Evaluation of gene expression measurements from commercial microarray platforms - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2003 Oct 1;31(19):5676-84.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg763.
Affiliations
- PMID: 14500831
- PMCID: PMC206463
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg763
Comparative Study
Evaluation of gene expression measurements from commercial microarray platforms
Paul K Tan et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003.
Abstract
Multiple commercial microarrays for measuring genome-wide gene expression levels are currently available, including oligonucleotide and cDNA, single- and two-channel formats. This study reports on the results of gene expression measurements generated from identical RNA preparations that were obtained using three commercially available microarray platforms. RNA was collected from PANC-1 cells grown in serum-rich medium and at 24 h following the removal of serum. Three biological replicates were prepared for each condition, and three experimental replicates were produced for the first biological replicate. RNA was labeled and hybridized to microarrays from three major suppliers according to manufacturers' protocols, and gene expression measurements were obtained using each platform's standard software. For each platform, gene targets from a subset of 2009 common genes were compared. Correlations in gene expression levels and comparisons for significant gene expression changes in this subset were calculated, and showed considerable divergence across the different platforms, suggesting the need for establishing industrial manufacturing standards, and further independent and thorough validation of the technology.
Figures
Figure 1
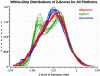
A comparison of distributions of log signal intensity values from repeated experiments on three different commercial microarray technologies. Heterogeneous intensity scales across platforms were rescaled using a Z-transformation with mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1.
Figure 2
Heat map of gene expression measurements normalized to a single array showing genes in rows and samples in columns.
Figure 3
Experimental error plots of Z-scores as a function of mean intensity. Data from experimental replicates were used for standard deviation calculations.
Figure 4
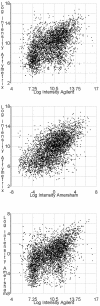
Correlations of the gene-matched mRNA measurements. Scatter plots are of the mean of log intensity values. Pearson’s correlation coefficients of these means and 95% confidence intervals are reported in Table 1.
Figure 5
Venn diagram of genes classified as differentially expressed by each platform using a mixed-model nested ANOVA and an alpha cut-off of 0.001.
References
- Yang X., Pratley,R.E., Tokraks,S., Bogardus,C. and Permana,P.A. (2002) Microarray profiling of skeletal muscle tissues from equally obese, non-diabetic insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant Pima Indians. Diabetologia, 45, 1584–1593. - PubMed
- Chuaqui R.F., Bonner,R.F., Best,C.J., Gillespie,J.W., Flaig,M.J., Hewitt,S.M., Phillips,J.L., Krizman,D.B., Tangrea,M.A., Ahram,M., Linehan,W.M., Knezevic,V. and Emmert-Buck,M.R. (2002) Post-analysis follow-up and validation of microarray experiments. Nature Genet., 32, 509–514. - PubMed
- Holloway A.J., Van Laar,R.K., Tothil,R.W. and Bowtell,D.D.L. (2002) Options available—from start to finish—for obtaining data from DNA microarrays II. Nature Genet., 32, 481–489. - PubMed
- Kuo W.P., Jenssen,T.K., Butte,A.J., Ohno-Machado,L. and Kohane,I.S. (2002) Analysis of matched mRNA measurements from two different microarray technologies. Bioinformatics, 18, 405–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases