Bacteriocin detection from whole bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry - PubMed (original) (raw)
Bacteriocin detection from whole bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
Thomas Hindré et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Feb.
Abstract
Class I bacteriocins (lantibiotics) and class II bacteriocins are antimicrobial peptides secreted by gram-positive bacteria. Using two lantibiotics, lacticin 481 and nisin, and the class II bacteriocin coagulin, we showed that bacteriocins can be detected without any purification from whole producer bacteria grown on plates by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). When we compared the results of MALDI-TOF-MS performed with samples of whole cells and with samples of crude supernatants of liquid cultures, the former samples led to more efficient bacteriocin detection and required less handling. Nisin and lacticin 481 were both detected from a mixture of their producer strains, but such a mixture can yield additional signals. We used this method to determine the masses of two lacticin 481 variants, which confirmed at the peptide level the effect of mutations in the corresponding structural gene.
Figures
FIG. 1.
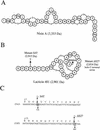
Lantibiotics nisin A and lacticin 481 and the mutations leading to the lacticin 481 variants S4T and ΔS27. (A and B) Amino acid sequences and bridging patterns of nisin A and of lacticin 481 (16) and its variants. The unusual residues are 2,3-didehydroalanine (Dha), 2,3-didehydrobutyrine (Dhb), lanthionine (alanine-S-alanine), 3-methyllanthionine (aminobutyric acid-S-alanine), and aminobutyric acid (Abu). (C) Mutations created within the lacticin 481 structural gene lctA. This gene codes for a precursor peptide, the C-terminal part of which (propeptide) yields mature lacticin 481 after creation of the unusual residues and cleavage of the N-terminal part (leader peptide) (18). Only the propeptide-encoding part of lctA is shown, and the nucleotide sequence is numbered as it is in the GenBank database (accession no. U91581). The propeptide sequence is indicated above the nucleotide sequence. Lysine +1 is the N-terminal amino acid of mature lacticin 481. The asterisks indicate stop codons. The mutated bases and amino acids are indicated by boldface type and underlining, and the changes in the DNA and peptide sequences are indicated below and above the vertical arrows, respectively.
FIG. 2.
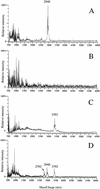
MALDI-TOF spectra of the lacticin 481-producing strain L. lactis ADRIA85LO30 (A), of L. lactis IL1403, which does not produce any bacteriocin (B), of the nisin-producing strain L. lactis NCDO1402 (C), and of a mixture of the lacticin 481- and nisin-producing strains L. lactis ADRIA85LO30 and NCDO1402 (D).
FIG. 3.
Detail of the peak cluster shown in Fig. 2A. The peaks at m/z 2,902, 2,924, and 2,940 correspond to the ions [M+H]+, [M+Na]+, and [M+K]+ of lacticin 481, respectively.
FIG. 4.
MALDI-TOF spectrum of the coagulin-producing strain B. coagulans I4. The peak at m/z 4,650 corresponds to the ion [M+K]+ of coagulin.
FIG. 5.
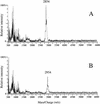
MALDI-TOF spectra of L. lactis IL1403(pEBΔS27) (A) and of L. lactis IL1403(pEBS4T) (B), which produce lacticin 481 mutant molecules which lack the C-terminal serine (ΔS27) or in which the serine at position 4 is replaced by a threonine (S4T).
Similar articles
- Rapid detection of Lactococcuslactis isolates producing the lantibiotics nisin, lacticin 481 and lacticin 3147 using MALDI-TOF MS.
García-Cayuela T, Requena T, Martínez-Cuesta MC, Peláez C. García-Cayuela T, et al. J Microbiol Methods. 2017 Aug;139:138-142. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Microbiol Methods. 2017. PMID: 28583849 - A Multibacteriocin Cheese Starter System, Comprising Nisin and Lacticin 3147 in Lactococcus lactis, in Combination with Plantaricin from Lactobacillus plantarum.
Mills S, Griffin C, O'Connor PM, Serrano LM, Meijer WC, Hill C, Ross RP. Mills S, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;83(14):e00799-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00799-17. Print 2017 Jul 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28476774 Free PMC article. - [Lantibiotics, a class of ribosomally synthesized peptide antibiotics].
Entian KD, Klein C. Entian KD, et al. Naturwissenschaften. 1993 Oct;80(10):454-60. doi: 10.1007/BF01136035. Naturwissenschaften. 1993. PMID: 8264800 Review. German. - Microbial production of bacteriocins: Latest research development and applications.
Juturu V, Wu JC. Juturu V, et al. Biotechnol Adv. 2018 Dec;36(8):2187-2200. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.10.007. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 30385277 Review.
Cited by
- Maturation by LctT is required for biosynthesis of full-length lantibiotic lacticin 481.
Uguen P, Hindré T, Didelot S, Marty C, Haras D, Le Pennec JP, Vallée-Réhel K, Dufour A. Uguen P, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jan;71(1):562-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.562-565.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15640237 Free PMC article. - Comparative proteome analysis of abdominal adipose tissues between fat and lean broilers.
Wu CY, Wu YY, Liu CD, Wang YX, Na W, Wang N, Li H. Wu CY, et al. Proteome Sci. 2016 Sep 1;14(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12953-016-0100-2. eCollection 2016. Proteome Sci. 2016. PMID: 27594807 Free PMC article. - Bioengineering: a bacteriocin perspective.
Cotter PD. Cotter PD. Bioengineered. 2012 Nov-Dec;3(6):313-9. doi: 10.4161/bioe.21601. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Bioengineered. 2012. PMID: 22922299 Free PMC article. - Purification and mass spectrometry based characterization of a pediocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici 13.
Altuntaş EG, Ayhan K, Peker S, Ayhan B, Demiralp DO. Altuntaş EG, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Oct;41(10):6879-85. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3573-z. Epub 2014 Jul 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25015266 - Quorum-sensing regulation of the production of Blp bacteriocins in Streptococcus thermophilus.
Fontaine L, Boutry C, Guédon E, Guillot A, Ibrahim M, Grossiord B, Hols P. Fontaine L, et al. J Bacteriol. 2007 Oct;189(20):7195-205. doi: 10.1128/JB.00966-07. Epub 2007 Aug 10. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17693498 Free PMC article.
References
- Chopin, A., M. C. Chopin, A. Moillo-Batt, and P. Langella. 1984. Two plasmid-determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid 11:260-263. - PubMed
- Claydon, M. A., S. N. Davey, V. Edwards-Jones, and D. B. Gordon. 1996. The rapid identification of intact microorganisms using mass spectrometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 14:1584-1586. - PubMed
- Cleveland, J., T. J. Montville, I. F. Nes, and M. L. Chikindas. 2001. Bacteriocins: safe, natural antimicrobials for food preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 71:1-20. - PubMed
- Delves-Broughton, J., P. Blackburn, R. J. Evans, and J. Hugenholtz. 1996. Applications of the bacteriocin, nisin. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 69:193-202. - PubMed
- Dufour, A., D. Thuault, A. Boulliou, C. M. Bourgeois, and J.-P. Le Pennec. 1991. Plasmid-encoded determinants for bacteriocin production and immunity in a Lactococcus lactis strain and purification of the inhibitory peptide. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137:2423-2429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources