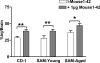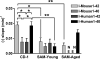Efflux of human and mouse amyloid beta proteins 1-40 and 1-42 from brain: impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Efflux of human and mouse amyloid beta proteins 1-40 and 1-42 from brain: impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
W A Banks et al. Neuroscience. 2003.
Abstract
Brain to blood transport is believed to be a major determinant of the amount of amyloid beta protein (AbetaP) found in brain. Impaired efflux has been suggested as a mechanism by which AbetaP can accumulate in the CNS and so lead to Alzheimer's disease (AD). To date, however, no study of the efflux of the form of AbetaP most relevant to AD, AbetaP1-42, has been conducted, even though a single amino acid substitution in AbetaP can greatly alter efflux. Here, we examined the efflux of AbetaP mouse1-42, mouse1-40, human1-42, and human1-40 in young CD-1, young senesence accelerated mouse (SAM) P8, and aged SAMP8 mice. The SAMP8 mouse with aging spontaneously overproduces AbetaP and develops cognitive impairments reversed by AbetaP-directed antibody or phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide. CD-1 mice transported all forms of AbetaP, although mouse1-42 and human1-40 were transported faster than the other forms. There was a decrease in the saturable transport of mouse1-42 in SAMP8 mice regardless of age. Efflux of mouse1-40 and human1-42 was only by a non-saturable mechanism in young SAMP8 mice and their efflux was totally absent in aged SAMP8 mice. These differences in the efflux of the various forms of AbetaP among the three groups of mice supports the hypothesis that impaired efflux is an important factor in the accumulation of AbetaP in the CNS.
Figures
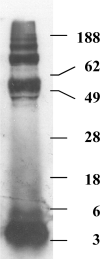
Figure 1
SDS gel of mouse AßP1-42 radioactively labeled with NaI by the chloramine-T method and purified on a column of sephadex G-10.
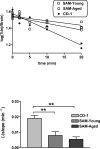
Figure 2
Efflux of AßPmouse1-42 from the CNS to Blood in CD-1, Young SAMP8, and Aged SAMP8 mice. Upper Panel: The relation between log(%Inj/brain) and time was statistically significant for each group of mice, demonstrating that AßP was cleared from the CNS. Lower Panel: the CD-1 mice cleared mouse1-42 more quickly than the SAMP8 mice.
Figure 3
Saturable Component to the Efflux of AßP mouse1-42 in CD-1, Young SAMP8, and Aged SAMP8 mice. All three groups of mice had a saturable component to efflux.
Figure 4
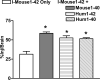
Slopes of All AßP peptides in Each Group of Mice. A 2-way ANOVA showed statistical significance among the slopes for interaction (p<0.001), a trend for peptide, and no effect for mouse group. Newman-Keuls range test found the statistical differences shown: *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
Figure 5
Effects of Various AßP's on the Efflux of radioactive Mouse1-42. Each of the peptides produced a statistically significant inhibition in the efflux of mouse1-42.
Similar articles
- Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.
Salisbury L, Baraitser L. Salisbury L, et al. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.
Lee CC, Chen CW, Yen HK, Lin YP, Lai CY, Wang JL, Groot OQ, Janssen SJ, Schwab JH, Hsu FM, Lin WH. Lee CC, et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924 - Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.
Pillay J, Gaudet LA, Saba S, Vandermeer B, Ashiq AR, Wingert A, Hartling L. Pillay J, et al. Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article. - Enabling Systemic Identification and Functionality Profiling for Cdc42 Homeostatic Modulators.
Malasala S, Azimian F, Chen YH, Twiss JL, Boykin C, Akhtar SN, Lu Q. Malasala S, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.05.574351. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.05.574351. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38260445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.
Triana L, Palacios Huatuco RM, Campilgio G, Liscano E. Triana L, et al. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
- IgG-assisted age-dependent clearance of Alzheimer's amyloid beta peptide by the blood-brain barrier neonatal Fc receptor.
Deane R, Sagare A, Hamm K, Parisi M, LaRue B, Guo H, Wu Z, Holtzman DM, Zlokovic BV. Deane R, et al. J Neurosci. 2005 Dec 14;25(50):11495-503. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3697-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16354907 Free PMC article. - The Blood-Brain Barrier, Oxidative Stress, and Insulin Resistance.
Banks WA, Rhea EM. Banks WA, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;10(11):1695. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111695. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829566 Free PMC article. Review. - Enhanced proteolytic clearance of plasma Aβ by peripherally administered neprilysin does not result in reduced levels of brain Aβ in mice.
Walker JR, Pacoma R, Watson J, Ou W, Alves J, Mason DE, Peters EC, Urbina HD, Welzel G, Althage A, Liu B, Tuntland T, Jacobson LH, Harris JL, Schumacher AM. Walker JR, et al. J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 6;33(6):2457-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3407-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23392674 Free PMC article. - Alzheimer's Retinopathy: Seeing Disease in the Eyes.
Mirzaei N, Shi H, Oviatt M, Doustar J, Rentsendorj A, Fuchs DT, Sheyn J, Black KL, Koronyo Y, Koronyo-Hamaoui M. Mirzaei N, et al. Front Neurosci. 2020 Sep 8;14:921. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00921. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33041751 Free PMC article. Review. - Suppression of glymphatic fluid transport in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Peng W, Achariyar TM, Li B, Liao Y, Mestre H, Hitomi E, Regan S, Kasper T, Peng S, Ding F, Benveniste H, Nedergaard M, Deane R. Peng W, et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Sep;93:215-25. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.05.015. Epub 2016 May 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 27234656 Free PMC article.
References
- Bacskai BJ, Kajdasz ST, Christie RH, Carter C, Games D, Seubert P, Schenk D, Hyman BT. Imaging of amyloid-β deposits in brains of living mice permits direct observation of clearance of plaques with immunotherapy. Nature Medicine. 2001;7:369–372. - PubMed
- Bading JR, Yamada S, Mackic JB, Kirkman L, Miller C, Calero M, Ghiso J, Frangione B, Zlokovic BV. Brain clearance of Alzheimer's amyloid-ß040 in the squirrel monkey: A SPECT study in a primate model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Drug Targeting. 2002;10:359–368. - PubMed
- Banks WA, Broadwell RD. Blood to brain and brain to blood passage of native horseradish peroxidase, wheat germ agglutinin and albumin: pharmacokinetic and morphological assessments. J Neurochem. 1994;62:2404–2419. - PubMed
- Banks WA, DiPalma CR, Farrell CL. Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier in obesity. Peptides. 1999;20:1341–1345. - PubMed
- Banks WA, Farr SA, Butt W, Kumar VB, Franko MW, Morley JE. Delivery across the blood-brain barrier of antisense directed againt amyloid β: reversal of learning and memory deficits in mice overexpressing amyloid precursor protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297:1113–1121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG029839-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012743/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041863/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG029839/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS41863/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA12743/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical