Histamine H4 antagonism: a therapy for chronic allergy? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Histamine H4 antagonism: a therapy for chronic allergy?
Bruce L Daugherty. Br J Pharmacol. 2004 May.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
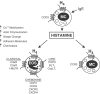
Mechanism of histamine-induced recruitment of eosinophils and mast cells in chronic allergic inflammation. Histamine H4 GPCRs are expressed on the surface of both eosinophils and mast cells. Antigen-IgE complex-dependent crosslinking of Fc_ɛ_RI on the surface of resident mast cells stimulates the secretion of histamine, which binds to and activates the H4 receptor on eosinophils. Signalling through the H4 receptor triggers a series of signal transduction events (calcium mobilization, actin polymerization, shape change, upregulation of adhesion molecule expression) leading to directional migration (chemotaxis) and accumulation of eosinophils into sites of inflammation. Upon release, histamine can also stimulate the recruitment of additional mast cells into the inflammatory site, by activation of the mast cell expressed H4 receptor. As shown in the figure, the H4 receptor is one of a number of G-protein coupled chemottractant receptors expressed on eosinophils. These include members of the chemokine receptor family, receptors for classical chemoattractants (complement cleavage fragments, formyl peptides and lipid mediators). Abbreviations: EOS, eosinophil; MC, mast cell; IgE, immunoglobulin E; H4, histamine receptor type 4; PAFR, platelet activating factor receptor; BLT1, leukotriene B4 receptor type 1; CysLT1, leukotriene D4 receptor type 1; CCR1, C-C chemokine receptor type 1; CCR3, C-C chemokine receptor type 3; CXCR2, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 2; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; C3aR, complement 3a receptor; C5aR, complement 5a receptor; f-MLFR, _N_-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine receptor.
Comment on
- Histamine induces cytoskeletal changes in human eosinophils via the H(4) receptor.
Buckland KF, Williams TJ, Conroy DM. Buckland KF, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;140(6):1117-27. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705530. Epub 2003 Oct 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14530216 Free PMC article. - Histamine H4 receptor mediates eosinophil chemotaxis with cell shape change and adhesion molecule upregulation.
Ling P, Ngo K, Nguyen S, Thurmond RL, Edwards JP, Karlsson L, Fung-Leung WP. Ling P, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2004 May;142(1):161-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705729. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15131002 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Functional Profiling of 2-Aminopyrimidine Histamine H4 Receptor Modulators.
Tichenor MS, Thurmond RL, Venable JD, Savall BM. Tichenor MS, et al. J Med Chem. 2015 Sep 24;58(18):7119-27. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00516. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25993395 Review. - Role of the Histamine H4-Receptor in Bronchial Asthma.
Neumann D. Neumann D. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;241:347-359. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_11. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27718056 Review. - Nothing to sneeze at.
Westly E. Westly E. Nat Med. 2010 Oct;16(10):1063-5. doi: 10.1038/nm1010-1063. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20930737 No abstract available. - The histamine H4 receptor in autoimmune disease.
Zhang M, Venable JD, Thurmond RL. Zhang M, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Nov;15(11):1443-52. doi: 10.1517/13543784.15.11.1443. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 17040202 Review. - [Expression of the histamine H4 receptor in human tissues and its clinical role].
Yamaura K, Suzuki M, Namiki T, Ueno K. Yamaura K, et al. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2010 Jun;135(6):235-9. doi: 10.1254/fpj.135.235. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20543513 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Histamine activates inflammatory response and depresses casein synthesis in mammary gland of dairy cows during SARA.
Chang G, Wang L, Ma N, Zhang W, Zhang H, Dai H, Shen X. Chang G, et al. BMC Vet Res. 2018 May 23;14(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1491-3. BMC Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 29792195 Free PMC article. - In vitro and in vivo characterization of A-940894: a potent histamine H4 receptor antagonist with anti-inflammatory properties.
Strakhova MI, Cuff CA, Manelli AM, Carr TL, Witte DG, Baranowski JL, Vortherms TA, Miller TR, Rundell L, McPherson MJ, Adair RM, Brito AA, Bettencourt BM, Yao BB, Wetter JM, Marsh KC, Liu H, Cowart MD, Brioni JD, Esbenshade TA. Strakhova MI, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 May;157(1):44-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00236.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19413570 Free PMC article. - Therapeutic potential of histamine H4 receptor antagonist as a preventive treatment for diabetic retinopathy in mice.
Kwon JW, Lee K, Kim SW, Park J, Hong JJ, Che JH, Seok SH. Kwon JW, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 30;14(1):22664. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72166-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39349555 Free PMC article. - The role of histamine H4 receptor in immune and inflammatory disorders.
Zampeli E, Tiligada E. Zampeli E, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 May;157(1):24-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00151.x. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19309354 Free PMC article. Review. - Hypolipidemic properties of Chlorella pyrenoidosa organic acids via AMPK/HMGCR/SREBP-1c pathway in vivo.
Chen J, Gong S, Wan X, Gao X, Wang C, Zeng F, Zhao C, Liu B, Huang Y. Chen J, et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Dec 11;9(1):459-468. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2014. eCollection 2021 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33473307 Free PMC article.
References
- CLARK R.A.F., SANDLER J.A., GALLIN J.I., KAPLAN A.P. Histamine modulation of eosinophil migration. J. Immunol. 1977;118:137–145. - PubMed
- HOFSTRA C.L., DESAI P.J., THURMOND R.L., FUNG-LEUNG W.-P. Histamine H4 receptor mediated chemotaxis and calcium mobilization of mast cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003;305:1212–1221. - PubMed
- JABLONOWSKI J.A., GRICE C.A., CHAI W., DVORAK C.A., VENABLE J.D., KWOK A.K., LY K.S., WEI J., BAKER S.M., DESAI P.J., JIANG W., WILSON S.J., THURMOND R.L., KARLSSON L., EDWARDS J.P., LOVENBERG T.W., CARRUTHERS N.I. The first potent and selective non-imidazole human histamine H4 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2003;46:3957–3960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical