Statins in hypercholesterolaemia: a dose-specific meta-analysis of lipid changes in randomised, double blind trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Statins in hypercholesterolaemia: a dose-specific meta-analysis of lipid changes in randomised, double blind trials
Jayne E Edwards et al. BMC Fam Pract. 2003.
Abstract
Background: Statins alter lipid concentrations. This systematic review determined the efficacy of particular statins, in terms of their ability to alter cholesterol.
Review methods: PubMed, the Cochrane Library, references lists of reports, and reviews were searched (September 2001) for randomised, double blind trials of statins for cholesterol in trials of 12 weeks or longer. Mean change in total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides was calculated using pooled data for particular statins, and for particular doses of a statin. Pre-planned sensitivity analyses were used to determine the effects of initial concentration of total cholesterol, study duration, the effects of major trials, and effects in placebo versus active controlled trials. Information was not collected on adverse events.
Results: Different statins at a range of doses reduced total cholesterol by 17-35% and LDL-cholesterol by 24-49% from baseline. Lower doses of statins generally produced less cholesterol lowering, though for most statins in trials of 12 weeks or longer there was at best only a weak relationship between dose and cholesterol reduction. Duration of treatment and baseline total cholesterol concentration did not alter the amount of the benefit attained.
Conclusions: Statins are effective medicines and confer benefit to patients in terms of primary and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease. Reductions in total cholesterol of 25% or more and LDL cholesterol of more than 30% were recorded for fixed doses of simvastatin 40 mg, atorvastatin 10 mg, and rosuvastatin 5 mg and 10 mg.
Figures
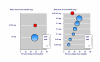
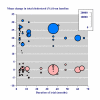
Figure 1
Percent change in total cholesterol concentration with particular doses of atorvastatin or cerivastatin. For dose titration, blue symbols represent titration over time to a fixed higher dose, and red symbols titration to achieve a target reduction in LDL or total cholesterol.
Figure 2
Percent change in total cholesterol concentration with particular doses of fluvastatin or lovastatin. For dose titration, blue symbols represent titration over time to a fixed higher dose, and red symbols titration to achieve a target reduction in LDL or total cholesterol.
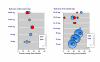
Figure 3
Percent change in total cholesterol concentration with particular doses of pravastatin or rosuvastatin. For dose titration, blue symbols represent titration over time to a fixed higher dose, and red symbols titration to achieve a target reduction in LDL or total cholesterol.
Figure 4
Percent change in total cholesterol concentration with particular doses of simvastatin. For dose titration, blue symbols represent titration over time to a fixed higher dose, and red symbols titration to achieve a target reduction in LDL or total cholesterol.
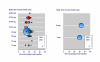
Figure 5
Study duration and percent change in total cholesterol concentration with statins at a range of doses.
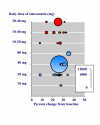
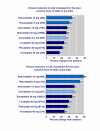
Figure 6
Percent reduction in total and LDL cholesterol concentration with the most commonly used dose of statin in the trials.
Similar articles
- Fluvastatin for lowering lipids.
Adams SP, Sekhon SS, Tsang M, Wright JM. Adams SP, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 6;3(3):CD012282. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012282.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29508377 Free PMC article. - [Statins in patients with kidney failure: efficacy, tolerance, and prescription guidelines in patients with chronic kidney disease and renal transplant].
Karie S, Launay-Vacher V, Deray G, Isnard-Bagnis C. Karie S, et al. Presse Med. 2006 Feb;35(2 Pt 1):219-29. doi: 10.1016/s0755-4982(06)74557-2. Presse Med. 2006. PMID: 16493350 French. - A systematic review and meta-analysis on the therapeutic equivalence of statins.
Weng TC, Yang YH, Lin SJ, Tai SH. Weng TC, et al. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010 Apr;35(2):139-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01085.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010. PMID: 20456733 - Lipid lowering efficacy of atorvastatin.
Adams SP, Tsang M, Wright JM. Adams SP, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD008226. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008226.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235655 Updated. - Cost-effectiveness analysis of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin, simvastatin, and pravastatin from a Canadian health system perspective.
Costa-Scharplatz M, Ramanathan K, Frial T, Beamer B, Gandhi S. Costa-Scharplatz M, et al. Clin Ther. 2008 Jul;30(7):1345-57. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(08)80061-6. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18691996
Cited by
- Prompt impact of first prospective statin mega-trials on postoperative lipid management of CABG patients: a 20-year follow-up in a single hospital.
Palomäki A, Hällberg V, Ala-Korpela M, Kovanen PT, Malminiemi K. Palomäki A, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Jul 26;15(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0292-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27460359 Free PMC article. - National Drug Formulary review of statin therapeutic group using the multiattribute scoring tool.
Ramli A, Aljunid SM, Sulong S, Md Yusof FA. Ramli A, et al. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2013;9:491-504. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S52078. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2013. PMID: 24353428 Free PMC article. - Cerivastatin for lowering lipids.
Adams SP, Tiellet N, Alaeiilkhchi N, Wright JM. Adams SP, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 25;1(1):CD012501. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012501.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31981471 Free PMC article. - Breaking down causes, consequences, and mediating effects of telomere length variation on human health.
Moix S, Sadler MC, Kutalik Z, Auwerx C. Moix S, et al. Genome Biol. 2024 May 17;25(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03269-9. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38760657 Free PMC article. - Pleiotropic effects of statins in the perioperative setting.
Galyfos G, Sianou A, Filis K. Galyfos G, et al. Ann Card Anaesth. 2017 Jan;20(Supplement):S43-S48. doi: 10.4103/0971-9784.197796. Ann Card Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 28074822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Anonymous PACT – Cardiovascular prescribing. Prescription Pricing Authority. 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical