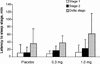Treatment of primary insomnia with melatonin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Treatment of primary insomnia with melatonin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study
Luis G Almeida Montes et al. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2003 May.
Abstract
Objective: To assess the hypnotic effect of melatonin in patients with primary insomnia.
Method: Ten patients (mean age 50 yr, range 30-72 yr) who met the DSM-IV criteria for primary insomnia received, in random order, 0.3 mg of melatonin, 1.0 mg of melatonin or placebo 60 minutes before bedtime. A crossover design was used so that each patient received each of the 3 treatments for a 7-day period (with a 5-day washout period between). After each 7-day treatment, night time electroencephalographic (EEG) records were collected, and each morning, subjects completed sleep logs and analogue-visual scales to document the amount and subjective quality of sleep.
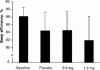
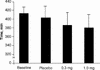
Results: There were no significant differences in sleep EEG, the amount or subjective quality of sleep or side effects between the placebo, 0.3-mg melatonin or 1.0-mg melatonin treatments.
Conclusion: Melatonin did not produce any sleep benefit in this sample of patients with primary insomnia.
Objectif: Évaluer l'effet hypnotique de la mélatonine chez les patients qui souffrent d'insomnie primaire.
Méthode: Dix patients (âge moyen de 50 ans, intervalle de 30 à 72 ans) qui satisfaisaient aux critères relatifs à l'insomnie primaire selon le DSM-IV ont reçu, au hasard, 0,3 mg de mélatonine, 1,0 mg de mélatonine ou un placebo 60 minutes avant le coucher. On a suivi un plan croisé afin que chaque patient reçoive chacun des trois traitements pendant une période de sept jours (traitements séparés par une période d'élimination de cinq jours). Les sujets se sont soumis à un électroencéphalogramme (EEG) chaque soir et ont rempli des registres sur le sommeil et des échelles analogiques-visuelles pour consigner la durée du sommeil et sa qualité subjective.
Résultats: Il n'y avait pas de différences importantes au niveau de l'EEG, de la durée du sommeil ou de sa qualité subjective, ou des effets secondaires entre le traitement au placebo, à 0,3 mg de mélatonine ou à 1,0 mg de mélatonine.
Conclusion: La mélatonine n'a produit aucun avantage pour le sommeil chez cet échantillon de patients qui souffraient d'insomnie primaire.
Figures
Fig. 1: Mean (and standard deviation) sleep efficiency at baseline and with placebo, 0.3-mg melatonin and 1.0-mg melatonin treatments.
Fig. 2: Mean (and standard deviation) total sleep time at baseline and with placebo, 0.3-mg melatonin and 1.0-mg melatonin treatments.
Fig. 3: Mean (and standard deviation) latency to stage 1, stage 2 and delta stage with placebo, 0.3-mg melatonin and 1.0-mg melatonin treatments.
Similar articles
- The efficacy and safety of the melatonin agonist beta-methyl-6-chloromelatonin in primary insomnia: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical trial.
Zemlan FP, Mulchahey JJ, Scharf MB, Mayleben DW, Rosenberg R, Lankford A. Zemlan FP, et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005 Mar;66(3):384-90. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v66n0316. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15766306 Clinical Trial. - Daytime melatonin administration in elderly good and poor sleepers: effects on core body temperature and sleep latency.
Lushington K, Pollard K, Lack L, Kennaway DJ, Dawson D. Lushington K, et al. Sleep. 1997 Dec;20(12):1135-44. doi: 10.1093/sleep/20.12.1135. Sleep. 1997. PMID: 9493923 Clinical Trial. - Efficacy of prolonged release melatonin in insomnia patients aged 55-80 years: quality of sleep and next-day alertness outcomes.
Wade AG, Ford I, Crawford G, McMahon AD, Nir T, Laudon M, Zisapel N. Wade AG, et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Oct;23(10):2597-605. doi: 10.1185/030079907X233098. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17875243 Clinical Trial. - Melatonin and melatonin agonists as treatments for benzodiazepines and hypnotics withdrawal in patients with primary insomnia. A systematic review.
Morera-Fumero AL, Fernandez-Lopez L, Abreu-Gonzalez P. Morera-Fumero AL, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020 Jul 1;212:107994. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.107994. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020. PMID: 32409111
Cited by
- Do herbal agents have a place in the treatment of sleep problems in long-term care?
Shimazaki M, Martin JL. Shimazaki M, et al. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2007 May;8(4):248-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2006.11.001. Epub 2007 Apr 18. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2007. PMID: 17498609 Free PMC article. Review. - Meta-analysis: melatonin for the treatment of primary sleep disorders.
Ferracioli-Oda E, Qawasmi A, Bloch MH. Ferracioli-Oda E, et al. PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063773. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691095 Free PMC article. - Melatonin as a Chronobiotic with Sleep-promoting Properties.
Cruz-Sanabria F, Carmassi C, Bruno S, Bazzani A, Carli M, Scarselli M, Faraguna U. Cruz-Sanabria F, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(4):951-987. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220217152617. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35176989 Free PMC article. Review. - Efficacy and hypnotic effects of melatonin in shift-work nurses: double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial.
Sadeghniiat-Haghighi K, Aminian O, Pouryaghoub G, Yazdi Z. Sadeghniiat-Haghighi K, et al. J Circadian Rhythms. 2008 Oct 29;6:10. doi: 10.1186/1740-3391-6-10. J Circadian Rhythms. 2008. PMID: 18957133 Free PMC article. - The efficacy and safety of exogenous melatonin for primary sleep disorders. A meta-analysis.
Buscemi N, Vandermeer B, Hooton N, Pandya R, Tjosvold L, Hartling L, Baker G, Klassen TP, Vohra S. Buscemi N, et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2005 Dec;20(12):1151-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.0243.x. J Gen Intern Med. 2005. PMID: 16423108 Free PMC article.
References
- Nagtegaal JE, Kerkhof GA, Smits MG. A placebo-controlled crossover study on the effects of melatonin administered five hours before the individual dim light melatonin onset. J Sleep Res.1998;7:135-43. - PubMed
- Brzezinski A. Melatonin in humans. N Engl J Med 1997;336:186-95. - PubMed
- Lerner AB, Case JD. Melatonin. Fed Proc 1960;19:590-2.
- Sack RL, Hughes RJ, Edgar DM, Lewy AJ. Sleep-promoting effects of melatonin: at what dose, in whom, under what conditions, and by what mechanisms? Sleep 1997;20:908-15. - PubMed
- Redman J, Armstrong S, Ng KT. Free-running activity rhythms in the rat: entrainment by melatonin. Science 1983;219:1089-91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous