571/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI031599/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI31599/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL70270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI022571/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI20241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI41995/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI031599/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI020241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T35 HL007718/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous