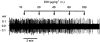Evidence that central 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B/C receptors regulate 5-HT cell firing in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the anaesthetised rat - PubMed (original) (raw)
Evidence that central 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B/C receptors regulate 5-HT cell firing in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the anaesthetised rat
L J Boothman et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul.
Erratum in
- Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Sep;140(1):227-8
Abstract
1. Systemic administration of phenethylamine-derived, 5-hydroxytryptamine(2) (5-HT(2)) receptor agonists inhibits the firing of midbrain 5-HT neurones, but the 5-HT receptors involved are poorly defined, and the contribution of peripheral mechanisms is uncertain. This study addresses these issues using extracellular recordings of 5-HT neurones in the dorsal raphe nucleus of anaesthetised rats. 2. The 5-HT(2) receptor agonists DOI ((+/-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine hydrochloride) and DOB ((+/-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine hydrobromide), caused a dose-related (10-100 micro g kg(-1) i.v.) inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity, with the highest dose reducing firing rates by >80%. 3. Pretreatment with the 5-HT(2) receptor antagonist ritanserin (1 mg kg(-1) i.v.) completely blocked the action of DOI. The 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist MDL 100,907 (0.2 mg kg(-1) i.v.) blocked the action of both DOI and DOB. In comparison, the 5-HT(2B/C) receptor antagonist SB 206553 (0.5 mg kg(-1) i.v.) caused a small, but statistically significant, shift to the right in the dose response to DOI and DOB. 4. Pretreatment with the peripherally acting 5-HT(2) receptor antagonist BW 501C67 (0.1 mg kg(-1) i.v.) had no effect on the DOI-induced inhibition of 5-HT cell firing, but completely blocked the DOI-induced rise in mean arterial blood pressure. 5. These data indicate that the inhibition of 5-HT cell firing induced by systemic administration of DOI and DOB is mediated predominantly by the 5-HT(2A) receptor-subtype, but that 5-HT(2B/C) receptors also play a minor role. Moreover, central and not peripheral mechanisms are involved. Given evidence that 5-HT(2) receptors are not located on 5-HT neurones, postsynaptic 5-HT feedback mechanisms are implicated.
Figures
Figure 1
Effect of the 5-HT2 agonist DOI on the firing of a 5-HT neurone in the DRN of an anaesthetised rat. Each vertical line in the spike train represents a single action potential. DOI was administered in increasing doses at 2 min intervals as indicated.
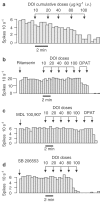
Figure 2
Rate metre recordings demonstrating the effect of DOI on 5-HT cell firing either (a) alone or in rats pretreated with (b) the 5-HT2 receptor antagonist ritanserin (1 mg kg−1 i.v.), (c) the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist MDL 100,907 (0.2 mg kg−1 i.v.) or (d) the 5-HT2B/C receptor antagonist SB 206553 (0.5 mg kg−1 i.v.). Antagonists were administered 5 min prior to DOI, which was given in increasing doses at 2 min intervals. Note also the characteristic inhibitory response of the 5-HT neurones to the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT (10 _μ_g kg−1 i.v.).
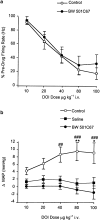
Figure 3
Effect of DOI (a) and DOB (b) in the presence of the 5-HT2 receptor antagonist ritanserin (1 mg kg−1 i.v.), the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist MDL 100,907 (0.2 mg kg−1 i.v.) or the 5-HT2B/C receptor antagonist SB 206553 (0.5 mg kg−1 i.v.). Antagonists were administered 5 min prior to either DOI or DOB, which was given in increasing doses at 2 min intervals. Controls received DOI or DOB alone. Data points are mean±s.e.m. of _n_observations at agonist doses of 10, 20, 40, 80, 100 _μ_g kg−1 respectively: (a) control _n_=8,8,8,8,6; ritanserin _n_=6,6,5,4,4; MDL 100,907 _n_=7,6,4,4,4; SB 206553 _n_=7,6,6,5,5; (b) control _n_=5,5,5,5,5; MDL 100907 _n_=3,3,3,3,3; SB 205663 _n_=8,8,8,6,6. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 for control versus ritanserin, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 for control versus MDL 100907, +P<0.05, ++P<0.01 for control versus SB 206553 (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test).
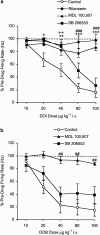
Figure 4
Effect of DOI on 5-HT neuronal activity (a) and mean arterial blood pressure (b) in the presence and absence of the peripheral 5-HT2 receptor antagonist BW 501C67 (0.1 mg kg−1 i.v.). DOI was given in increasing doses at 2 min intervals. When tested, BW 501C67 was administered 5 min prior to DOI. Controls received DOI alone and the saline condition received five sequential injections of saline. Data points are mean±s.e.m. of n observations at agonist doses of 10, 20, 40, 80,100 _μ_g kg−1 respectively: (a) control _n_=8,8,8,8,6; BW 501C67 _n_=8,7,6,6,5; (b) control _n_=6,6,6,6,6; saline _n_=4,4,4,4,4; BW 501C67 _n_=6,6,6,6,6. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 for control versus saline, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 for control versus BW 501C67 (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test).
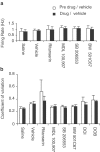
Figure 5
Effect of 5-HT receptor antagonists and vehicle alone on the firing rate (a), and firing regularity (b) of 5-HT neurones. Data for 5-HT2 receptor agonists are also included in (b). Measurements were made during the final 1 min of a 5 min pretreatment for antagonists or a 2 min period for agonist or vehicle. Doses were ritanserin (1.0 mg kg−1 i.v.), MDL 100,907 (0.2 mg kg−1 i.v.), SB 206553 (0.5 mg kg−1 i.v.), BW 501C67 (0.1 mg kg−1 i.v.), DOI (40 _μ_g kg−1 i.v.), DOB (40 _μ_g kg−1 i.v.). Data are mean±s.e.m. from groups of 3–10 rats. _P_>0.05 versus predrug values (Student's two-tailed paired _t_-tests).
Similar articles
- Further pharmacological characterization of 5-HT(2C) receptor agonist-induced inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity in the dorsal raphe nucleus in vivo.
Quérée P, Peters S, Sharp T. Quérée P, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;158(6):1477-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00406.x. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19845681 Free PMC article. - In vivo evidence that 5-HT(2C) receptors inhibit 5-HT neuronal activity via a GABAergic mechanism.
Boothman L, Raley J, Denk F, Hirani E, Sharp T. Boothman L, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;149(7):861-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706935. Epub 2006 Oct 16. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17043669 Free PMC article. - Investigation of the role of 5-HT2 receptor subtypes in the control of the bladder and the urethra in the anaesthetized female rat.
Mbaki Y, Ramage AG. Mbaki Y, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;155(3):343-56. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.273. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18604238 Free PMC article. - Vasoconstrictor responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine in the autoperfused hindquarters of spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Calama E, Morán A, Ortiz de Urbina AV, Martín ML, San Román L. Calama E, et al. Pharmacology. 2004 Jun;71(2):66-72. doi: 10.1159/000076942. Pharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15118345 - Role of the medial prefrontal cortex in 5-HT1A receptor-induced inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity in the rat.
Hajós M, Hajós-Korcsok E, Sharp T. Hajós M, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Apr;126(8):1741-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702510. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10372816 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Genetic polymorphism in HTR2A rs6313 is associated with internet addiction disorder.
Dai Y, Zhang C, Zhang L, Wen C, Li H, Zhu T. Dai Y, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 14;15:1292877. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1292877. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38419907 Free PMC article. - Genetic variation in cortico-amygdala serotonin function and risk for stress-related disease.
Holmes A. Holmes A. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008 Sep;32(7):1293-314. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.03.006. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008. PMID: 18439676 Free PMC article. Review. - A Complex Impact of Systemically Administered 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands on Conditioned Fear.
Hagsäter SM, Pettersson R, Pettersson C, Atanasovski D, Näslund J, Eriksson E. Hagsäter SM, et al. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Sep 21;24(9):749-757. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyab040. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34228806 Free PMC article. - Distinct 5-HT receptor subtypes regulate claustrum excitability by serotonin and the psychedelic, DOI.
Anderson TL, Keady JV, Songrady J, Tavakoli NS, Asadipooya A, Neeley RE, Turner JR, Ortinski PI. Anderson TL, et al. Prog Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;240:102660. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102660. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Prog Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39218140 - Inhibition of 5-HT neuron activity and induction of depressive-like behavior by high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus.
Temel Y, Boothman LJ, Blokland A, Magill PJ, Steinbusch HW, Visser-Vandewalle V, Sharp T. Temel Y, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 23;104(43):17087-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704144104. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17942692 Free PMC article.
References
- AGHAJANIAN G.K.Feedback regulation of central monoaminergic neurones: evidence from single cell recording studies Essays in Neurochemistry and Neuropharmacology 1978Chichester: J. Wiley and Sons Ltd; 1–32.ed. M Youdim, D.S., Lovenberg, W., Lagnado, J. pp - PubMed
- AGHAJANIAN G.K., FOOTE W.E., SHEARD M.H. Action of psychotogenic drugs on single midbrain raphe neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1970;171:178–187. - PubMed
- AGHAJANIAN G.K., WANG R.Y. Habenular and other midbrain raphe afferents demonstrated by a modified retrograde tracing technique. Brain Res. 1977;122:229–242. - PubMed
- ARTIGAS F., CELADA P., LARUELLE M., ADELL A. How does pindolol improve antidepressant action. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001;22:224–228. - PubMed
- BARNES N.M., SHARP T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:1083–1152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources