GEPAS: A web-based resource for microarray gene expression data analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
GEPAS: A web-based resource for microarray gene expression data analysis
Javier Herrero et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003.
Abstract
We present a web-based pipeline for microarray gene expression profile analysis, GEPAS, which stands for Gene Expression Profile Analysis Suite (http://gepas.bioinfo.cnio.es). GEPAS is composed of different interconnected modules which include tools for data pre-processing, two-conditions comparison, unsupervised and supervised clustering (which include some of the most popular methods as well as home made algorithms) and several tests for differential gene expression among different classes, continuous variables or survival analysis. A multiple purpose tool for data mining, based on Gene Ontology, is also linked to the tools, which constitutes a very convenient way of analysing clustering results. On-line tutorials are available from our main web server (http://bioinfo.cnio.es).
Figures
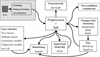
Figure 1
The pipeline of microarray data analysis. After the operations of image processing and data normalisation are performed (grey box on top left), the data enters the pipeline through the preprocessor. Then, depending on the type of analysis the user needs to perform, these can be sent to different modules that implement different tools.
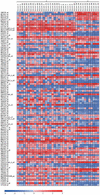
Figure 2
Representation provided by Pomelo of the 100 genes most differentially expressed among two different cancer types, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) labelled as 0 and 1, respectively in the top of the figure. The genes are arranged in increasing order of adjusted p-value. If an adjusted p-value of 0.05 is used, there are 92 genes that present significant differential expression among the classes. Thermal scale in the bottom represents fold of activation or repression in log2 scale. Data from (25).
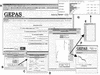
Figure 3
Use of SOTAarray and SotaTree modules. Arrows represent clicks for the user. (A) The interface to the SOTArray. (B) The results page, from which different plots can be obtained. (C) SOTA tree program was invoked from the results page. This graphical interface allows for some interactive changes in the final appearance of the tree represented. (D) A dendrogram representing the clusters found in the dataset. The diameter of the circle is proportional to the number of co-expressing genes in the cluster. By clicking the circle or the histogram representing the average profile, the list of genes (E) and a representation of its profiles (F), respectively, can be obtained. This is done by the internal module ExtractCluster. (G) Shows part of the graphical representation of FatiGO module, which displays the percentages of GO terms in the selected cluster with respect to the rest of genes and the adjusted p-values obtained for this difference.
Similar articles
- GEPAS, an experiment-oriented pipeline for the analysis of microarray gene expression data.
Vaquerizas JM, Conde L, Yankilevich P, Cabezón A, Minguez P, Díaz-Uriarte R, Al-Shahrour F, Herrero J, Dopazo J. Vaquerizas JM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W616-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki500. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980548 Free PMC article. - GEPAS, a web-based tool for microarray data analysis and interpretation.
Tárraga J, Medina I, Carbonell J, Huerta-Cepas J, Minguez P, Alloza E, Al-Shahrour F, Vegas-Azcárate S, Goetz S, Escobar P, Garcia-Garcia F, Conesa A, Montaner D, Dopazo J. Tárraga J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul 1;36(Web Server issue):W308-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn303. Epub 2008 May 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18508806 Free PMC article. - Next station in microarray data analysis: GEPAS.
Montaner D, Tárraga J, Huerta-Cepas J, Burguet J, Vaquerizas JM, Conde L, Minguez P, Vera J, Mukherjee S, Valls J, Pujana MA, Alloza E, Herrero J, Al-Shahrour F, Dopazo J. Montaner D, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W486-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl197. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845056 Free PMC article. - TM4 microarray software suite.
Saeed AI, Bhagabati NK, Braisted JC, Liang W, Sharov V, Howe EA, Li J, Thiagarajan M, White JA, Quackenbush J. Saeed AI, et al. Methods Enzymol. 2006;411:134-93. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)11009-5. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 16939790 Review. - Microarray data analysis: from hypotheses to conclusions using gene expression data.
Armstrong NJ, van de Wiel MA. Armstrong NJ, et al. Cell Oncol. 2004;26(5-6):279-90. doi: 10.1155/2004/943940. Cell Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15623938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Functional genomic analyses of Enterobacter, Anopheles and Plasmodium reciprocal interactions that impact vector competence.
Dennison NJ, Saraiva RG, Cirimotich CM, Mlambo G, Mongodin EF, Dimopoulos G. Dennison NJ, et al. Malar J. 2016 Aug 22;15(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1468-2. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 27549662 Free PMC article. - Comparison of two ecotypes of the metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (J. & C. PRESL) at the transcriptional level.
Plessl M, Rigola D, Hassinen VH, Tervahauta A, Kärenlampi S, Schat H, Aarts MG, Ernst D. Plessl M, et al. Protoplasma. 2010 Mar;239(1-4):81-93. doi: 10.1007/s00709-009-0085-0. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Protoplasma. 2010. PMID: 19937357 - Statistical identification of gene association by CID in application of constructing ER regulatory network.
Liu LY, Chen CY, Chen MJ, Tsai MS, Lee CH, Phang TL, Chang LY, Kuo WH, Hwa HL, Lien HC, Jung SM, Lin YS, Chang KJ, Hsieh FJ. Liu LY, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Mar 17;10:85. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-85. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19292896 Free PMC article. - METAGENassist: a comprehensive web server for comparative metagenomics.
Arndt D, Xia J, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Guo AC, Cruz JA, Sinelnikov I, Budwill K, Nesbø CL, Wishart DS. Arndt D, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(Web Server issue):W88-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks497. Epub 2012 May 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22645318 Free PMC article. - Utilization of lymphoblastoid cell lines as a system for the molecular modeling of autism.
Baron CA, Liu SY, Hicks C, Gregg JP. Baron CA, et al. J Autism Dev Disord. 2006 Nov;36(8):973-82. doi: 10.1007/s10803-006-0134-x. J Autism Dev Disord. 2006. PMID: 16845580
References
- Lockhart D.J., Dong,H., Byrne,M.C., Follettie,M.T., Gallo,M.V., Chee,M.S., Mittmann,M., Wang,C., Kobayashi,M., Horton,H. and Brown,E.L. (1996) Expression monitoring by hybridisation to high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Biotechnol., 14, 1675–1680. - PubMed
- Stoeckert C.J., Causton,H.C. and Ball,C.A. (2002) Microarray databases: standards and ontologies. Nature Genet., 32, 469–473. - PubMed
- Brazma A. and Vilo,J. (2000) Gene expression data analysis. FEBS Lett., 480, 17–24. - PubMed
- Herrero J., Díaz-Uriarte,R. and Dopazo,J. (2003) Gene expression data preprocessing. Bioinformatics, 19, 655–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources