Cingulate hypoactivity in cocaine users during a GO-NOGO task as revealed by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cingulate hypoactivity in cocaine users during a GO-NOGO task as revealed by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging
Jacqueline N Kaufman et al. J Neurosci. 2003.
Abstract
Although extensive evidence exists for the reinforcing properties of drugs of abuse such as cocaine, relatively less research has addressed the functional neuroanatomical correlates of the cognitive sequelae of these drugs. We present a functional magnetic resonance imaging study of a GO-NOGO task in which successful performance required prepotent behaviors to be inhibited. Significant cingulate, pre-supplementary motor and insula hypoactivity was observed for both successful NOGOs and errors of commission in chronic cocaine users relative to cocaine-naive controls. This attenuated response, in the presence of comparable activation levels in other task-related cortical areas, suggests cortical and psychological specificity in the locus of drug abuse-related cognitive dysfunction. The results suggest that addiction may be accompanied by a disruption of brain structures critical for the higher-order, cognitive control of behavior.
Figures
Figure 1.
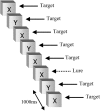
Subjects were presented with 1 Hz serial stream of alternating Xs and Ys (GO stimuli), all of which were responded to with a button press. Periodic lure presentations (NOGO stimuli) in which the target did not alternate required an inhibition of a response.
Figure 2.
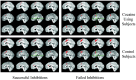
Sagittal sections show midline regions involved in the inhibitory control task. Examination of successful inhibitions (left column) and failed inhibitions (right column) between cocaine using subjects (upper row) and control subjects (bottom row) demonstrate consistent regions of activation for both groups. However, smaller volumes of activation survive thresholding for cocaine subjects for these regions, consistent with significant hypoactivity for cocaine users in midline structures.
Figure 3.
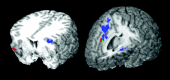
Cocaine users were significantly hypoactive relative to controls for both successful inhibitions (red) and errors of commission (blue). Overlapping hypoactivity for these two conditions was observed in the anterior cingulate.
Similar articles
- Role of the anterior cingulate and medial orbitofrontal cortex in processing drug cues in cocaine addiction.
Goldstein RZ, Tomasi D, Rajaram S, Cottone LA, Zhang L, Maloney T, Telang F, Alia-Klein N, Volkow ND. Goldstein RZ, et al. Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 23;144(4):1153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.024. Epub 2006 Dec 29. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17197102 Free PMC article. - The neurobiology of cognitive control in successful cocaine abstinence.
Connolly CG, Foxe JJ, Nierenberg J, Shpaner M, Garavan H. Connolly CG, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Feb 1;121(1-2):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.08.007. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 21885214 Free PMC article. - Executive dysfunction in cocaine addiction: evidence for discordant frontal, cingulate, and cerebellar activity.
Hester R, Garavan H. Hester R, et al. J Neurosci. 2004 Dec 8;24(49):11017-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3321-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15590917 Free PMC article. - Attenuated neural response to emotional cues in cocaine-dependence: a preliminary analysis of gender differences.
Canterberry M, Peltier MR, Brady KT, Hanlon CA. Canterberry M, et al. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2016 Sep;42(5):577-586. doi: 10.1080/00952990.2016.1192183. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2016. PMID: 27441590 Free PMC article. - Inhibitory behavioral control: A stochastic dynamic causal modeling study comparing cocaine dependent subjects and controls.
Ma L, Steinberg JL, Cunningham KA, Lane SD, Bjork JM, Neelakantan H, Price AE, Narayana PA, Kosten TR, Bechara A, Moeller FG. Ma L, et al. Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Mar 24;7:837-47. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.03.015. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26082893 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Neural correlates of visual motion prediction.
Cheong D, Zubieta JK, Liu J. Cheong D, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039854. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768145 Free PMC article. - Are executive function and impulsivity antipodes? A conceptual reconstruction with special reference to addiction.
Bickel WK, Jarmolowicz DP, Mueller ET, Gatchalian KM, McClure SM. Bickel WK, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Jun;221(3):361-87. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2689-x. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22441659 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of cognitive control in cocaine dependence.
Garavan H, Hester R. Garavan H, et al. Neuropsychol Rev. 2007 Sep;17(3):337-45. doi: 10.1007/s11065-007-9034-x. Epub 2007 Aug 7. Neuropsychol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17680368 Review. - Role of the anterior cingulate and medial orbitofrontal cortex in processing drug cues in cocaine addiction.
Goldstein RZ, Tomasi D, Rajaram S, Cottone LA, Zhang L, Maloney T, Telang F, Alia-Klein N, Volkow ND. Goldstein RZ, et al. Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 23;144(4):1153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.024. Epub 2006 Dec 29. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17197102 Free PMC article. - Brain Network Topology and Structural-Functional Connectivity Coupling Mediate the Association Between Gut Microbiota and Cognition.
Zhang S, Xu X, Li Q, Chen J, Liu S, Zhao W, Cai H, Zhu J, Yu Y. Zhang S, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Mar 29;16:814477. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.814477. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35422686 Free PMC article.
References
- Aron AR, Fletcher PC, Bullmore ET, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW ( 2003) Stop-signal inhibition disrupted by damage to right inferior frontal gyrus in humans. Nat Neurosci 6: 115-116. - PubMed
- Bechara A ( 2003) Risky business: emotion, decision-making, and addiction. J Gambl Stud 19: 23-51. - PubMed
- Bechara A, Dolan S, Denburg N, Hindes A, Anderson SW, Nathan PE ( 2001) Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39: 376-389. - PubMed
- Botvinick MM, Braver TS, Barch DM, Carter CS, Cohen JD ( 2001) Conflict monitoring and cognitive control. Psychol Rev 108: 624-652. - PubMed
- Brass M, Zysset S, von Cramon DY ( 2001) The inhibition of imitative response tendencies. NeuroImage 14: 1416-1423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical