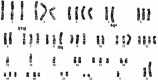Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics
Yan Li et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004 Aug.
Abstract
Purpose: To establish a "stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell model system" for in-depth study of the underlying mechanisms of HCC metastasis.
Methods: Using MHCC97- a metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line reported in 1999-as the parent cells, we subsequently established three cell lines (MHCC97-L, HMCC97-H, and HCCLM3) with increasing spontaneous metastatic potential. Now, the fourth cell line with unique multiple metastatic characteristics has been established by six rounds of in vivo selection.
Results: This cell line, designated as HCCLM6, is a polygonal epithelial cell with hypotriploid karyotype, the modal chromosomes are 55-58, and marker chromosomal abnormalities include i(1) (q10), i(8)(q10), der (4) t(4;8)(q31;q22), i(X)(q10). The cell population doubling time was 32 h. Fluorescent PCR showed HBV DNA integration in the cellular genome. Thirty-five days after HCCLM6 was injected subcutaneously into BALB/c nude mice, prominent lung metastases occurred in 100% of the recipient animals. When tumor tissue was orthotopically implanted into the liver of nude mouse, widespread loco-regional and pulmonary metastases occurred. Inoculation of this cell into the footpad of nude mice also produced 75% regional lymph node metastasis. Compared with MHCC97-L which was not metastastatic via subcutaneous or footpad inoculation and 40% metastatic via orthotopic inoculation, HCCLM6 had increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and cytokeratin 19 (CK19), and decreased expression of Rb2/p130. The establishment of this new cell line has completed our stepwise metastatic HCC cell mode system, which was characterized by a similar genetic background but with significant differences in spontaneous metastasis behavior.
Conclusions: The study supports the theory that cancer metastasis is a highly selective dynamic process and the cell model system could be a useful platform for the study of HCC metastasis.
Figures
Fig. 1
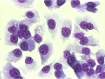
Cell morphology of HCCLM6. The cells were cultured on culture chamber for 2 days and then stained in Giemsa solution, showing epithelial cells with conspicuous nucleoli (200×)
Fig. 2
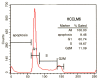
Flow cytometry of HCCLM6, showing the percentage of cells at different phases of the cell cycle
Fig. 3
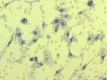
In vitro invasion assay of HCCLM6, showing cells penetrated the matrigel artificial basement membrane
Fig. 4
Karyotyping of HCCLM6. Metaphase chromosomes were prepared and G-banding was performed. The cells show a hypotriploid karyotype with marker chromosomes as i(1) (q10), i(8)(q10), i(X)(q10), and der (4) t(4;8)(q31;q22)
Fig. 5
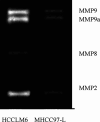
Gelatin zymography of HCCLM6 and MHCC97-L, showing increased expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 in the former. In addition, HCCLM6 also expressed MMP8, which was not expressed in MHCC97-L
Fig. 6A–C
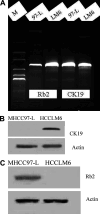
RT-PCR and Western blotting results for Rb2/p130 cytokeratin 19. A expression of Rb2 and CK19 by RT-PCR (marker from top to bottom: 200, 400, 500, 600, 800, 1000 and 2000 bp); B CK19 expression by western blotting; C Rb2/p130 expression by western blotting
Fig. 7A–D
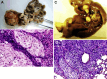
Spontaneous metastases of HCCLM6. Widespread metastases occurred 35 days after tumor tissue implantation into the liver. A abdominal metastases to mesenteric lymph nodes and hepatogastric ligament (black triangles);B microphotography of tumor metastasis to lymph nodes, replacing the lymph tissue with massive tumor cells. (HE stain, 200×);C massive metastatic nodules to the lungs;D microphotography showing huge lung metastasis engulfing the bronchiole (HE stain, 100×)
References
- Albini A, Iwamoto Y, Kleinman HK, Martin GR, Aaronson SA, Kozlowski JM, McEwan RN (1987) A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res 47:3239–3245 - PubMed
- Baldi A, Esposito V, De Luca A, Fu Y, Meoli I, Giordano GG, Caputi M, Baldi F, Giordano A (1997) Differential expression of Rb2/p130 and p107 in normal human tissue and in primary lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 3:1691–1697 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous