Human metapneumovirus in severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Human metapneumovirus in severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis
Julie Greensill et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003 Mar.
Abstract
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to detect segments of the M (matrix), N (nucleoprotein), and F (fusion) genes of human metapneumovirus in bronchoalveolar fluid from 30 infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Seventy percent of them were coinfected with metapneumovirus. Such coinfection might be a factor influencing the severity of bronchiolitis.
Figures
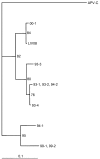
Figure
The phylogenetic relationship of human metapneumovirus from Liverpool (LIV08) to those from Holland and to avian pneumovirus. The divergence bar is shown at the bottom of the figure.
Similar articles
- Dual infection of infants by human metapneumovirus and human respiratory syncytial virus is strongly associated with severe bronchiolitis.
Semple MG, Cowell A, Dove W, Greensill J, McNamara PS, Halfhide C, Shears P, Smyth RL, Hart CA. Semple MG, et al. J Infect Dis. 2005 Feb 1;191(3):382-6. doi: 10.1086/426457. Epub 2004 Dec 23. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15633097 Free PMC article. - Most human metapneumovirus and human respiratory syncytial virus in infant nasal secretions is cell free.
Semple MG, Booth JA, Ebrahimi B. Semple MG, et al. J Clin Virol. 2007 Nov;40(3):241-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2007.08.019. J Clin Virol. 2007. PMID: 17920332 - Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus, Brazil.
Cuevas LE, Nasser AM, Dove W, Gurgel RQ, Greensill J, Hart CA. Cuevas LE, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003 Dec;9(12):1626-8. doi: 10.3201/eid0912.030522. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 14720409 Free PMC article. - [Bronchiolitis in infants. Virology].
Freymuth F. Freymuth F. Arch Pediatr. 2001 Jan;8 Suppl 1:77S-80S. doi: 10.1016/s0929-693x(01)80160-3. Arch Pediatr. 2001. PMID: 11232447 Review. French. No abstract available. - The distinguishing features of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus.
Papenburg J, Boivin G. Papenburg J, et al. Rev Med Virol. 2010 Jul;20(4):245-60. doi: 10.1002/rmv.651. Rev Med Virol. 2010. PMID: 20586081 Review.
Cited by
- First report of respiratory syncytial virus and human metapneumovirus co-infection in a 2-year-old kawasaki patient in iran.
Shatizadeh Malekshahi S, Mokhtari Azad T, Shahmahmoodi Sh, Yavarian J, Rezaei F, Naseri M. Shatizadeh Malekshahi S, et al. Iran J Public Health. 2010;39(4):140-2. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Iran J Public Health. 2010. PMID: 23113048 Free PMC article. - Severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infants is associated with reduced airway interferon gamma and substance P.
Semple MG, Dankert HM, Ebrahimi B, Correia JB, Booth JA, Stewart JP, Smyth RL, Hart CA. Semple MG, et al. PLoS One. 2007 Oct 17;2(10):e1038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001038. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17940602 Free PMC article. - Human metapneumovirus in paediatric patients.
Principi N, Bosis S, Esposito S. Principi N, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006 Apr;12(4):301-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01325.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006. PMID: 16524405 Free PMC article. Review. - A 1-year experience with human metapneumovirus in children aged <5 years.
Esper F, Martinello RA, Boucher D, Weibel C, Ferguson D, Landry ML, Kahn JS. Esper F, et al. J Infect Dis. 2004 Apr 15;189(8):1388-96. doi: 10.1086/382482. Epub 2004 Apr 2. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15073675 Free PMC article. - Diagnosis of human metapneumovirus and rhinovirus in patients with respiratory tract infections by an internally controlled multiplex real-time RNA PCR.
Scheltinga SA, Templeton KE, Beersma MF, Claas EC. Scheltinga SA, et al. J Clin Virol. 2005 Aug;33(4):306-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.08.021. J Clin Virol. 2005. PMID: 15994117 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical