A 3.9-centimorgan-resolution human single-nucleotide polymorphism linkage map and screening set - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
doi: 10.1086/377137. Epub 2003 Jul 3.
Ravi Sachidanandam, Andrew G Clark, Leonid Kruglyak, Ellen Wijsman, Jerzy Kakol, Steven Buyske, Buena Chui, Patrick Cohen, Claudia de Toma, Margaret Ehm, Stephen Glanowski, Chunsheng He, Jeremy Heil, Kyriacos Markianos, Ivy McMullen, Margaret A Pericak-Vance, Arkadiy Silbergleit, Lincoln Stein, Michael Wagner, Alexander F Wilson, Jeffrey D Winick, Emily S Winn-Deen, Carl T Yamashiro, Howard M Cann, Eric Lai, Arthur L Holden
Affiliations
- PMID: 12844283
- PMCID: PMC1180367
- DOI: 10.1086/377137
Comparative Study
A 3.9-centimorgan-resolution human single-nucleotide polymorphism linkage map and screening set
Tara C Matise et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Aug.
Abstract
Recent advances in technologies for high-throughout single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based genotyping have improved efficiency and cost so that it is now becoming reasonable to consider the use of SNPs for genomewide linkage analysis. However, a suitable screening set of SNPs and a corresponding linkage map have yet to be described. The SNP maps described here fill this void and provide a resource for fast genome scanning for disease genes. We have evaluated 6,297 SNPs in a diversity panel composed of European Americans, African Americans, and Asians. The markers were assessed for assay robustness, suitable allele frequencies, and informativeness of multi-SNP clusters. Individuals from 56 Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain pedigrees, with >770 potentially informative meioses altogether, were genotyped with a subset of 2,988 SNPs, for map construction. Extensive genotyping-error analysis was performed, and the resulting SNP linkage map has an average map resolution of 3.9 cM, with map positions containing either a single SNP or several tightly linked SNPs. The order of markers on this map compares favorably with several other linkage and physical maps. We compared map distances between the SNP linkage map and the interpolated SNP linkage map constructed by the deCode Genetics group. We also evaluated cM/Mb distance ratios in females and males, along each chromosome, showing broadly defined regions of increased and decreased rates of recombination. Evaluations indicate that this SNP screening set is more informative than the Marshfield Clinic's commonly used microsatellite-based screening set.
Figures
Figure 1
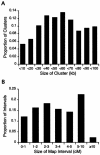
Map features. A, Distribution of sizes of autosomal map intervals. B, Distribution of sizes of SNP clusters.
Figure 2
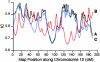
Female and male smoothed cM/Mb ratios, plotted along chromosome 16. Data are plotted separately for the p and q arms.
Figure 3
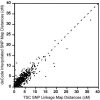
Map distance for corresponding map intervals on the TSC SNP linkage map and the deCode interpolated SNP linkage map.
Figure 4
IC for chromosome 12, on SNP linkage maps and Marshfield screening set 10. A, Complete SNP map with 97 markers (black). B, Marshfield map with 17 markers (red). C, SNP map with 47 markers (blue).
Similar articles
- Linkage mapping bovine EST-based SNP.
Snelling WM, Casas E, Stone RT, Keele JW, Harhay GP, Bennett GL, Smith TP. Snelling WM, et al. BMC Genomics. 2005 May 19;6:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-74. BMC Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15943875 Free PMC article. - A combined linkage-physical map of the human genome.
Kong X, Murphy K, Raj T, He C, White PS, Matise TC. Kong X, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2004 Dec;75(6):1143-8. doi: 10.1086/426405. Epub 2004 Oct 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15486828 Free PMC article. - Linkage maps of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) genome derived from RAD sequencing.
Gonen S, Lowe NR, Cezard T, Gharbi K, Bishop SC, Houston RD. Gonen S, et al. BMC Genomics. 2014 Feb 27;15:166. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-166. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24571138 Free PMC article. - Guidelines for genotyping in genomewide linkage studies: single-nucleotide-polymorphism maps versus microsatellite maps.
Evans DM, Cardon LR. Evans DM, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2004 Oct;75(4):687-92. doi: 10.1086/424696. Epub 2004 Aug 13. Am J Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15311375 Free PMC article. - Cosmopolitan linkage disequilibrium maps.
Gibson J, Tapper W, Zhang W, Morton N, Collins A. Gibson J, et al. Hum Genomics. 2005 Mar;2(1):20-7. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-2-1-20. Hum Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15814065 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Whole genomewide linkage screen for neural tube defects reveals regions of interest on chromosomes 7 and 10.
Rampersaud E, Bassuk AG, Enterline DS, George TM, Siegel DG, Melvin EC, Aben J, Allen J, Aylsworth A, Brei T, Bodurtha J, Buran C, Floyd LE, Hammock P, Iskandar B, Ito J, Kessler JA, Lasarsky N, Mack P, Mackey J, McLone D, Meeropol E, Mehltretter L, Mitchell LE, Oakes WJ, Nye JS, Powell C, Sawin K, Stevenson R, Walker M, West SG, Worley G, Gilbert JR, Speer MC. Rampersaud E, et al. J Med Genet. 2005 Dec;42(12):940-6. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2005.031658. Epub 2005 Apr 14. J Med Genet. 2005. PMID: 15831595 Free PMC article. - Genomewide linkage scan of 409 European-ancestry and African American families with schizophrenia: suggestive evidence of linkage at 8p23.3-p21.2 and 11p13.1-q14.1 in the combined sample.
Suarez BK, Duan J, Sanders AR, Hinrichs AL, Jin CH, Hou C, Buccola NG, Hale N, Weilbaecher AN, Nertney DA, Olincy A, Green S, Schaffer AW, Smith CJ, Hannah DE, Rice JP, Cox NJ, Martinez M, Mowry BJ, Amin F, Silverman JM, Black DW, Byerley WF, Crowe RR, Freedman R, Cloninger CR, Levinson DF, Gejman PV. Suarez BK, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Feb;78(2):315-33. doi: 10.1086/500272. Epub 2006 Jan 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16400611 Free PMC article. - Joint linkage and imprinting analyses of GAW15 rheumatoid arthritis and gene expression data.
Zhou X, Chen W, Swartz MD, Lu Y, Yu R, Amos CI, Wu CC, Shete S. Zhou X, et al. BMC Proc. 2007;1 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S53. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-1-s1-s53. Epub 2007 Dec 18. BMC Proc. 2007. PMID: 18466553 Free PMC article. - Ethnicity and human genetic linkage maps.
Jorgenson E, Tang H, Gadde M, Province M, Leppert M, Kardia S, Schork N, Cooper R, Rao DC, Boerwinkle E, Risch N. Jorgenson E, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Feb;76(2):276-90. doi: 10.1086/427926. Epub 2004 Dec 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15627237 Free PMC article. - Diverse mutational mechanisms cause pathogenic subtelomeric rearrangements.
Luo Y, Hermetz KE, Jackson JM, Mulle JG, Dodd A, Tsuchiya KD, Ballif BC, Shaffer LG, Cody JD, Ledbetter DH, Martin CL, Rudd MK. Luo Y, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Oct 1;20(19):3769-78. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr293. Epub 2011 Jul 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21729882 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Additional Data for the TSC SNP Linkage Map, http://compgen.rutgers.edu/SNPmap/ (for additional data from the construction and analysis of the TSC SNP linkage map)
- Allele Frequency Panels, http://snp.cshl.org/allele_frequency_project/panels.shtml
- Center for Medical Genetics, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for Marshfield linkage maps)
- CEPH Genotype Database, http://www.cephb.fr/cephdb/
References
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101 - PubMed
- Carlson CS, Eberle MA, Rieder MJ, Smith JD, Kruglyak L, Nickerson DA (2003) Additional SNPs and linkage-disequilibrium analyses are necessary for whole-genome association studies in humans. Nat Genet 33:518–521 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous