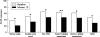Infliximab treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, with dose titration based on the Disease Activity Score: dose adjustments are common but not always sufficient to assure sustained benefit - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Infliximab treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, with dose titration based on the Disease Activity Score: dose adjustments are common but not always sufficient to assure sustained benefit
P Sidiropoulos et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Feb.
Abstract
Background: Randomised controlled trials have shown that treatment with anti-tumour necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents is effective in refractory rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Objective: To determine the effectiveness of anti-TNF in a general unselected group of patients with refractory RA.
Methods: 68 patients with active RA despite treatment with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs were studied during 12 infliximab infusions. Infliximab (3 mg/kg/infusion) was given every 8 or 6 weeks. Clinical efficacy was assessed by the Disease Activity Score (DAS) index (44 joints). Dose adjustments were based on residual disease activity (DAS score >2.4). The primary end points were the percentage of patients achieving good or moderate response by the EULAR response criteria and the proportion of patients requiring dose adjustment.
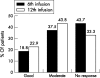
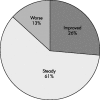
Results: 20 (29%) patients discontinued treatment owing to side effects, early inefficacy, or other considerations. Among the patients who continued treatment, 27 (56%) and 32 (67%) were responders on the 6th and 12th infliximab infusion, respectively. In the same patients, disease activity gradually improved without modifications in the initial dosing in 10 (21%), whereas in 38 (79%) the dose of infliximab and/or methotrexate was increased. Intensification of treatment led to a significant decrease in the mean DAS score in this group (from 5.27 just before dose modification to 4.54 before the 12th infusion, p<0.002). The EULAR response category improved in only 10/38 (26%), however.
Conclusions: In this initial observational study of patients with RA treated with recommended doses of infliximab, adjustments in treatment were common but not always sufficient to maintain adequate disease control. Longitudinal controlled trials are needed to define the optimal dose escalation in patients with suboptimal response.
Figures
Figure 1
Response rates at the 6th and 12th infusions of infliximab according to EULAR response criteria (% of patients).
Figure 2
Improvement in clinical parameters (n = 48). *p<0.001; **p<0.002.
Figure 3
Mean DAS over time for each group of patients: the first with stable treatment (n = 10) and the second with treatment modification (n = 38).
Figure 4
Changes in EULAR response categories after treatment adjustments (n = 38).
Similar articles
- Aiming at low disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with initial combination therapy or initial monotherapy strategies: the BeSt study.
Allaart CF, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Breedveld FC, Dijkmans BA; FARR study group. Allaart CF, et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006 Nov-Dec;24(6 Suppl 43):S-77-82. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 17083767 Clinical Trial. - Infliximab efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis after an inadequate response to etanercept or adalimumab: results of a target-driven active switch study.
Fleischmann R, Goldman JA, Leirisalo-Repo M, Zanetakis E, El-Kadi H, Kellner H, Bolce R, DeHoratius R, Wang J, Decktor D. Fleischmann R, et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Nov;30(11):2139-49. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2014.942416. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014. PMID: 25050591 Clinical Trial. - Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of dosage regimens.
Zintzaras E, Dahabreh IJ, Giannouli S, Voulgarelis M, Moutsopoulos HM. Zintzaras E, et al. Clin Ther. 2008 Nov;30(11):1939-55. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.11.007. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 19108784 Review. - Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, tocilizumab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis not previously treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and after the failure of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs only: systematic review and economic evaluation.
Stevenson M, Archer R, Tosh J, Simpson E, Everson-Hock E, Stevens J, Hernandez-Alava M, Paisley S, Dickinson K, Scott D, Young A, Wailoo A. Stevenson M, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2016 Apr;20(35):1-610. doi: 10.3310/hta20350. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 27140438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- An open label, single dose study to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and effects on CD25 expression of ciclosporin in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite treatment with methotrexate and infliximab.
Sidiropoulos PI, Siakka P, Raptopoulou A, Mamoulaki M, Choulaki C, Koutala H, Kouroumali H, Kritikos H, Boumpas DT. Sidiropoulos PI, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Apr;65(4):538-41. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.036152. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16126800 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy of an immunotoxin to folate receptor beta in the intra-articular treatment of antigen-induced arthritis.
Nagai T, Kyo A, Hasui K, Takao S, Matsuyama T. Nagai T, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 May 2;14(3):R106. doi: 10.1186/ar3831. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22551402 Free PMC article. - Evidence for differential acquired drug resistance to anti-tumour necrosis factor agents in rheumatoid arthritis.
Finckh A, Simard JF, Gabay C, Guerne PA; SCQM physicians. Finckh A, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Jun;65(6):746-52. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.045062. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16339288 Free PMC article. - Anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: an update on safety.
Hyrich KL, Silman AJ, Watson KD, Symmons DP. Hyrich KL, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Dec;63(12):1538-43. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.024737. Epub 2004 Jul 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15242866 Free PMC article. Review. - Baseline tumour necrosis factor alpha levels predict the necessity for dose escalation of infliximab therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Takeuchi T, Miyasaka N, Tatsuki Y, Yano T, Yoshinari T, Abe T, Koike T. Takeuchi T, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jul;70(7):1208-15. doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.153023. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21478189 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jan;39(1):34-40 - PubMed
- Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1105-10 - PubMed
- Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1552-63 - PubMed
- N Engl J Med. 1999 Jan 28;340(4):253-9 - PubMed
- Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002 Jun;41(6):601-4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical