Phylogenomic identification of five new human homologs of the DNA repair enzyme AlkB - PubMed (original) (raw)
Phylogenomic identification of five new human homologs of the DNA repair enzyme AlkB
Michal A Kurowski et al. BMC Genomics. 2003.
Abstract
Background: Combination of biochemical and bioinformatic analyses led to the discovery of oxidative demethylation - a novel DNA repair mechanism catalyzed by the Escherichia coli AlkB protein and its two human homologs, hABH2 and hABH3. This discovery was based on the prediction made by Aravind and Koonin that AlkB is a member of the 2OG-Fe2+ oxygenase superfamily.
Results: In this article, we report identification and sequence analysis of five human members of the (2OG-Fe2+) oxygenase superfamily designated here as hABH4 through hABH8. These experimentally uncharacterized and poorly annotated genes were not associated with the AlkB family in any database, but are predicted here to be phylogenetically and functionally related to the AlkB family (and specifically to the lineage that groups together hABH2 and hABH3) rather than to any other oxygenase family. Our analysis reveals the history of ABH gene duplications in the evolution of vertebrate genomes.
Conclusions: We hypothesize that hABH 4-8 could either be back-up enzymes for hABH1-3 or may code for novel DNA or RNA repair activities. For example, enzymes that can dealkylate N3-methylpurines or N7-methylpurines in DNA have not been described. Our analysis will guide experimental confirmation of these novel human putative DNA repair enzymes.
Figures
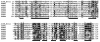
Figure 1
The multiple sequence alignment of E. coli AlkB and all human members of the AlkB family described previously (ABH1-3) and in this study (ABH4-8). Residues conserved in at least 4 members of the family are highlighted in black, residues with similar physico-chemical character are highlighted in gray. The length of loops omitted for the clarity of the presentation are shown in parentheses. The N- and C-terminal residues are numbered. The predicted catalytic residues are indicated with asterisks (*).
Figure 2
The maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the AlkB family. Only representative members (from human and E. coli), corresponding to the sequences in Fig. 1 are shown for the clarity of presentation. The position of the root was inferred from the large 2OG-Fe2+ oxygenase superfamily tree (data not shown). The topology of the presented tree received very high p-value support according to the Shimodaira-Hasegawa [31] and "approximately unbiased" [32] tests (0.998 and 0.988, respectively).
Similar articles
- Expression and sub-cellular localization of human ABH family molecules.
Tsujikawa K, Koike K, Kitae K, Shinkawa A, Arima H, Suzuki T, Tsuchiya M, Makino Y, Furukawa T, Konishi N, Yamamoto H. Tsujikawa K, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Sep-Oct;11(5):1105-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00094.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17979886 Free PMC article. - Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA.
Aas PA, Otterlei M, Falnes PO, Vågbø CB, Skorpen F, Akbari M, Sundheim O, Bjørås M, Slupphaug G, Seeberg E, Krokan HE. Aas PA, et al. Nature. 2003 Feb 20;421(6925):859-63. doi: 10.1038/nature01363. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12594517 - Human AlkB homolog 1 is a mitochondrial protein that demethylates 3-methylcytosine in DNA and RNA.
Westbye MP, Feyzi E, Aas PA, Vågbø CB, Talstad VA, Kavli B, Hagen L, Sundheim O, Akbari M, Liabakk NB, Slupphaug G, Otterlei M, Krokan HE. Westbye MP, et al. J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):25046-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803776200. Epub 2008 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18603530 Free PMC article. - DNA repair by bacterial AlkB proteins.
Falnes PØ, Rognes T. Falnes PØ, et al. Res Microbiol. 2003 Oct;154(8):531-8. doi: 10.1016/S0923-2508(03)00150-5. Res Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14527653 Review. - Non-homologous functions of the AlkB homologs.
Ougland R, Rognes T, Klungland A, Larsen E. Ougland R, et al. J Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;7(6):494-504. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjv029. Epub 2015 May 23. J Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26003568 Review.
Cited by
- Structural Basis of Nucleic Acid Recognition and 6mA Demethylation by Caenorhabditis elegans NMAD-1A.
Shang G, Yang M, Li M, Ma L, Liu Y, Ma J, Chen Y, Wang X, Fan S, Xie M, Wu W, Dai S, Chen Z. Shang G, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 5;25(2):686. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020686. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255759 Free PMC article. - N (6)-Methyladenosine (m(6)A) Methylation in mRNA with A Dynamic and Reversible Epigenetic Modification.
Wu R, Jiang D, Wang Y, Wang X. Wu R, et al. Mol Biotechnol. 2016 Jul;58(7):450-9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-016-9947-9. Mol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27179969 Review. - Human AlkB homologue 1 (ABH1) exhibits DNA lyase activity at abasic sites.
Müller TA, Meek K, Hausinger RP. Müller TA, et al. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Jan 2;9(1):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.10.011. Epub 2009 Dec 2. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 19959401 Free PMC article. - Crystal structure of the RNA demethylase ALKBH5 from zebrafish.
Chen W, Zhang L, Zheng G, Fu Y, Ji Q, Liu F, Chen H, He C. Chen W, et al. FEBS Lett. 2014 Mar 18;588(6):892-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Feb 20. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24561204 Free PMC article. - ALKBH8-mediated formation of a novel diastereomeric pair of wobble nucleosides in mammalian tRNA.
van den Born E, Vågbø CB, Songe-Møller L, Leihne V, Lien GF, Leszczynska G, Malkiewicz A, Krokan HE, Kirpekar F, Klungland A, Falnes PØ. van den Born E, et al. Nat Commun. 2011 Feb 1;2:172. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1173. Nat Commun. 2011. PMID: 21285950
References
- Hegg EL, Que L., Jr The 2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad – an emerging structural motif in mononuclear non-heme iron(II) enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1997;250:625–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials