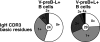Surrogate light chain expressing human peripheral B cells produce self-reactive antibodies - PubMed (original) (raw)
Surrogate light chain expressing human peripheral B cells produce self-reactive antibodies
Eric Meffre et al. J Exp Med. 2004.
Abstract
Human B cells that coexpress surrogate and conventional light chains (V-preB+L+) show an unusual heavy and light chain antibody repertoire that display evidence of receptor editing. However, it is unclear whether V-preB+L+ B cells have been silenced by receptor editing or still express autoreactive antibodies. Here we report that 68% of the antibodies expressed by V-preB+L+ B cells are autoreactive. A majority of these autoantibodies are true antinuclear antibodies (ANA), and 50% of the ANAs are also reactive with a diverse group of antigens that include dsDNA, ssDNA, immunoglobulin, insulin, and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Such antibodies are rarely encountered among conventional B cells. We conclude that V-preB+L+ B cells are a unique subset of normal circulating human B cells that escape central tolerance mechanisms and express self-reactive antibodies including potentially harmful ANAs.
Figures
Figure 1.
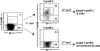
V-preB+L+ B cell purification scheme. Dot plots show V-preB and Igκ+λ expression on B cells preenriched for V-preB expression using magnetic beads (left), and after the first sort for V-preB+L+ (top right) or conventional V-preB−L+ B cells (bottom right). These populations were subsequently sorted into 96-well plates during a second round of cell sorting.
Figure 2.
Increased frequency of positively charged amino acids in IgH CDR3s from V-preB+L+ B cells. Pie charts show segment size proportional to the number of clones from V-preB−L+ (left) and V-preB+L+ B cells (right) displaying 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 or more positively charged amino acids per IgH CDR3. The number of sequences analyzed in each group is indicated in the center.
Figure 3.
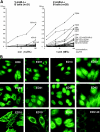
V-preB+L+ B cells express self-reactive antibodies. (A) Antibodies from V-preB+L+ B cells react against HEp-2 cell lysates. ELISAs for anti-HEp-2 cell reactivity using recombinant antibodies from 21 V-preB−L+ (left) and 28 V-preB+L+ B cells (right). The percentage of autoreactive clones for each fraction is indicated. (B) V-preB+L+ antibodies express ANAs. Antibodies from V-preB+L+ B cells show various patterns of ANA including nucleolar (KR9), mitotic spindle apparatus (ED11), speckled (ED20, ED44), and other uncharacterized patterns (ED13, ED38, ED41, ED45), and cytoskeletal reactivity against stress fiber (ED16), vinculin (ED19), and vimentin (ED37). Antibodies isolated from conventional B cells such as EDV-40 do not show ANA staining.
Figure 4.
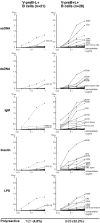
V-preB+L+ antibodies are polyreactive. Recombinant antibodies from conventional V-preB−L+ (left) and V-preB+L+ B cells (right) were tested for anti–single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), IgM, insulin, and LPS reactivity by ELISA. Human M55 mAb (dotted line) was included as a positive control polyreactive antibody (22). The percentage of polyreactive clones for each fraction is indicated.
Figure 5.
Polyreactive antibodies from V-preB+L+ B cells and M55 display similar IgH CDR3 features. Hydrophobic D reading frame and JH6 segments are in olive and brown boxes, respectively. Basic residues are in blue, and acidic amino acids are in red.
Similar articles
- Circulating human B cells that express surrogate light chains and edited receptors.
Meffre E, Davis E, Schiff C, Cunningham-Rundles C, Ivashkiv LB, Staudt LM, Young JW, Nussenzweig MC. Meffre E, et al. Nat Immunol. 2000 Sep;1(3):207-13. doi: 10.1038/79739. Nat Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10973277 - Circulating human B cells that express surrogate light chains display a unique antibody repertoire.
Meffre E, Chiorazzi M, Nussenzweig MC. Meffre E, et al. J Immunol. 2001 Aug 15;167(4):2151-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.2151. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11489999 - Receptor editing: an approach by autoreactive B cells to escape tolerance.
Gay D, Saunders T, Camper S, Weigert M. Gay D, et al. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):999-1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.999. J Exp Med. 1993. PMID: 8459227 Free PMC article. - Immunoglobulin variable gene expression in human autoantibodies.
van Es JH, Schutte ME, Ebeling SB, Gmelig-Meyling FH, Logtenberg T. van Es JH, et al. Immunol Ser. 1991;55:119-31. Immunol Ser. 1991. PMID: 1720024 Review. No abstract available. - Repertoire selection by pre-B-cell receptors and B-cell receptors, and genetic control of B-cell development from immature to mature B cells.
Melchers F, ten Boekel E, Seidl T, Kong XC, Yamagami T, Onishi K, Shimizu T, Rolink AG, Andersson J. Melchers F, et al. Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:33-46. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933589 Review.
Cited by
- Deficiency of base excision repair enzyme NEIL3 drives increased predisposition to autoimmunity.
Massaad MJ, Zhou J, Tsuchimoto D, Chou J, Jabara H, Janssen E, Glauzy S, Olson BG, Morbach H, Ohsumi TK, Schmitz K, Kyriacos M, Kane J, Torisu K, Nakabeppu Y, Notarangelo LD, Chouery E, Megarbane A, Kang PB, Al-Idrissi E, Aldhekri H, Meffre E, Mizui M, Tsokos GC, Manis JP, Al-Herz W, Wallace SS, Geha RS. Massaad MJ, et al. J Clin Invest. 2016 Nov 1;126(11):4219-4236. doi: 10.1172/JCI85647. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27760045 Free PMC article. - Circulating Human CD27-IgA+ Memory B Cells Recognize Bacteria with Polyreactive Igs.
Berkowska MA, Schickel JN, Grosserichter-Wagener C, de Ridder D, Ng YS, van Dongen JJ, Meffre E, van Zelm MC. Berkowska MA, et al. J Immunol. 2015 Aug 15;195(4):1417-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402708. Epub 2015 Jul 6. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26150533 Free PMC article. - B-cell-lineage immunogen design in vaccine development with HIV-1 as a case study.
Haynes BF, Kelsoe G, Harrison SC, Kepler TB. Haynes BF, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2012 May 7;30(5):423-33. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2197. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22565972 Free PMC article. - Lentiviral-mediated gene therapy restores B cell tolerance in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome patients.
Pala F, Morbach H, Castiello MC, Schickel JN, Scaramuzza S, Chamberlain N, Cassani B, Glauzy S, Romberg N, Candotti F, Aiuti A, Bosticardo M, Villa A, Meffre E. Pala F, et al. J Clin Invest. 2015 Oct 1;125(10):3941-51. doi: 10.1172/JCI82249. Epub 2015 Sep 14. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26368308 Free PMC article. - Independent Roles of Switching and Hypermutation in the Development and Persistence of B Lymphocyte Memory.
Gitlin AD, von Boehmer L, Gazumyan A, Shulman Z, Oliveira TY, Nussenzweig MC. Gitlin AD, et al. Immunity. 2016 Apr 19;44(4):769-81. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 26944202 Free PMC article.
References
- Wardemann, H., S. Yurasov, A. Schaefer, J.W. Young, E. Meffre, and M.C. Nussenzweig. 2003. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science. 301:1374–1377. - PubMed
- Radic, M.Z., J. Mackle, J. Erikson, C. Mol, W.F. Anderson, and M. Weigert. 1993. Residues that mediate DNA binding of autoimmune antibodies. J. Immunol. 150:4966–4977. - PubMed
- Klonowski, K.D., L.L. Primiano, and M. Monestier. 1999. Atypical VH-D-JH rearrangements in newborn autoimmune MRL mice. J. Immunol. 162:1566–1572. - PubMed
- Meffre, E., E. Davis, C. Schiff, C. Cunningham-Rundles, L.B. Ivashkiv, L.M. Staudt, J.W. Young, and M.C. Nussenzweig. 2000. Circulating human B cells that express surrogate light chains and edited receptors. Nat. Immunol. 1:207–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources