The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2003 May-Aug;9(5-8):125-34.
Affiliations
- PMID: 14571320
- PMCID: PMC1430829
Review
The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation
Valentin A Pavlov et al. Mol Med. 2003 May-Aug.
Abstract
This review outlines the mechanisms underlying the interaction between the nervous and immune systems of the host in response to an immune challenge. The main focus is the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, which we recently described as a novel function of the efferent vagus nerve. This pathway plays a critical role in controlling the inflammatory response through interaction with peripheral a7 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on macrophages. We describe the modulation of systemic and local inflammation by the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and its function as an interface between the brain and the immune system. The clinical implications of this novel mechanism also are discussed.
Figures
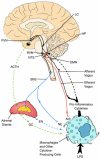
Figure 1
Neural and humoral pathways in immunomodulation. During immune challenge activated macrophages and other immune and nonimmune cells release cytokines that signal the brain for activation of immunomodulatory mechanisms. Central immunomodulation is achieved by the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, HPA axis, and SNS (see text for details). AP, area postrema; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; DMN, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; RVM, rostral ventrolateral medulla; LC, locus coeruleus; SNS, sympathetic nervous system; ACTH, adrenocorticotropin hormone; GC, glucocorticoids; EN, epinephrine; NE, norepinephrine; ACh, acetylcholine; LPS, lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin).
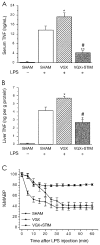
Figure 2
Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the endotoxin-induced serum TNF response, hepatic TNF response, and development of endotoxemic shock. Rats were subjected to sham surgery (A and B: Sham, □; C:•; n = 7), bilateral cervical vagotomy (A and B: VGX, ▧, C:▴; n = 7), or vagotomy and electrical stimulation (A and B: VGX + STIM, ▩ C: ▪; n = 7). A: Serum TNF response. B: Hepatic TNF response. C: Development of endotoxemic shock. Mean arterial blood pressure data are normalized to MABP at time = 0. Sham-surgery, vagotomy, and electrical stimulation with vagotomy did not significantly affect MABP in vehicle-treated controls (not shown). Data are means +/− SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005 compared with SHAM + endotoxin; #P < 0.05 compared with VGX + endotoxin. Taken from Borovikova and others (16) with _Nature_’s copyright permission <
>.
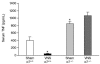
Figure 3
Vagus nerve stimulation does not inhibit TNF in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit–deficient mice. α7 Subunit–deficient mice (−/−) or age- and sex-matched wild-type littermates (+/+) were subjected to either sham operation (Sham) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS, left vagus, 1 volt, 2 ms, 1 Hz); blood was collected 2 h after endotoxin administration. Serum TNF levels were determined by ELISA. Sham α7+/+, n = 10; VNS α7+/+, Sham α7−/−, VNS α7−/−, n = 11. *P < 0.05 compared with Sham α7+/+. Taken from Wang and others (105) with _Nature_’s copyright permission: <
>.
Similar articles
- The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ. Pavlov VA, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2005 Nov;19(6):493-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2005.03.015. Brain Behav Immun. 2005. PMID: 15922555 Review. - Vagal-immune interactions involved in cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Zila I, Mokra D, Kopincova J, Kolomaznik M, Javorka M, Calkovska A. Zila I, et al. Physiol Res. 2017 Sep 22;66(Suppl 2):S139-S145. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.933671. Physiol Res. 2017. PMID: 28937230 Review. - The Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway as a Conceptual Framework to Treat Inflammation-Mediated Renal Injury.
Jarczyk J, Yard BA, Hoeger S. Jarczyk J, et al. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019;44(4):435-448. doi: 10.1159/000500920. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019. PMID: 31307039 Review. - Neuro-immune interactions in the cholinergic anti-inflammatory reflex.
Reardon C. Reardon C. Immunol Lett. 2016 Oct;178:92-6. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Immunol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27542331 Review. - The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a critical review.
Martelli D, McKinley MJ, McAllen RM. Martelli D, et al. Auton Neurosci. 2014 May;182:65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2013.12.007. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Auton Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24411268 Review.
Cited by
- Workplace based mindfulness practice and inflammation: a randomized trial.
Malarkey WB, Jarjoura D, Klatt M. Malarkey WB, et al. Brain Behav Immun. 2013 Jan;27(1):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Brain Behav Immun. 2013. PMID: 23078984 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - What's New in Traumatic Brain Injury: Update on Tracking, Monitoring and Treatment.
Reis C, Wang Y, Akyol O, Ho WM, Ii RA, Stier G, Martin R, Zhang JH. Reis C, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 26;16(6):11903-65. doi: 10.3390/ijms160611903. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26016501 Free PMC article. Review. - Neuroimmune Cross Talk in the Gut. Neuroendocrine and neuroimmune pathways contribute to the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome.
O'Malley D. O'Malley D. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):G934-G941. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00272.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27742703 Free PMC article. Review. - Lipopolysaccharide upregulates α7 acetylcholine receptors: stimulation with GTS-21 mitigates growth arrest of macrophages and improves survival in burned mice.
Khan MA, Farkhondeh M, Crombie J, Jacobson L, Kaneki M, Martyn JA. Khan MA, et al. Shock. 2012 Aug;38(2):213-9. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31825d628c. Shock. 2012. PMID: 22683726 Free PMC article. - Cholinergic signaling via the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates the migration of monocyte-derived macrophages during acute inflammation.
Keever KR, Cui K, Casteel JL, Singh S, Hoover DB, Williams DL, Pavlov VA, Yakubenko VP. Keever KR, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Jan 4;21(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-03001-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38178134 Free PMC article.
References
- Sell S. (2001) Immunology, immunopathology, and immunity (6th ed). ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
- Baumann H, Gauldie J. The acute phase response. Immunol Today. 1994;15:74–80. - PubMed
- Koj A. Initiation of acute phase response and synthesis of cytokines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1317:84–94. - PubMed
- Tracey KJ, et al. Shock and tissues injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986;234:470–4. - PubMed
- Wang H, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285:248–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical