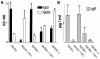High levels of susceptibility and T helper 2 response in MyD88-deficient mice infected with Leishmania major are interleukin-4 dependent - PubMed (original) (raw)
High levels of susceptibility and T helper 2 response in MyD88-deficient mice infected with Leishmania major are interleukin-4 dependent
Andrea Debus et al. Infect Immun. 2003 Dec.
Abstract
Myeloid differentiation protein 88 (MyD88) is a general adaptor for the signaling cascade through receptors of the Toll/IL-1R family. When infected with Leishmania major parasites, MyD88-deficient mice displayed a dramatically enhanced parasite burden in their tissues similar to that found in susceptible BALB/c mice. In contrast, MyD88 knockout mice did not develop ulcerating lesions despite a lack of interleukin-12 (IL-12) production and a predominant T helper 2 cell response. Blockade of IL-4 produced early (day 1) after infection restored a protective T helper 1 response in MyD88 knockout mice.
Figures
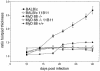
FIG. 1.
Lesion development after infection with L. major. Female BALB/c, C57BL/6, and MyD88-deficient C57BL/6 mice were infected with 2 × 106 stationary-phase promastigotes of L. major in 50 μl of PBS subcutaneously in the right hind footpad. Mice received either 500 μl of PBS (controls) or 1 mg of anti-IL-4 antibody 11B11 in 500 μl of PBS intraperitoneally on day 1 after infection. The data shown represent the mean values and standard error of the mean of the footpad swelling of six mice in one of two similar experiments.
FIG. 2.
Humoral immune response in _L. major_-infected mice. The titers of _L. major_-specific IgG1 and IgG2a antibodies (A) and concentrations of total IgE (B) were determined on day 35 after infection. The mean and standard deviation are shown.
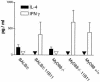
FIG. 3.
Cytokine secretion by cells from lesion-draining lymph nodes on day 35 after infection. Cells (2 × 106/ml) were stimulated in vitro for 48 h. Concentrations of IL-4 and IFN-γ were determined by ELISA. The mean and standard deviation of three mice per group are shown.
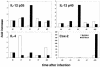
FIG. 4.
Expression of cytokine and COX-2 mRNAs in lesion-draining lymph nodes during the course of infection. Total RNA was isolated from the lymph nodes of two mice per group at each time point indicated. After reverse transcription, the concentrations of IL-12p35, p40, IL-4, and COX-2 cDNAs were determined by real-time PCR and normalized for two housekeeping genes. The data shown are the means of four determinations.
Similar articles
- Genetically resistant mice lacking MyD88-adapter protein display a high susceptibility to Leishmania major infection associated with a polarized Th2 response.
Muraille E, De Trez C, Brait M, De Baetselier P, Leo O, Carlier Y. Muraille E, et al. J Immunol. 2003 Apr 15;170(8):4237-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4237. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12682257 - Deletion of IL-4Ralpha on CD4 T cells renders BALB/c mice resistant to Leishmania major infection.
Radwanska M, Cutler AJ, Hoving JC, Magez S, Holscher C, Bohms A, Arendse B, Kirsch R, Hunig T, Alexander J, Kaye P, Brombacher F. Radwanska M, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2007 May 11;3(5):e68. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030068. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17500591 Free PMC article. - Anti-leishmania effector functions of CD4+ Th1 cells and early events instructing Th2 cell development and susceptibility to Leishmania major in BALB/c mice.
Louis JA, Conceiçao-Silva F, Himmelrich H, Tacchini-Cottier F, Launois P. Louis JA, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;452:53-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5355-7_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 9889959 Review. - Interleukin-4-independent acceleration of cutaneous leishmaniasis in susceptible BALB/c mice following treatment with anti-CTLA4 antibody.
Heinzel FP, Maier RA Jr. Heinzel FP, et al. Infect Immun. 1999 Dec;67(12):6454-60. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.12.6454-6460.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10569763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Insights on Host-Parasite Immunomodulation Mediated by Extracellular Vesicles of Cutaneous Leishmania shawi and Leishmania guyanensis.
Weber JI, Rodrigues AV, Valério-Bolas A, Nunes T, Carvalheiro M, Antunes W, Alexandre-Pires G, da Fonseca IP, Santos-Gomes G. Weber JI, et al. Cells. 2023 Apr 7;12(8):1101. doi: 10.3390/cells12081101. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190011 Free PMC article. - Leishmania major Strain-Dependent Macrophage Activation Contributes to Pathogenicity in the Absence of Lymphocytes.
Alshaweesh J, Nakamura R, Tanaka Y, Hayashishita M, Musa A, Kikuchi M, Inaoka DK, Hamano S. Alshaweesh J, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0112622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01126-22. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36190414 Free PMC article. - The pathogenicity and virulence of Leishmania - interplay of virulence factors with host defenses.
Gupta AK, Das S, Kamran M, Ejazi SA, Ali N. Gupta AK, et al. Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):903-935. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2074130. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35531875 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcription Factors Interplay Orchestrates the Immune-Metabolic Response of Leishmania Infected Macrophages.
Bichiou H, Bouabid C, Rabhi I, Guizani-Tabbane L. Bichiou H, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Apr 7;11:660415. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.660415. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33898331 Free PMC article. Review. - Autophagy downstream of endosomal Toll-like receptor signaling in macrophages is a key mechanism for resistance to Leishmania major infection.
Franco LH, Fleuri AKA, Pellison NC, Quirino GFS, Horta CV, de Carvalho RVH, Oliveira SC, Zamboni DS. Franco LH, et al. J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 11;292(32):13087-13096. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.780981. Epub 2017 Jun 12. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28607148 Free PMC article.
References
- Adachi, O., T. Kawai, K. Takeda, M. Matsumoto, H. Tsutsui, M. Sakagami, K. Nakanishi, and S. Akira. 1998. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity 9:143-150. - PubMed
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2:675-680. - PubMed
- Barton, G. M., and R. Medzhitov. 2002. Toll-like receptors and their ligands. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 270:81-92. - PubMed
- Biedermann, T., S. Zimmermann, H. Himmelrich, A. Gumy, O. Egeter, A. K. Sakrauski, I. Seegmuller, H. Voigt, P. Launois, A. D. Levine, H. Wagner, K. Heeg, J. A. Louis, and M. Rocken. 2001. IL-4 instructs TH1 responses and resistance to Leishmania major in susceptible BALB/c mice. Nat. Immunol. 2:1054-1060. - PubMed
- Edelson, B. T., and E. R. Unanue. 2002. MyD88-dependent but Toll-like receptor 2-independent innate immunity to Listeria: no role for either in macrophage listericidal activity. J. Immunol. 169:3869-3875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases