Predisposition locus for major depression at chromosome 12q22-12q23.2 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2003 Dec;73(6):1271-81.
doi: 10.1086/379978. Epub 2003 Nov 5.
Nicola J Camp, Charles H Hensel, Chris D Neff, Deanna L Russell, Dana C Hughes, Agnes M Plenk, Michael R Lowry, R Lynn Richards, Catherine Carter, Georges C Frech, Steven Stone, Kerry Rowe, Chi Ai Chau, Kathleen Cortado, Angelene Hunt, Karanina Luce, Gayanne O'Neil, Jeff Poarch, Jennifer Potter, Gregg H Poulsen, Heidi Saxton, Michelle Bernat-Sestak, Victor Thompson, Alexander Gutin, Mark H Skolnick, Donna Shattuck, Lisa Cannon-Albright
Affiliations
- PMID: 14606042
- PMCID: PMC1180393
- DOI: 10.1086/379978
Comparative Study
Predisposition locus for major depression at chromosome 12q22-12q23.2
Victor Abkevich et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Dec.
Abstract
Major depression disorder is a common psychiatric disease with a major economic impact on society. In many cases, no effective treatment is available. The etiology of major depression is complex, but it is clear that the disease is, to a large extent, determined genetically, especially among individuals with a familial history of major depression, presumably through the involvement of multiple predisposition genes in addition to an environmental component. As a first step toward identification of chromosomal loci contributing to genetic predisposition to major depression, we have conducted a genomewide scan by using 628 microsatellite markers on 1,890 individuals from 110 Utah pedigrees with a strong family history of major depression. We identified significant linkage to major depression in males at marker D12S1300 (multipoint heterogeneity LOD score 4.6; P=.00003 after adjustment for multiple testing). With additional markers, the linkage evidence became highly significant, with the multipoint heterogeneity LOD score at marker D12S1706 increasing to 6.1 (P=.0000007 after adjustment for multiple testing). This study confirms the presence of one or more genes involved in psychiatric diseases on the q arm of chromosome 12 and provides strong evidence for the existence of a sex-specific predisposition gene to major depression at 12q22-q23.2.
Figures
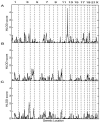
Figure 1
Results of genomic search for loci linked to MDD. Multipoint HLOD scores for the dominant model are plotted on the _Y_-axis, and marker positions (in cM) are plotted on the _X_-axis. Vertical dashed lines delimit the chromosomes, and chromosome numbers (odd numbers only) are indicated at the top of the figure. A, HLOD for DEPM phenotype. B, HLOD for DEPF phenotype. C, HLOD for DEP phenotype.
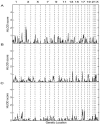
Figure 2
Results of genomic search for loci linked to MDD. Multipoint HLOD scores for the recessive model are plotted on the _Y_-axis, and marker positions (in cM) are plotted on the _X_-axis. Vertical dashed lines delimit the chromosomes, and chromosome numbers (odd numbers only) are indicated at the top of the figure. A, HLOD for DEPM phenotype. B, HLOD for DEPF phenotype. C, HLOD for DEP phenotype.
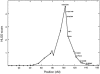
Figure 3
Results of linkage analyses for chromosome 12, from the genomic search for loci linked to MDD. Multipoint HLOD scores for the dominant model and DEPM phenotype are plotted on the _Y_-axis, and marker positions (in cM) are plotted on the _X_-axis. Black dots correspond to the position of markers used in the analysis. Markers at which the strongest linkages were observed for psychiatric disorders (see fig. 6) are indicated.
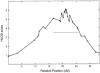
Figure 4
Linkage analyses of chromosomal region 12q21.1-q23.3 with additional markers (dominant model, DEPM phenotype). Black dots correspond to the position of markers used in the analysis. The dashed line indicates the region within boundaries determined by recombination events in three pedigrees with the strongest linkage evidence (see fig. 5).
Figure 5
Recombinations in three pedigrees with the strongest linkage evidence (>1.5 LOD score units) to chromosomal region 12q22-q23.2. Four affected males share the haplotype with recombination at marker D12S1607 in pedigree 101. One affected male shares the haplotype with recombination at marker D12S1607 in pedigree 102. Three affected males share the haplotype with recombination at marker 12-MYR0256 in pedigree 102. One affected male shares the haplotype with recombination at marker 12-MYR0287 in pedigree 103. Two affected males share the haplotype with recombination at marker D12S309 in pedigree 103.
Figure 6
A map of chromosomal region 12q22-q24, showing relevant markers for different psychiatric diseases and corresponding linkage evidence. Markers and references are as follows: D12S1300 (Wilcox et al. 2002); D12S1706 (present study); D12S346 (Fullerton et al. 2003); IGF1 (Maziade et al. 2002); PAH (Brzustowicz et al. ; Ekholm et al. 2001); D12S84 (Morissette et al. 1999); ATP2A2 (Craddock et al. ; Jones et al. 2002); D12S366 (Barden et al., cited by Detera-Wadleigh et al. 1999); D12S342 (McQuillin et al., cited by Detera-Wadleigh et al. ; Degn et al. 2001), D12S1639 (Ewald 2002). The P value of .001 corresponds to a LOD score of 2.4, and the P value of .00002 corresponds to LOD score of 4.0.
Similar articles
- Genome-wide scan for hypertension linkage to chromosome 12q23.1 - q23.3 in a Chinese family.
Dong Y, Yang L, Fang F, Zhang J, Jiang G, Xu S. Dong Y, et al. Indian J Med Res. 2013 May;137(5):935-41. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23760380 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide linkage analyses of extended Utah pedigrees identifies loci that influence recurrent, early-onset major depression and anxiety disorders.
Camp NJ, Lowry MR, Richards RL, Plenk AM, Carter C, Hensel CH, Abkevich V, Skolnick MH, Shattuck D, Rowe KG, Hughes DC, Cannon-Albright LA. Camp NJ, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005 May 5;135B(1):85-93. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30177. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005. PMID: 15806581 - Genome-wide multipoint parametric linkage analysis of pulse pressure in large, extended utah pedigrees.
Camp NJ, Hopkins PN, Hasstedt SJ, Coon H, Malhotra A, Cawthon RM, Hunt SC. Camp NJ, et al. Hypertension. 2003 Sep;42(3):322-8. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000084874.85653.46. Epub 2003 Jul 21. Hypertension. 2003. PMID: 12874090 - Restless legs syndrome: confirmation of linkage to chromosome 12q, genetic heterogeneity, and evidence of complexity.
Desautels A, Turecki G, Montplaisir J, Xiong L, Walters AS, Ehrenberg BL, Brisebois K, Desautels AK, Gingras Y, Johnson WG, Lugaresi E, Coccagna G, Picchietti DL, Lazzarini A, Rouleau GA. Desautels A, et al. Arch Neurol. 2005 Apr;62(4):591-6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.4.591. Arch Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15824258 - The genetics of major depression.
Flint J, Kendler KS. Flint J, et al. Neuron. 2014 Feb 5;81(3):484-503. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.027. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24507187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Overview of the genetics of major depressive disorder.
Lohoff FW. Lohoff FW. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2010 Dec;12(6):539-46. doi: 10.1007/s11920-010-0150-6. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2010. PMID: 20848240 Free PMC article. Review. - Gene-environment interaction and the genetics of depression.
Lesch KP. Lesch KP. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004 May;29(3):174-84. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15173894 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetics of major mood disorders.
Berrettini W. Berrettini W. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2004 Sep;1(2):38-48. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2004. PMID: 21197377 Free PMC article. - Ethiopathogenesis of depressive disorders.
Pasquini M, Berardelli I, Biondi M. Pasquini M, et al. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2014 Dec 19;10:166-71. doi: 10.2174/1745017901410010166. eCollection 2014. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2014. PMID: 25614753 Free PMC article. - The genetics of major depression: moving beyond the monoamine hypothesis.
Shyn SI, Hamilton SP. Shyn SI, et al. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2010 Mar;33(1):125-40. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2009.10.004. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 20159343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edition. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
- Angst J, Angst F, Stassen HH (1999) Suicide risk in patients with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 60 Suppl 2:57–62 - PubMed
- Bertelsen A, Harvald B, Hauge M (1977) A Danish twin study of manic-depressive disorders. Br J Psychiatry 130:330–351 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials