Functional conservation of Dhh1p, a cytoplasmic DExD/H-box protein present in large complexes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Functional conservation of Dhh1p, a cytoplasmic DExD/H-box protein present in large complexes
Stephanie S-I Tseng-Rogenski et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003.
Abstract
The DHH1 gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a putative RNA helicase of remarkable sequence similarity to several other DExD/H-box proteins, including Xp54 in Xenopus laevis and Ste13p in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. We show here that over-expression of Xp54, an integral component of the stored messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) particles, can rescue the loss of Dhh1p in yeast. Localization and sedimentation studies showed that Dhh1p exists predominantly in the cytoplasm and is present in large complexes whose sizes appear to vary according to the growth stage of the cell culture. In addition, deletion of dhh1, when placed in conjunction with the mutant dbp5 and ded1 alleles, resulted in a synergistically lethal effect, suggesting that Dhh1p may have a role in mRNA export and translation. Finally, similar to Ste13p, Dhh1p is required for sporulation in the budding yeast. Taken together, our data provide evidence that the functions of Dhh1p are conserved through evolution.
Figures
Figure 1
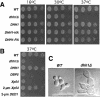
Over-expression of Xp54 complements _dhh1_Δ. (A) Growth phenotypes of the _dhh1_Δ strain. Cells were grown to mid-log phase, serially diluted and spotted on three plates, which were then separately incubated at 16, 30 and 37°C. WT, wild-type strain; _dhh1_Δ, the dhh1 deletion strain; DHH1, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with a plasmid-borne DHH1 allele; DHH1–HA, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with a plasmid-borne DHH1–HA allele; DHH1–PA, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with a plasmid-borne DHH1–PA allele. (B) Over-expression of Xp54 rescues the Ts– phenotype of the _dhh1_Δ strain. DBP5, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with a DBP5 gene carried on a CEN plasmid; Xp54, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with an Xp54 gene carried on a CEN plasmid; 2-µm Xp54, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with an Xp54 gene carried on a 2 µm plasmid; 2-µm DED1, _dhh1_Δ strain transformed with a DED1 gene carried on a 2 µm plasmid. (C) Abnormal cellular morphology of the _dhh1_Δ cells. Wild-type (WT) and _dhh1_Δ strains were grown in liquid YPD medium to mid-log phase at 30°C. Cells were then imaged by light microscopy using Nomaski optics.
Figure 2
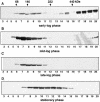
Dhh1p is present in several large complexes with different sizes at different cell culture stages. DHH1–PA strain grown in liquid cultures at 30°C to (A) early-log phase (OD600 = 0.4), (B) mid-log phase (OD600 = 0.8), (C) late-log phase (OD600 = 2.5) or (D) stationary phase (OD600 = 4.8; 4 days after inoculation). Protein extracts were sedimented through 10–30% glycerol gradients and fractionated from top to the bottom of the gradient. Proteins in each fraction were further separated by SDS–PAGE and blotted for immuno-detection of Dhh1p–PA (see Materials and Methods). The positions of the protein size markers (kDa) are indicated.
Figure 3
Dhh1p is present in large complexes that sediment between 40S and 80S. The DHH1–PA strain was grown to early log phase (OD600 = 0.4). Protein extract was loaded onto a 7–37% sucrose gradient for immunoblot analysis as described in Figure 2. The positions for the protein size markers (kDa), 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits and the 80S ribosome are indicated.
Figure 4
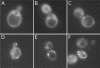
Dhh1p is localized in distinct cytoplasmic foci. Strain YTC335 expressing a functional Dhh1p–GFP was grown in synthetic medium lacking tryptophan and adenine to (C) 0.4 OD600, (D) 0.8 OD600, (E) 2.5 OD600 and (F) saturation (4 days after inoculation). Cells were harvested, stained with DAPI and imaged by light microscopy. Localization of (A) Dbp5p–GFP and (B) Ded1p–GFP were used as controls for imaging techniques.
Similar articles
- The DEAD-box RNA helicase Dbp5 functions in translation termination.
Gross T, Siepmann A, Sturm D, Windgassen M, Scarcelli JJ, Seedorf M, Cole CN, Krebber H. Gross T, et al. Science. 2007 Feb 2;315(5812):646-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1134641. Science. 2007. PMID: 17272721 - Interaction between Not1p, a component of the Ccr4-not complex, a global regulator of transcription, and Dhh1p, a putative RNA helicase.
Maillet L, Collart MA. Maillet L, et al. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 25;277(4):2835-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107979200. Epub 2001 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11696541 - Xp54 and related (DDX6-like) RNA helicases: roles in messenger RNP assembly, translation regulation and RNA degradation.
Weston A, Sommerville J. Weston A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jun 12;34(10):3082-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl409. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16769775 Free PMC article. Review. - Dbp5 - from nuclear export to translation.
Tieg B, Krebber H. Tieg B, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1829(8):791-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.10.010. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23128325 Review.
Cited by
- A role for the eIF4E-binding protein 4E-T in P-body formation and mRNA decay.
Ferraiuolo MA, Basak S, Dostie J, Murray EL, Schoenberg DR, Sonenberg N. Ferraiuolo MA, et al. J Cell Biol. 2005 Sep 12;170(6):913-24. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200504039. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16157702 Free PMC article. - The DExD/H box ATPase Dhh1 functions in translational repression, mRNA decay, and processing body dynamics.
Carroll JS, Munchel SE, Weis K. Carroll JS, et al. J Cell Biol. 2011 Aug 22;194(4):527-37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201007151. Epub 2011 Aug 15. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21844211 Free PMC article. - Quantification of elongation stalls and impact on gene expression in yeast.
Hou W, Harjono V, Harvey AT, Subramaniam AR, Zid BM. Hou W, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 20:2023.03.19.533377. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.19.533377. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 36993688 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - A novel translational control mechanism involving RNA structures within coding sequences.
Jungfleisch J, Nedialkova DD, Dotu I, Sloan KE, Martinez-Bosch N, Brüning L, Raineri E, Navarro P, Bohnsack MT, Leidel SA, Díez J. Jungfleisch J, et al. Genome Res. 2017 Jan;27(1):95-106. doi: 10.1101/gr.209015.116. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Genome Res. 2017. PMID: 27821408 Free PMC article. - Functional association of Loc1 and Puf6 with RNA helicase Dhh1 in translational regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ste12.
Jung D, Seo JS, Nam J, Kim J. Jung D, et al. PLoS One. 2019 Jul 19;14(7):e0220137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220137. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31323064 Free PMC article.
References
- Davidson E.H. (1986) Gene Activity in Early Development, 3rd Edn. Academic Press, Orlando.
- Wickens M. and Goldstrohm,A. (2003) A place to die, a place to sleep. Science, 300, 753–755. - PubMed
- Anderson P. and Kedersha,N. (2002) Stressful initiations. J. Cell Sci., 115, 3227–3234. - PubMed
- Kedersha N. and Anderson,P. (2002) Stress granules: sites of mRNA triage that regulate mRNA stability and translatability. Biochem. Soc. Trans., 30, 963–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases