Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses
Julian P T Higgins et al. BMJ. 2003.
Abstract
Cochrane Reviews have recently started including the quantity _I_2 to help readers assess the consistency of the results of studies in meta-analyses. What does this new quantity mean, and why is assessment of heterogeneity so important to clinical practice?
Figures
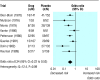
Fig 1
Eight trials of amantadine for prevention of influenza. Outcome is cases of influenza. Summary odds ratios calculated with random effects method
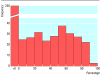
Fig 2
Distribution of observed values of _I_2 based on odds ratios from 509 meta-analyses of dichotomous outcomes in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Data are from the first subgroup (if any) in the first meta-analysis (if any) in each review, if it involved a dichotomous outcome and at least two trials with events. Meta-analyses conducted with metan in STATA
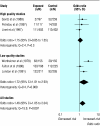
Fig 3
Meta-analyses of six case-control studies relating residential exposure to electromagnetic fields to childhood leukaemia. Summary odds ratio calculated by random effects method
Comment in
- Association between maternal age at conception and risk of idiopathic clubfoot.
Liu YB, Zhao L, Ding J, Zhu J, Xie CL, Wu ZK, Yang X, Li H. Liu YB, et al. Acta Orthop. 2016 Jun;87(3):291-5. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2016.1153359. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Acta Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26901038 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Diagnostic statistical procedures in medical meta-analyses.
Olkin I. Olkin I. Stat Med. 1999 Sep 15-30;18(17-18):2331-41. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19990915/30)18:17/18<2331::aid-sim259>3.0.co;2-l. Stat Med. 1999. PMID: 10474143 - Interpretation of tests of heterogeneity and bias in meta-analysis.
Ioannidis JP. Ioannidis JP. J Eval Clin Pract. 2008 Oct;14(5):951-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.00986.x. J Eval Clin Pract. 2008. PMID: 19018930 Review. - [Meta-analyses based on individual patient data (IPD)].
Bekkering GE, Cools F, Aertgeerts B, de Backer TL, Kellen E, van der Stichele RH, Buntinx F. Bekkering GE, et al. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2009 Feb 28;153(9):402-6. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2009. PMID: 19348098 Review. Dutch. No abstract available. - Meta-analytic methods for diagnostic test accuracy.
Irwig L, Macaskill P, Glasziou P, Fahey M. Irwig L, et al. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995 Jan;48(1):119-30; discussion 131-2. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(94)00099-c. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995. PMID: 7853038 Review. - What's with epidemiologic meta-analyses?
Partanen T. Partanen T. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1996 Aug;22(4):241-2. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.137. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1996. PMID: 8881011 No abstract available.
References
- Guyatt G, Sinclair J, Cook D, Jaeschke R, Schünemann H, Pauker S. Moving from evidence to action. In: Guyatt G, Rennie D, eds. Users' guides to the medical literature: a manual for evidence-based clinical practice. Chicago: American Medical Association, 2002: 599-608.
- Petitti DB. Approaches to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat Med 2001;20: 3625-33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources