Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study
Christos Sotiriou et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003.
Abstract
Comprehensive gene expression patterns generated from cDNA microarrays were correlated with detailed clinico-pathological characteristics and clinical outcome in an unselected group of 99 node-negative and node-positive breast cancer patients. Gene expression patterns were found to be strongly associated with estrogen receptor (ER) status and moderately associated with grade, but not associated with menopausal status, nodal status, or tumor size. Hierarchical cluster analysis segregated the tumors into two main groups based on their ER status, which correlated well with basal and luminal characteristics. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis identified 16 genes that were significantly associated with relapse-free survival at a stringent significance level of 0.001 to account for multiple comparisons. Of 231 genes previously reported by others [van't Veer, L. J., et al. (2002) Nature 415, 530-536] as being associated with survival, 93 probe elements overlapped with the set of 7,650 probe elements represented on the arrays used in this study. Hierarchical cluster analysis based on the set of 93 probe elements segregated our population into two distinct subgroups with different relapse-free survival (P < 0.03). The number of these 93 probe elements showing significant univariate association with relapse-free survival (P < 0.05) in the present study was 14, representing 11 unique genes. Genes involved in cell cycle, DNA replication, and chromosomal stability were consistently elevated in the various poor prognostic groups. In addition, glutathione S-transferase M3 emerged as an important survival marker in both studies. When taken together with other array studies, our results highlight the consistent biological and clinical associations with gene expression profiles.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Dendrogram of 99 breast cancer specimens analyzed by hierarchical clustering analysis using 706 probe elements selected for the high variability across all tumors (see Materials and Methods). The tumors were separated into two main groups mainly associated with ER status as determined by the ligand-binding (LB) assay and confirmed by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The dendrogram further branched into smaller subgroups within the ER+ and ER-classes based on their basal and luminal characteristics: Her-2/neu subgroup, dark blue; basal-like 1 subgroup, pink; basal-like 2 subgroup, yellow; luminal-like 1 subgroup, light blue; luminal-like 2 subgroup, red; and luminal-like 3 subgroup, green. Black bars represent ER+ tumors assessed by IHC (a), ER+ tumors assessed by LB assay (b), grade 3 (c), and node-positive tumors (d).
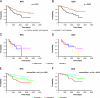
Fig. 2.
RFS and BCS analysis of the 99 breast cancer patients based on the gene expression cluster analysis classification. RFS (A) and BCS (B) of the predominantly ER- and predominantly ER+ clusters (the Her-2/neu and basal-like 1 and 2 subgroups were considered in one group and the luminal-like subgroups 1, 2, and 3 were considered in the other group). RFS (C) and BCS (D) of the Her-2/neu and basal-like 1 and 2 subgroups. RFS (E) and BCS (F) of the luminal-like 1, 2, and 3 subgroups.
Similar articles
- Distinct molecular mechanisms underlying clinically relevant subtypes of breast cancer: gene expression analyses across three different platforms.
Sørlie T, Wang Y, Xiao C, Johnsen H, Naume B, Samaha RR, Børresen-Dale AL. Sørlie T, et al. BMC Genomics. 2006 May 26;7:127. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-127. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16729877 Free PMC article. - Gene expression profiles of breast cancer obtained from core cut biopsies before neoadjuvant docetaxel, adriamycin, and cyclophoshamide chemotherapy correlate with routine prognostic markers and could be used to identify predictive signatures.
Rody A, Karn T, Gätje R, Kourtis K, Minckwitz G, Loibl S, Munnes M, Ruckhäberle E, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M, Ahr A. Rody A, et al. Zentralbl Gynakol. 2006 Apr;128(2):76-81. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-921508. Zentralbl Gynakol. 2006. PMID: 16673249 Clinical Trial. - Basal-like phenotype is not associated with patient survival in estrogen-receptor-negative breast cancers.
Jumppanen M, Gruvberger-Saal S, Kauraniemi P, Tanner M, Bendahl PO, Lundin M, Krogh M, Kataja P, Borg A, Fernö M, Isola J. Jumppanen M, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(1):R16. doi: 10.1186/bcr1649. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17263897 Free PMC article. - [Molecular classification of breast cancer].
Zepeda-Castilla EJ, Recinos-Money E, Cuéllar-Hubbe M, Robles-Vidal CD, Maafs-Molina E. Zepeda-Castilla EJ, et al. Cir Cir. 2008 Jan-Feb;76(1):87-93. Cir Cir. 2008. PMID: 18492427 Review. Spanish. - Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: classification, prognostication, and prediction.
Reis-Filho JS, Pusztai L. Reis-Filho JS, et al. Lancet. 2011 Nov 19;378(9805):1812-23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61539-0. Lancet. 2011. PMID: 22098854 Review.
Cited by
- p16 expression correlates with basal-like triple-negative breast carcinoma.
Abou-Bakr AA, Eldweny HI. Abou-Bakr AA, et al. Ecancermedicalscience. 2013 May 14;7:317. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2013.317. Print 2013. Ecancermedicalscience. 2013. PMID: 23717338 Free PMC article. - EPMA position paper in cancer: current overview and future perspectives.
Grech G, Zhan X, Yoo BC, Bubnov R, Hagan S, Danesi R, Vittadini G, Desiderio DM. Grech G, et al. EPMA J. 2015 Apr 15;6(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13167-015-0030-6. eCollection 2015. EPMA J. 2015. PMID: 25908947 Free PMC article. - Prediction of breast cancer metastasis by gene expression profiles: a comparison of metagenes and single genes.
Burton M, Thomassen M, Tan Q, Kruse TA. Burton M, et al. Cancer Inform. 2012;11:193-217. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S10375. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Cancer Inform. 2012. PMID: 23304070 Free PMC article. - Flat epithelial atypia with and without atypical ductal hyperplasia: to re-excise or not. Results of a 5-year prospective study.
Uzoaru I, Morgan BR, Liu ZG, Bellafiore FJ, Gaudier FS, Lo JV, Pakzad K. Uzoaru I, et al. Virchows Arch. 2012 Oct;461(4):419-23. doi: 10.1007/s00428-012-1312-1. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Virchows Arch. 2012. PMID: 22961104 - Polypeptide-based nanogels co-encapsulating a synergistic combination of doxorubicin with 17-AAG show potent anti-tumor activity in ErbB2-driven breast cancer models.
Desale SS, Raja SM, Kim JO, Mohapatra B, Soni KS, Luan H, Williams SH, Bielecki TA, Feng D, Storck M, Band V, Cohen SM, Band H, Bronich TK. Desale SS, et al. J Control Release. 2015 Jun 28;208:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25660204 Free PMC article.
References
- van't Veer, L. J., Dai, H., van de Vijver, M. J., He, Y. D., Hart, A. A., Mao, M., Peterse, H. L., van der Kooy, K., Marton, M. J., Witteveen, A. T., et al. (2002) Nature 415, 530-536. - PubMed
- Gruvberger, S., Ringner, M., Chen, Y., Panavally, S., Saal, L. H., Borg, A., Ferno, M., Peterson, C. & Meltzer, P. S. (2001) Cancer Res. 61, 5979-5984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical