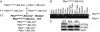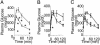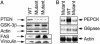Liver-specific deletion of negative regulator Pten results in fatty liver and insulin hypersensitivity [corrected] - PubMed (original) (raw)
Liver-specific deletion of negative regulator Pten results in fatty liver and insulin hypersensitivity [corrected]
Bangyan Stiles et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004.
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 6;101(14):5180
Abstract
In the liver, insulin controls both lipid and glucose metabolism through its cell surface receptor and intracellular mediators such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and serine-threonine kinase AKT. The insulin signaling pathway is further modulated by protein tyrosine phosphatase or lipid phosphatase. Here, we investigated the function of phosphatase and tension homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN), a negative regulator of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway, by targeted deletion of Pten in murine liver. Deletion of Pten in the liver resulted in increased fatty acid synthesis, accompanied by hepatomegaly and fatty liver phenotype. Interestingly, Pten liver-specific deletion causes enhanced liver insulin action with improved systemic glucose tolerance. Thus, deletion of Pten in the liver may provide a valuable model that permits the study of the metabolic actions of insulin signaling in the liver, and PTEN may be a promising target for therapeutic intervention for type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Liver-specific deletion of Pten. (A) Breeding strategy. (B) Liver-specific deletion of the Pten gene. PCR analysis of DNA from different tissues of _Pten_lox/lox;Alb-Cre+ mice. (C) Western analysis for PTEN (Top), _p_-AKT (Middle) and AKT (Bottom).
Fig. 2.
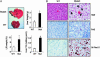
Pten deletion results in hepatomegaly and liver steatosis. (A) Hepatomegaly of mutant mice. Photo shows livers from mutant (Upper) and WT mouse (Lower); mutant mice have heavier livers (Upper Right; n = 6), increased liver to body weight ratio (Lower Left; n = 6), and increased TG storage (Lower Right; n = 6). *, P ≤ 0.05. (B) Histological analysis of liver sections from WT and mutant mice. (Top) Hematoxylin/eosin staining. (Middle) Periodic acid Schiff's staining (Bottom) Oil red O staining. (Bar, 50 μM.)
Fig. 3.
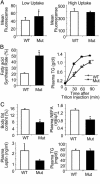
Pten deletion enhances FA synthesis and secretion by hepatocytes. (A) Uptake of long-chain FA by WT and mutant primary hepatocytes. (Left) Low-uptake group. (Right) High-uptake group. n = 3. (B) FA synthesis rate is calculated as newly synthesized portion of palmitate (Left, n = 6). Lipid secretion rate is measured as plasma TG levels at indicated time points after triton injection (Right, n = 3). (C) Lipid indexes of 1-month-old Pten WT and mutant mice: (Left Upper) body fat content of WT (n = 7) and mutant mice (n = 6). (Right Upper) Plasma NEFA levels in WT (n = 6) and mutant (n = 6) mice. (Left Lower) Plasma leptin levels in WT (n = 5) and mutant mice (n = 5). (Right Lower) Plasma TG levels in WT (n = 5) and mutant mice (n = 5). *, P ≤ 0.05.
Fig. 4.
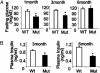
Fasting plasma glucose and insulin levels. (A) Fasting plasma glucose levels in 1- (Left), 3- (Center), and 6-month-old (Right) mice. Open bars, WT (n = 9); filled bars, mutant (n = 11). (B) Fasting plasma insulin concentrations in 3- (Left) and 6-month-old (Right) mice. n = 6. *, P ≤ 0.05.
Fig. 5.
i.p. GTT. (A) One-month GTT with WT (n = 9) and mutant (n = 11) mice. (B) Three-month GTT with WT (n = 6) and mutant (n = 8) mice. (C) Six-month GTT with WT (n = 11) and mutant (n = 8) mice. *, P ≤ 0.05
Fig. 6.
Pten deletion results in inhibition of gluconeogenesis and activation of lipogenesis enzymes in the liver. (A) Western blot analysis of GSK-3β and FAS. Blots were probed with PTEN (first section), phospho-GSK-3β (second section), and FAS (fourth section). Actin and vinculin were used as loading controls. (B) Northern blot analysis of PEPCK and G6Pase gene expressions in mouse liver. Actin was used as loading control.
Similar articles
- Insulin hypersensitivity and resistance to streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice lacking PTEN in adipose tissue.
Kurlawalla-Martinez C, Stiles B, Wang Y, Devaskar SU, Kahn BB, Wu H. Kurlawalla-Martinez C, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(6):2498-510. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2498-2510.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15743841 Free PMC article. - Hepatic PTEN deficiency improves muscle insulin sensitivity and decreases adiposity in mice.
Peyrou M, Bourgoin L, Poher AL, Altirriba J, Maeder C, Caillon A, Fournier M, Montet X, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Foti M. Peyrou M, et al. J Hepatol. 2015 Feb;62(2):421-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.09.012. Epub 2014 Sep 16. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25234947 - Tuberous sclerosis complex-1 deficiency attenuates diet-induced hepatic lipid accumulation.
Kenerson HL, Yeh MM, Yeung RS. Kenerson HL, et al. PLoS One. 2011 Mar 29;6(3):e18075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018075. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21479224 Free PMC article. - Zonation of glucose and fatty acid metabolism in the liver: mechanism and metabolic consequences.
Hijmans BS, Grefhorst A, Oosterveer MH, Groen AK. Hijmans BS, et al. Biochimie. 2014 Jan;96:121-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 23792151 Review. - PTEN, Insulin Resistance and Cancer.
Li A, Qiu M, Zhou H, Wang T, Guo W. Li A, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(25):3667-3676. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170704124611. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28677502 Review.
Cited by
- Gut Microbiome and Hepatic Transcriptomic Determinants of HCC Development in Mice with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis.
Dolapchiev LI, Gonzales KA, Cruz LR, Gagea M, Stevenson HL, Kwan SY, Beretta L. Dolapchiev LI, et al. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Oct 3;11:1891-1905. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S485532. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39372712 Free PMC article. - Comparative analysis of SV40 17kT and LT function in vivo demonstrates that LT's C-terminus re-programs hepatic gene expression and is necessary for tumorigenesis in the liver.
Comerford SA, Schultz N, Hinnant EA, Klapproth S, Hammer RE. Comerford SA, et al. Oncogenesis. 2012 Sep 10;1(9):e28. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2012.27. Oncogenesis. 2012. PMID: 23552841 Free PMC article. - PPARγ contributes to PKM2 and HK2 expression in fatty liver.
Panasyuk G, Espeillac C, Chauvin C, Pradelli LA, Horie Y, Suzuki A, Annicotte JS, Fajas L, Foretz M, Verdeguer F, Pontoglio M, Ferré P, Scoazec JY, Birnbaum MJ, Ricci JE, Pende M. Panasyuk G, et al. Nat Commun. 2012 Feb 14;3:672. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1667. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22334075 Free PMC article. - Mice with a disruption of the imprinted Grb10 gene exhibit altered body composition, glucose homeostasis, and insulin signaling during postnatal life.
Smith FM, Holt LJ, Garfield AS, Charalambous M, Koumanov F, Perry M, Bazzani R, Sheardown SA, Hegarty BD, Lyons RJ, Cooney GJ, Daly RJ, Ward A. Smith FM, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;27(16):5871-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02087-06. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17562854 Free PMC article. - Inhibiting the Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway Lowers O-GlcNAcylation Levels and Sensitizes Cancer to Environmental Stress.
Walter LA, Lin YH, Halbrook CJ, Chuh KN, He L, Pedowitz NJ, Batt AR, Brennan CK, Stiles BL, Lyssiotis CA, Pratt MR. Walter LA, et al. Biochemistry. 2020 Sep 1;59(34):3169-3179. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00560. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 31625393 Free PMC article.
References
- Bruning, J. C., Michael, M. D., Winnay, J. N., Hayashi, T., Horsch, D., Accili, D., Goodyear, L. J. & Kahn, C. R. (1998) Mol. Cell 2, 559-569. - PubMed
- Michael, M. D., Kulkarni, R. N., Postic, C., Previs, S. F., Shulman, G. I., Magnuson, M. A. & Kahn, C. R. (2000) Mol. Cell 6, 87-97. - PubMed
- Abel, E. D., Peroni, O., Kim, J. K., Kim, Y. B., Boss, O., Hadro, E., Minnemann, T., Shulman, G. I. & Kahn, B. B. (2001) Nature 409, 729-733. - PubMed
- Zisman, A., Peroni, O. D., Abel, E. D., Michael, M. D., Mauvais-Jarvis, F., Lowell, B. B., Wojtaszewski, J. F., Hirshman, M. F., Virkamaki, A., Goodyear, L. J., et al. (2000) Nat. Med. 6, 924-928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials