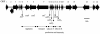Functional characterization of a composite bacteriocin locus from malt isolate Lactobacillus sakei 5 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Functional characterization of a composite bacteriocin locus from malt isolate Lactobacillus sakei 5
Anne Vaughan et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Dec.
Abstract
Lactobacillus sakei 5, isolated from malted barley, produces three bacteriocins. Genetic and functional analysis of the purified bacteriocins showed that this strain produces a plasmid-encoded bacteriocin that is identical to sakacin P, as well as two novel, chromosomally encoded bacteriocins, which were designated sakacin T and sakacin X. The structural genes specifying sakacin T and sakacin X are part of the sakacin TX locus, which consists of two adjacent but divergently oriented gene clusters. The first gene cluster includes stxP, stxR, stxK, and stxT, which, based on functional and comparative sequence analysis, are believed to encode an inducing peptide and proteins involved in regulation and secretion of these bacteriocins. The second gene cluster includes the structural and immunity genes for sakacin T, a class IIb two-peptide bacteriocin composed of SakTalpha and SakTbeta, and sakacin X, a class IIa bacteriocin. Interestingly, a so-called transport accessory protein was absent from the locus, and based on our results it appears that a dedicated accessory protein is not required for processing and transport of sakacin T and sakacin X.
Figures
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the sakacin TX locus sequenced to date, obtained by using a combination of ligation-anchored PCR and the primer walking strategy. A total of 22 potential ORFs are shown. The arrows indicate ORFs and the proposed directions of transcription. ORFs with deduced functions in production and secretion of active sakacin T and sakacin X are indicated by stx or sak. Sections of the stx locus assumed to be dedicated to production, immunity, regulation, and transport are indicated.
FIG. 2.
(A) PCR-derived inserts in pLPV111 derivatives with bacteriocin structural and immunity genes. The plasmid designations are indicated on the left, and the phenotypes when the plasmids are introduced (in conjunction with pSAK20) into L. sakei Lb790 are indicated on the right. (B) Inserts in pSAK20, containing the genes necessary for processing and transport of the bacteriocins used, and pSAK20 derivatives used in this study. The phenotypes when these constructs were introduced into L. sakei Lb790 or L. sakei 23K harboring the pLPV111 derivatives with bacteriocin structural and immunity genes are indicated.
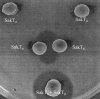
FIG. 3.
Bacteriocin activity and complementation of the SakTα and SakTβ peptides. L. sakei Lb790(pSAK20) containing pLPT8 (SakTα) and L. sakei Lb790(pSAK20) containing pLPT6 (SakTβ) were grown and overlaid with the sensitive indicator strain L. sakei LMG2313. Cultures were grown adjacent to each other and as a mixed culture (SakTα + SakTβ↓).
Similar articles
- Transcriptional analysis of bacteriocin production by malt isolate Lactobacillus sakei 5.
Vaughan A, O' Mahony J, Eijsink VG, O' Connell-Motherway M, van Sinderen D. Vaughan A, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004 Jun 15;235(2):377-84. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.05.011. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15183888 - An analysis of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from malted barley.
Vaughan A, Eijsink VG, O'Sullivan TF, O'Hanlon K, van Sinderen D. Vaughan A, et al. J Appl Microbiol. 2001 Jul;91(1):131-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01365.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11442722 - Characterization of a new bacteriocin operon in sakacin P-producing Lactobacillus sakei, showing strong translational coupling between the bacteriocin and immunity genes.
Mathiesen G, Huehne K, Kroeckel L, Axelsson L, Eijsink VG. Mathiesen G, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jul;71(7):3565-74. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.3565-3574.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16000763 Free PMC article. - Sakacin P non-producing Lactobacillus sakei strains contain homologues of the sakacin P gene cluster.
Møretrø T, Naterstad K, Wang E, Aasen IM, Chaillou S, Zagorec M, Axelsson L. Møretrø T, et al. Res Microbiol. 2005 Nov;156(9):949-60. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2005.05.005. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Res Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16085395 - Biosynthesis of bacteriocins in lactic acid bacteria.
Nes IF, Diep DB, Håvarstein LS, Brurberg MB, Eijsink V, Holo H. Nes IF, et al. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1996 Oct;70(2-4):113-28. doi: 10.1007/BF00395929. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1996. PMID: 8879403 Review.
Cited by
- Structural analysis and characterization of lacticin Q, a novel bacteriocin belonging to a new family of unmodified bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria.
Fujita K, Ichimasa S, Zendo T, Koga S, Yoneyama F, Nakayama J, Sonomoto K. Fujita K, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 May;73(9):2871-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02286-06. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17351096 Free PMC article. - Quorum-sensing regulation of the production of Blp bacteriocins in Streptococcus thermophilus.
Fontaine L, Boutry C, Guédon E, Guillot A, Ibrahim M, Grossiord B, Hols P. Fontaine L, et al. J Bacteriol. 2007 Oct;189(20):7195-205. doi: 10.1128/JB.00966-07. Epub 2007 Aug 10. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17693498 Free PMC article. - Comparative genomics of Lactobacillus sakei with emphasis on strains from meat.
Nyquist OL, McLeod A, Brede DA, Snipen L, Aakra Å, Nes IF. Nyquist OL, et al. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011 Apr;285(4):297-311. doi: 10.1007/s00438-011-0608-1. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21369871 - Class IIa bacteriocins: diversity and new developments.
Cui Y, Zhang C, Wang Y, Shi J, Zhang L, Ding Z, Qu X, Cui H. Cui Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 6;13(12):16668-707. doi: 10.3390/ijms131216668. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23222636 Free PMC article. Review. - Controlled functional expression of the bacteriocins pediocin PA-1 and bactofencin A in Escherichia coli.
Mesa-Pereira B, O'Connor PM, Rea MC, Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP. Mesa-Pereira B, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 8;7(1):3069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02868-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28596555 Free PMC article.
References
- Aukrust, T., and H. Blom. 1992. Transformation of Lactobacillus strains used in meat and vegetable fermentations. Food Res. Int. 25:253-261.
- Axelsson, L., T. Katla, M. Bjswsl]ornslett, V. G. H. Eijsink, and A. Holck. 1998. A system for heterologous expression of bacteriocins in Lactobacillus sake. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 168:137-143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources