Characterization of divIVA and other genes located in the chromosomal region downstream of the dcw cluster in Streptococcus pneumoniae - PubMed (original) (raw)
Characterization of divIVA and other genes located in the chromosomal region downstream of the dcw cluster in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Daniela Fadda et al. J Bacteriol. 2003 Oct.
Abstract
We analyzed the chromosome region of Streptococcus pneumoniae located downstream of the division and cell wall (dcw) cluster that contains the homolog of the Bacillus subtilis cell division gene divIVA and some genes of unknown function. Inactivation of divIVA in S. pneumoniae resulted in severe growth inhibition and defects in cell shape, nucleoid segregation, and cell division. Inactivation of the ylm genes resulted in some morphological and/or division abnormalities, depending on the inactivated gene. Transcriptional analysis revealed a relationship between these genes and the ftsA and ftsZ cell division genes, also indicating that the connection between the dcw cluster and the divIVA region is more extensive than just chromosomal position and gene organization.
Figures
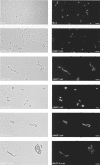
FIG.1.
Phase-contrast analysis of the Rx1 wild-type strain and the insertion-deletion mutants. Bacterial cells were cultured in TSB medium, sampled at selected times during the exponential phase of growth, fixed with 1% (vol/vol) formaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature, treated with DAPI as previously described (2), and examined by using an Axioskop HBO50 equipped with a Plan-Neofluar 100× oil lens. For each strain, phase-contrast (left panels) and DAPI stain fluorescence (right panels) micrographs are shown. The scale bars correspond to 3 μm.
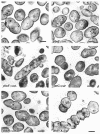
FIG. 2.
Electronic transmission analysis of the Rx1 wild-type strain and of the insertion-deletion mutants. Cells were cultured in TSB medium to mid-exponential phase, fixed in 1% (vol/vol) glutaraldehyde for 2 h at room temperature, processed as previously described (11), and then observed and photographed in a Zeiss EM 10 electron microscope. The abnormalities of various null mutants are described in the text and summarized in Table 1. The scale bars correspond to 0.3 μm.
FIG. 3.
Transcriptional analysis of the region downstream of each insertion by RT-PCR. The random primer Pd(N)6 or the specific primer PDIVR was used to generate cDNA. Total RNA from the S. pneumoniae Rx1 strain and ylm::cat mutants was used as the template in a reverse transcriptase reaction with primers (PAF, PZR, PFF, PFR, PGF, PGR, PHF, PHR, and PDIVF) internal to each gene. Expression of the genes in the wild-type Rx1 strain and in the insertion-deletion mutants would give products of the following sizes: ylmF (F), 477 bp; ylmG (G), 202 bp; ylmH (H), 661 bp; and divIVA (DIV), 663 bp. A positive control, _ftsA_-ftsZ (AZ), 1,902 bp, was included in all reactions. Negative controls included identical reactions to which no cDNA template was added. DNA contamination of the RNA samples was ruled out by performing PCR directly on the RNAs (data not shown). The source of the respective RNA template used for each set of reactions is indicated under each panel. M, _Hin_dIII-digested λ phage.
Similar articles
- Unconventional organization of the division and cell wall gene cluster of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Massidda O, Anderluzzi D, Friedli L, Feger G. Massidda O, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 1998 Nov;144 ( Pt 11):3069-3078. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-11-3069. Microbiology (Reading). 1998. PMID: 9846742 - DivIVA controls the dynamics of septum splitting and cell elongation in Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Trouve J, Zapun A, Bellard L, Juillot D, Pelletier A, Freton C, Baudoin M, Carballido-Lopez R, Campo N, Wong Y-S, Grangeasse C, Morlot C. Trouve J, et al. mBio. 2024 Oct 16;15(10):e0131124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01311-24. Epub 2024 Sep 17. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39287436 Free PMC article. - Insertional mutation of orfD of the DCW cluster of Streptococcus pneumoniae attenuates virulence.
Palmen R, Ogunniyi AD, Berroy P, Larpin S, Paton JC, Trombe MC. Palmen R, et al. Microb Pathog. 1999 Dec;27(6):337-48. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1999.0310. Microb Pathog. 1999. PMID: 10588907 - ylm Has More than a (Z Anchor) Ring to It!
White ML, Eswara PJ. White ML, et al. J Bacteriol. 2021 Jan 11;203(3):e00460-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00460-20. Print 2021 Jan 11. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 32900832 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of transcription of cell division genes in the Escherichia coli dcw cluster.
Vicente M, Gomez MJ, Ayala JA. Vicente M, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998 Apr;54(4):317-24. doi: 10.1007/s000180050158. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9614967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A specific c-type cytochrome maturation system is required for oxygenic photosynthesis.
Kuras R, Saint-Marcoux D, Wollman FA, de Vitry C. Kuras R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 5;104(23):9906-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702340104. Epub 2007 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17535914 Free PMC article. - Genetic and biochemical characterization of the MinC-FtsZ interaction in Bacillus subtilis.
Blasios V, Bisson-Filho AW, Castellen P, Nogueira ML, Bettini J, Portugal RV, Zeri AC, Gueiros-Filho FJ. Blasios V, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060690. Epub 2013 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577149 Free PMC article. - The YlmG protein has a conserved function related to the distribution of nucleoids in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria.
Kabeya Y, Nakanishi H, Suzuki K, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Matsui M, Miyagishima SY. Kabeya Y, et al. BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Apr 2;10:57. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-57. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20359373 Free PMC article. - EF1025, a Hypothetical Protein From Enterococcus faecalis, Interacts With DivIVA and Affects Cell Length and Cell Shape.
Sharma K, Sultana T, Liao M, Dahms TES, Dillon JR. Sharma K, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 12;11:83. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00083. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32117116 Free PMC article. - Structural and genetic analyses reveal the protein SepF as a new membrane anchor for the Z ring.
Duman R, Ishikawa S, Celik I, Strahl H, Ogasawara N, Troc P, Löwe J, Hamoen LW. Duman R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 26;110(48):E4601-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313978110. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24218584 Free PMC article.
References
- Bramhill, D. 1997. Bacterial cell division. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13:395-424. - PubMed
- Claverys, J. P., A. Dintilhac, E. V. Pestova, B. Martin, and D. A. Morrison. 1995. Construction and evaluation of new drug-resistance cassettes for gene disruption mutagenesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae, using an ami test platform. Gene 164:123-128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases