Exploiting microarrays to reveal differential gene expression in the nervous system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Exploiting microarrays to reveal differential gene expression in the nervous system
Robert S Griffin et al. Genome Biol. 2003.
Abstract
Microarrays have been used in a wide variety of experimental systems, but realizing their full potential is contingent on sophisticated and rigorous experimental design and data analysis. This article highlights what is needed to get the most out of microarrays in terms of accurately and effectively revealing differential gene expression and regulation in the nervous system.
Figures
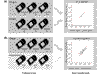
Figure 1
Filtering array data. It is essential to remove as many false positives as possible at the earliest stages of analysis. Random errors occurring in oligonucleotide array data were assessed by comparing three biologically independent control arrays to three other biologically independent control arrays. Genes with a t test p < 0.05 in this comparison are plotted (a). Comparison of these results with the frequency of genes differing at p < 0.05 between control and experimental triplicate arrays (b) were used to define a set of criteria based on present/absent, fold change, t test p value, and a signal threshold that minimized the estimated random error [31].
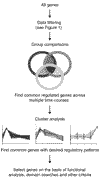
Figure 2
Candidate gene identification. Schematic of a protocol that may be used to select a few genes that obey a defined set of criteria. See text for further details.
Similar articles
- Gene expression analysis of neural cells and tissues using DNA microarrays.
Karsten SL, Kudo LC, Geschwind DH. Karsten SL, et al. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2008 Oct;Chapter 4:Unit 4.28. doi: 10.1002/0471142301.ns0428s45. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18972379 - Gene expression profiling of the nervous system in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Ibrahim SM, Mix E, Böttcher T, Koczan D, Gold R, Rolfs A, Thiesen HJ. Ibrahim SM, et al. Brain. 2001 Oct;124(Pt 10):1927-38. doi: 10.1093/brain/124.10.1927. Brain. 2001. PMID: 11571211 - DNA microarrays: vital statistics.
Tilstone C. Tilstone C. Nature. 2003 Aug 7;424(6949):610-2. doi: 10.1038/424610a. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12904757 No abstract available. - Differential display in the time of microarrays.
Broude NE. Broude NE. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2002 May;2(3):209-16. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2.3.209. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2002. PMID: 12050859 Review. - Progress in realizing the promise of microarrays in systems neurobiology.
Dougherty JD, Geschwind DH. Dougherty JD, et al. Neuron. 2005 Jan 20;45(2):183-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.007. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 15664168 Review.
Cited by
- GCH1, BH4 and pain.
Latremoliere A, Costigan M. Latremoliere A, et al. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Oct;12(10):1728-41. doi: 10.2174/138920111798357393. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21466440 Free PMC article. Review. - Progranulin promotes peripheral nerve regeneration and reinnervation: role of notch signaling.
Altmann C, Vasic V, Hardt S, Heidler J, Häussler A, Wittig I, Schmidt MHH, Tegeder I. Altmann C, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2016 Oct 22;11(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0132-1. Mol Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 27770818 Free PMC article. - Correlational analysis for identifying genes whose regulation contributes to chronic neuropathic pain.
Persson AK, Gebauer M, Jordan S, Metz-Weidmann C, Schulte AM, Schneider HC, Ding-Pfennigdorff D, Thun J, Xu XJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Darvasi A, Fried K, Devor M. Persson AK, et al. Mol Pain. 2009 Feb 19;5:7. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-7. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19228393 Free PMC article. - Targeted disruption of the orphan receptor Gpr151 does not alter pain-related behaviour despite a strong induction in dorsal root ganglion expression in a model of neuropathic pain.
Holmes FE, Kerr N, Chen YJ, Vanderplank P, McArdle CA, Wynick D. Holmes FE, et al. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jan;78:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2016.11.010. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27913310 Free PMC article. - Sex differences in lumbar spinal cord gene expression following experimental lumbar radiculopathy.
LaCroix-Fralish ML, Tawfik VL, Spratt KF, DeLeo JA. LaCroix-Fralish ML, et al. J Mol Neurosci. 2006;30(3):283-95. doi: 10.1385/JMN:30:3:283. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17401154
References
- Marton MJ, DeRisi JL, Bennett HA, Iyer VR, Meyer MR, Roberts CJ, Stoughton R, Burchard J, Slade D, Dai H, et al. Drug target validation and identification of secondary drug target effects using DNA microarrays. Nat Med. 1998;4:1293–1301. - PubMed
- Tavazoie S, Hughes JD, Campbell MJ, Cho RJ, Church GM. Systematic determination of genetic network architecture. Nat Genet. 1999;22:281–285. - PubMed
- Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, Sturla LM, Angelo M, McLaughlin ME, Kim JY, Goumnerova LC, Black PM, Lau C, et al. Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature. 2002;415:436–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS3825/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS45459/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS045459/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS39518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD38533/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources