Subdissociative dose ketamine produces a deficit in manipulation but not maintenance of the contents of working memory - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Subdissociative dose ketamine produces a deficit in manipulation but not maintenance of the contents of working memory
Rebekah A E Honey et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003 Nov.
Abstract
We investigated the effects of subdissociative dose ketamine on executive processes during a working memory task. A total of 11 healthy volunteers participated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, within-subjects study. They attended on three occasions, receiving intravenous infusions of placebo, a lower ketamine dose, and a higher ketamine dose. On each occasion, they underwent a series of tasks engaging working memory function in verbal and visuo-spatial domains. Further tasks explored aspects of long-term memory, planning, attention, and perceptual processing. With respect to working memory/executive function, a highly specific pattern of impairment was observed. Impairments were seen only at the higher dose of ketamine and restricted to a subgroup of the verbal working memory tasks: While visuo-spatial working memory showed no evidence of impairment, and while simple maintenance processes during verbal working memory were also unimpaired, higher dose ketamine produced a significant impairment in the manipulation of information within working memory. This process-specific effect of ketamine was reflected in a drug-by-task interaction. The specificity of this ketamine effect suggests that the earliest effect of NMDA receptor blockade is in higher order control of executive function rather than in more basic maintenance processes.
Figures
Figure 1
Timeline demonstrating the timing of tasks, ketamine infusion, and blood samples during the study.
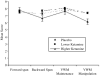
Figure 2
Mean scores (± S.E. mean) of digit span and verbal working memory for placebo, 50 ng/ml ketamine, and 100 ng/ml ketamine conditions.
Similar articles
- Impairment of specific episodic memory processes by sub-psychotic doses of ketamine: the effects of levels of processing at encoding and of the subsequent retrieval task.
Honey GD, Honey RA, Sharar SR, Turner DC, Pomarol-Clotet E, Kumaran D, Simons JS, Hu X, Rugg MD, Bullmore ET, Fletcher PC. Honey GD, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Sep;181(3):445-57. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0001-z. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15983801 Clinical Trial. - Acute ketamine administration alters the brain responses to executive demands in a verbal working memory task: an FMRI study.
Honey RA, Honey GD, O'Loughlin C, Sharar SR, Kumaran D, Bullmore ET, Menon DK, Donovan T, Lupson VC, Bisbrown-Chippendale R, Fletcher PC. Honey RA, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004 Jun;29(6):1203-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300438. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15100698 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Acute effects of ketamine on memory systems and psychotic symptoms in healthy volunteers.
Morgan CJ, Mofeez A, Brandner B, Bromley L, Curran HV. Morgan CJ, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004 Jan;29(1):208-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300342. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004. PMID: 14603267 Clinical Trial. - The effects of a subpsychotic dose of ketamine on recognition and source memory for agency: implications for pharmacological modelling of core symptoms of schizophrenia.
Honey GD, O'loughlin C, Turner DC, Pomarol-Clotet E, Corlett PR, Fletcher PC. Honey GD, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Feb;31(2):413-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300846. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16123767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Acute and chronic effects of ketamine upon human memory: a review.
Morgan CJ, Curran HV. Morgan CJ, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Nov;188(4):408-24. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0572-3. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 17006715 Review.
Cited by
- Ketamine : from medicine to misuse.
Wolff K, Winstock AR. Wolff K, et al. CNS Drugs. 2006;20(3):199-218. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200620030-00003. CNS Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16529526 Review. - Chronic administration of ketamine mimics the perturbed sense of body ownership associated with schizophrenia.
Tang J, Morgan HL, Liao Y, Corlett PR, Wang D, Li H, Tang Y, Chen J, Liu T, Hao W, Fletcher PC, Chen X. Tang J, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 May;232(9):1515-26. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3782-0. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25404087 - Effects of modafinil on working memory processes in humans.
Müller U, Steffenhagen N, Regenthal R, Bublak P. Müller U, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004 Dec;177(1-2):161-9. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-1926-3. Epub 2004 Jun 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004. PMID: 15221200 Clinical Trial. - Impairment of specific episodic memory processes by sub-psychotic doses of ketamine: the effects of levels of processing at encoding and of the subsequent retrieval task.
Honey GD, Honey RA, Sharar SR, Turner DC, Pomarol-Clotet E, Kumaran D, Simons JS, Hu X, Rugg MD, Bullmore ET, Fletcher PC. Honey GD, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Sep;181(3):445-57. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0001-z. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15983801 Clinical Trial. - KETAMINE AS A POSSIBLE MODERATOR OF HYPNOTIZABILITY: A FEASIBILITY STUDY.
Patterson DR, Hoffer C, Jensen MP, Wiechman SA, Sharar SR. Patterson DR, et al. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2018 Jul-Sep;66(3):298-307. doi: 10.1080/00207144.2018.1460559. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2018. PMID: 29856288 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Adler CM, Goldberg TE, Malhotra AK, Pickar D, Breier A. Effects of ketamine on thought disorder, working memory, and semantic memory in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;43:811–816. - PubMed
- Andreasen NC, Grove WM. Thought, language, and communication in schizophrenia: diagnosis and prognosis. Schizophr Bull. 1986;12:348–359. - PubMed
- Braver TS, Cohen JD, Nystrom LE, Jonides J, Smith EE, Noll DC. A parametric study of prefrontal cortex involvement in human working memory. Neuroimage. 1997;5:49–62. - PubMed
- Breier A, Malhotra AK, Pinals DA, Weisenfeld NI, Pickar D. Association of ketamine-induced psychosis with focal activation of the prefrontal cortex in healthy volunteers. Am J Psychiatry. 1997;154:805–811. - PubMed
- Bressi S, Miele L, Bressi C, Astori S, Gimosti E, Linciano AD, Sessini M, Invernizzi GL. Deficit of central executive component of working memory in schizophrenia. New Trends in Experimental and Clinical Psychiatry. 1996;12:243–252.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical