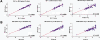Customized molecular phenotyping by quantitative gene expression and pattern recognition analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Customized molecular phenotyping by quantitative gene expression and pattern recognition analysis
Shreeram Akilesh et al. Genome Res. 2003 Jul.
Abstract
Description of the molecular phenotypes of pathobiological processes in vivo is a pressing need in genomic biology. We have implemented a high-throughput real-time PCR strategy to establish quantitative expression profiles of a customized set of target genes. It enables rapid, reproducible data acquisition from limited quantities of RNA, permitting serial sampling of mouse blood during disease progression. We developed an easy to use statistical algorithm--Global Pattern Recognition--to readily identify genes whose expression has changed significantly from healthy baseline profiles. This approach provides unique molecular signatures for rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and graft versus host disease, and can also be applied to defining the molecular phenotype of a variety of other normal and pathological processes.
Figures
Figure 1
Reproducibility and sensitivity of the ImmunoQuantArray. Raw Ct values for each of the 96 genes in the IQA are plotted. The linear regression best-fit line is shown and its correlation coefficient indicated. (A) Spleen cDNAs (left panel) or blood cDNAs (middle panel) from two C57BL/6J males. The average of the two spleen cDNA Cts is compared with the average two blood cDNA Cts (right panel). (B) The average spleen cDNA Cts of five BALB/cJ (left), three 129X1/SvJ (middle), or five BXSB/MpJ-Yaa+ (right) males was compared with the average spleen cDNA Cts of five C57BL/6J males. The point lying closest to the ordinate is 18S rRNA.
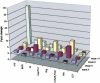
Figure 2
Serial molecular phenotyping of BXSB-Yaa SLE. Spleen cDNAs from cohorts of three to five BXSB/MpJ-Yaa males and age-matched BXSB.B6-Yaa+ controls were subjected to IMQ/GPR analysis at weeks 4, 6, 8, and 14. The fold changes (normalized to 18S rRNA) of genes that received a GPR score ≥0.4 and were significant after normalization to 18S rRNA are plotted.
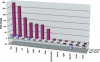
Figure 3
Molecular phenotype of GVHD progression. Bone marrow and splenocytes from C57BL/6J females were used to induce GVHD in five allogenic 129P3/J males (C57BL6/J → 129P3/J). Five syngeneic transplant recipients (C57BL6/J → C57BL6/J) were used as controls. cDNAs were prepared from samples collected on days 7 and 9 after the transplant and were subjected to IMQ/GPR analysis. The fold changes of genes that received a GPR score ≥0.4 and were significant after normalization to 18S rRNA are shown.
Similar articles
- Identification and quantification of disease-related gene clusters.
Firneisz G, Zehavi I, Vermes C, Hanyecz A, Frieman JA, Glant TT. Firneisz G, et al. Bioinformatics. 2003 Sep 22;19(14):1781-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg252. Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 14512349 - Sex genes for genomic analysis in human brain: internal controls for comparison of probe level data extraction.
Galfalvy HC, Erraji-Benchekroun L, Smyrniotopoulos P, Pavlidis P, Ellis SP, Mann JJ, Sibille E, Arango V. Galfalvy HC, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003 Sep 8;4:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-37. Epub 2003 Sep 8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12962547 Free PMC article. - A modular analysis framework for blood genomics studies: application to systemic lupus erythematosus.
Chaussabel D, Quinn C, Shen J, Patel P, Glaser C, Baldwin N, Stichweh D, Blankenship D, Li L, Munagala I, Bennett L, Allantaz F, Mejias A, Ardura M, Kaizer E, Monnet L, Allman W, Randall H, Johnson D, Lanier A, Punaro M, Wittkowski KM, White P, Fay J, Klintmalm G, Ramilo O, Palucka AK, Banchereau J, Pascual V. Chaussabel D, et al. Immunity. 2008 Jul 18;29(1):150-64. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.05.012. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 18631455 Free PMC article. - Gene expression studies in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mandel M, Achiron A. Mandel M, et al. Lupus. 2006;15(7):451-6. doi: 10.1191/0961203306lu2332oa. Lupus. 2006. PMID: 16898181 Review. - Microarray analysis of gene expression in lupus.
Crow MK, Wohlgemuth J. Crow MK, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(6):279-87. doi: 10.1186/ar1015. Epub 2003 Oct 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003. PMID: 14680503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- GDF5 regulates TGFß-dependent angiogenesis in breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells: in vitro and in vivo control by anti-TGFß peptides.
Margheri F, Schiavone N, Papucci L, Magnelli L, Serratì S, Chillà A, Laurenzana A, Bianchini F, Calorini L, Torre E, Dotor J, Feijoo E, Fibbi G, Del Rosso M. Margheri F, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50342. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050342. Epub 2012 Nov 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23226264 Free PMC article. - Alteration of the serine protease PRSS56 causes angle-closure glaucoma in mice and posterior microphthalmia in humans and mice.
Nair KS, Hmani-Aifa M, Ali Z, Kearney AL, Ben Salem S, Macalinao DG, Cosma IM, Bouassida W, Hakim B, Benzina Z, Soto I, Söderkvist P, Howell GR, Smith RS, Ayadi H, John SW. Nair KS, et al. Nat Genet. 2011 Jun;43(6):579-84. doi: 10.1038/ng.813. Epub 2011 May 1. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21532570 Free PMC article. - Correct dosage of Fog2 and Gata4 transcription factors is critical for fetal testis development in mice.
Bouma GJ, Washburn LL, Albrecht KH, Eicher EM. Bouma GJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 18;104(38):14994-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701677104. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17848526 Free PMC article. - Expression of miRNAs in ovine fetal gonads: potential role in gonadal differentiation.
Torley KJ, da Silveira JC, Smith P, Anthony RV, Veeramachaneni DN, Winger QA, Bouma GJ. Torley KJ, et al. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011 Jan 11;9:2. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-9-2. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21223560 Free PMC article.
References
- Alizadeh, A.A., Eisen, M.B., Davis, R.E., Ma, C., Lossos, I.S., Rosenwald, A., Boldrick, J.C., Sabet, H., Tran, T., Yu, X., et al. 2000. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403: 503-511. - PubMed
- Bijl, M., Horst, G., Limburg, P.C., and Kallenberg, C.G. 2001. Fas expression on peripheral blood lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Relation to lymphocyte activation and disease activity. Lupus 10: 866-872. - PubMed
- Bustin, S.A. 2000. Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 25: 169-193. - PubMed
- Choi, E.Y., Christianson, G.J., Yoshimura, Y., Jung, N., Sproule, T.J., Malarkannan, S., Joyce, S., and Roopenian, D.C. 2002. Real-time T cell profiling identifies H60 as a major minor histocompatibility antigen in murine graft-versus-host disease. Blood 100: 4259-4265. - PubMed
- Duggan, D.J., Bittner, M., Chen, Y., Meltzer, P., and Trent, J.M. 1999. Expression profiling using cDNA microarrays. Nat. Genet. 21: 10-14. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
- http://www.jax.org/staff/roopenian/labsite/index.html; access to the GPR algorithm and documentation.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources