The role of nuclear factor-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO) in B cell development and survival - PubMed (original) (raw)
The role of nuclear factor-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO) in B cell development and survival
Shinyop Kim et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003.
Abstract
The transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) is essential for immune and inflammatory responses. NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO) is a scaffolding component of the IkappaB kinase complex required for NF-kappaB activation in vitro. Because NF-kappaB activation is involved in B cell development and function, we set out to determine whether NEMO is required for these processes. NEMO(-/-) mice die very early during embryogenesis, and fetal livers from NEMO(-/-) embryos can not reconstitute either B or T lymphopoiesis in irradiated host mice. We therefore used NEMO(-/-) embryonic stem cells and the OP9 in vitro differentiation system to demonstrate that NEMO is not required for B cell development but plays an important role in B cell survival.
Figures
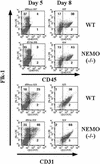
Figure 1
Early stages of the in vitro differentiation of WT and NEMO(−/−) ES cells cocultured with OP9 bone marrow cells. Surface expression levels of CD45, Flk-1, and CD31 on days 5 and 8 of coculture were analyzed by immunostaining and flow cytometric analysis. Numbers in quadrants represent percentage of positively staining cells. For all figures, results shown are representative of two independent experiments involving two cocultures per genotype.
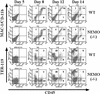
Figure 2
Time course of hematopoietic differentiation in WT and NEMO(−/−) ES/OP9 cocultures. CD45, Mac-1, and Ter-119 surface expression on days 5, 8, 12, and 14 were analyzed as in Fig. 1.
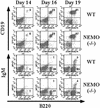
Figure 3
B cell development in WT and NEMO(−/−) ES/OP9 cocultures. Surface expression of B220, CD19, and IgM on days 14, 16, and 19 was analyzed as in Fig. 1.
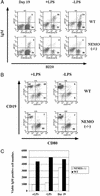
Figure 4
Impaired survival and mitogenic response of IgM+/B220+ cells from stimulated NEMO(−/−) cocultures. (A) On day 19, WT and NEMO(−/−) ES/OP9 cocultures were either mock-stimulated (−LPS) or treated with LPS (10 μg/ml) for 3 days. Each coculture was analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the relative percentage of IgM+/B220+ cells. (B) Surface expression of the activation marker CD80. On day 19, NEMO(−/−) and WT cocultures were either mock-stimulated or treated with LPS (10 μg/ml) for 3 days. The percentage of CD19+/CD80+ cells was determined by flow cytometry. (C) The number of viable IgM+ B cells in cocultures of A as calculated by immunostaining and flow cytometry.
Figure 5
Impaired survival of isolated NEMO-deficient immature B cells. (A) Surface expression of the activation marker CD80. On day 19, CD19+/IgM+ cells were isolated from NEMO(−/−) and WT cocultures by cell sorting. Isolated CD19+/IgM+ B cells were either mock-stimulated or treated with LPS (10 μg/ml) for 2 days. The percentage of IgM+/CD80+ cells was determined by immunostaining and flow cytometry. (B) Surface expression of IgM. On day 19, CD19+/IgM− cells were isolated from NEMO(−/−) and WT cocultures by cell sorting. Isolated CD19+/IgM− B cells were stimulated as in A. The percentage of IgM+/CD19+ cells was determined by immunostaining and flow cytometry.
Similar articles
- IkappaB kinase signaling is essential for maintenance of mature B cells.
Pasparakis M, Schmidt-Supprian M, Rajewsky K. Pasparakis M, et al. J Exp Med. 2002 Sep 16;196(6):743-52. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020907. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12235208 Free PMC article. - Severe liver degeneration and lack of NF-kappaB activation in NEMO/IKKgamma-deficient mice.
Rudolph D, Yeh WC, Wakeham A, Rudolph B, Nallainathan D, Potter J, Elia AJ, Mak TW. Rudolph D, et al. Genes Dev. 2000 Apr 1;14(7):854-62. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 10766741 Free PMC article. - Lymphotoxin-beta receptor mediates NEMO-independent NF-kappaB activation.
Saitoh T, Nakano H, Yamamoto N, Yamaoka S. Saitoh T, et al. FEBS Lett. 2002 Dec 4;532(1-2):45-51. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03622-0. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12459460 - NF-kappa B defects in humans: the NEMO/incontinentia pigmenti connection.
Courtois G, Israël A. Courtois G, et al. Sci STKE. 2000 Nov 14;2000(58):pe1. doi: 10.1126/stke.2000.58.pe1. Sci STKE. 2000. PMID: 11752619 Review. - Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.
Häcker H, Karin M. Häcker H, et al. Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
- Oncolytic targeting of renal cell carcinoma via encephalomyocarditis virus.
Roos FC, Roberts AM, Hwang II, Moriyama EH, Evans AJ, Sybingco S, Watson IR, Carneiro LA, Gedye C, Girardin SE, Ailles LE, Jewett MA, Milosevic M, Wilson BC, Bell JC, Der SD, Ohh M. Roos FC, et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2010 Jul;2(7):275-88. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201000081. EMBO Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20623734 Free PMC article. - The Complex Role of HBeAg and Its Precursors in the Pathway to Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Padarath K, Deroubaix A, Kramvis A. Padarath K, et al. Viruses. 2023 Mar 27;15(4):857. doi: 10.3390/v15040857. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37112837 Free PMC article. Review. - GIMAP1 Is Essential for the Survival of Naive and Activated B Cells In Vivo.
Webb LM, Datta P, Bell SE, Kitamura D, Turner M, Butcher GW. Webb LM, et al. J Immunol. 2016 Jan 1;196(1):207-16. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501582. Epub 2015 Nov 30. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26621859 Free PMC article. - IkappaBalpha/IkappaBepsilon deficiency reveals that a critical NF-kappaB dosage is required for lymphocyte survival.
Goudeau B, Huetz F, Samson S, Di Santo JP, Cumano A, Beg A, Israël A, Mémet S. Goudeau B, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Dec 23;100(26):15800-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2535880100. Epub 2003 Dec 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14665694 Free PMC article. - Innate immune-directed NF-κB signaling requires site-specific NEMO ubiquitination.
Jun JC, Kertesy S, Jones MB, Marinis JM, Cobb BA, Tigno-Aranjuez JT, Abbott DW. Jun JC, et al. Cell Rep. 2013 Jul 25;4(2):352-61. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.036. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23871670 Free PMC article.
References
- Baeuerle P A, Baltimore D. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
- Barnes P J, Karin M. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Cell. 1986;46:705–716. - PubMed
- Sen R, Baltimore D. Cell. 1986;47:921–928. - PubMed
- Brown K, Gerstberger S, Carlson L, Franzoso G, Siebenlist U. Science. 1995;267:1485–1488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous