EVA: Evaluation of protein structure prediction servers - PubMed (original) (raw)
EVA: Evaluation of protein structure prediction servers
Ingrid Y Y Koh et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003.
Abstract
EVA (http://cubic.bioc.columbia.edu/eva/) is a web server for evaluation of the accuracy of automated protein structure prediction methods. The evaluation is updated automatically each week, to cope with the large number of existing prediction servers and the constant changes in the prediction methods. EVA currently assesses servers for secondary structure prediction, contact prediction, comparative protein structure modelling and threading/fold recognition. Every day, sequences of newly available protein structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) are sent to the servers and their predictions are collected. The predictions are then compared to the experimental structures once a week; the results are published on the EVA web pages. Over time, EVA has accumulated prediction results for a large number of proteins, ranging from hundreds to thousands, depending on the prediction method. This large sample assures that methods are compared reliably. As a result, EVA provides useful information to developers as well as users of prediction methods.
Figures
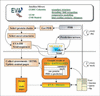
Figure 1
Flowchart of EVA. Every day, EVA downloads the newest protein structures from PDB (4). The structures are added to mySQL databases, sequences are extracted for every protein chain and are sent to each prediction server by META-PredictProtein (5) (except for threading in which only novel structures are sent). META-PP collects the results and sends them to EVA. Every week, predictions of secondary structure, threading/fold recognition, comparative modelling and inter-residue contacts are evaluated at the EVA satellites at Columbia University, University of California, San Francisco, and CNB Madrid. The central EVA site at Columbia collects all the assessments from the satellites and the results from the database searches, and publishes the updated web pages. Finally, all web pages are mirrored at the satellites.
Similar articles
- EVA: continuous automatic evaluation of protein structure prediction servers.
Eyrich VA, Martí-Renom MA, Przybylski D, Madhusudhan MS, Fiser A, Pazos F, Valencia A, Sali A, Rost B. Eyrich VA, et al. Bioinformatics. 2001 Dec;17(12):1242-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1242. Bioinformatics. 2001. PMID: 11751240 - EVAcon: a protein contact prediction evaluation service.
Graña O, Eyrich VA, Pazos F, Rost B, Valencia A. Graña O, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W347-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki411. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980486 Free PMC article. - META-PP: single interface to crucial prediction servers.
Eyrich VA, Rost B. Eyrich VA, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 1;31(13):3308-10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg572. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12824314 Free PMC article. - Servers for protein structure prediction.
Fischer D. Fischer D. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Apr;16(2):178-82. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.03.004. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16546376 Review. - State-of-the-art web services for de novo protein structure prediction.
Abriata LA, Dal Peraro M. Abriata LA, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2021 May 20;22(3):bbaa139. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa139. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34020540 Review.
Cited by
- Membrane protein prediction methods.
Punta M, Forrest LR, Bigelow H, Kernytsky A, Liu J, Rost B. Punta M, et al. Methods. 2007 Apr;41(4):460-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.07.026. Methods. 2007. PMID: 17367718 Free PMC article. Review. - Tools for comparative protein structure modeling and analysis.
Eswar N, John B, Mirkovic N, Fiser A, Ilyin VA, Pieper U, Stuart AC, Marti-Renom MA, Madhusudhan MS, Yerkovich B, Sali A. Eswar N, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 1;31(13):3375-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg543. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12824331 Free PMC article. - MODBASE, a database of annotated comparative protein structure models, and associated resources.
Pieper U, Eswar N, Braberg H, Madhusudhan MS, Davis FP, Stuart AC, Mirkovic N, Rossi A, Marti-Renom MA, Fiser A, Webb B, Greenblatt D, Huang CC, Ferrin TE, Sali A. Pieper U, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jan 1;32(Database issue):D217-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh095. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14681398 Free PMC article. - A dynamic Bayesian network approach to protein secondary structure prediction.
Yao XQ, Zhu H, She ZS. Yao XQ, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Jan 25;9:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-49. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18218144 Free PMC article. - Sequence-based prediction of protein domains.
Liu J, Rost B. Liu J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jul 7;32(12):3522-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh684. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15240828 Free PMC article.
References
- Eyrich V., Martí-Renom,M.A., Przybylski,D., Fiser,A., Pazos,F., Valencia,A., Sali,A. and Rost,B. (2001) EVA: continuous automatic evaluation of protein structure prediction servers. Bioinformatics, 17, 1242–1243. - PubMed
- Rost B. and Eyrich,V. (2001) EVA: large-scale analysis of secondary structure prediction. Proteins, 45 (Suppl. 5), S192–S199. - PubMed
- Marti-Renom M.A., Madhusudhan,M.S., Fiser,A., Rost,B. and Sali,A. (2002) Reliability of assessment of protein structure prediction methods. Structure, 10, 435–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-GM63029-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM54762/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5-P20-LM7276/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM062413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 LM007276/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063029/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM062529/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM054762/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM62529/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1-P50-GM62413-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials