rVISTA 2.0: evolutionary analysis of transcription factor binding sites - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2004 Jul 1;32(Web Server issue):W217-21.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh383.
Affiliations
- PMID: 15215384
- PMCID: PMC441521
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh383
rVISTA 2.0: evolutionary analysis of transcription factor binding sites
Gabriela G Loots et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004.
Abstract
Identifying and characterizing the transcription factor binding site (TFBS) patterns of cis-regulatory elements represents a challenge, but holds promise to reveal the regulatory language the genome uses to dictate transcriptional dynamics. Several studies have demonstrated that regulatory modules are under positive selection and, therefore, are often conserved between related species. Using this evolutionary principle, we have created a comparative tool, rVISTA, for analyzing the regulatory potential of noncoding sequences. Our ability to experimentally identify functional noncoding sequences is extremely limited, therefore, rVISTA attempts to fill this great gap in genomic analysis by offering a powerful approach for eliminating TFBSs least likely to be biologically relevant. The rVISTA tool combines TFBS predictions, sequence comparisons and cluster analysis to identify noncoding DNA regions that are evolutionarily conserved and present in a specific configuration within genomic sequences. Here, we present the newly developed version 2.0 of the rVISTA tool, which can process alignments generated by both the zPicture and blastz alignment programs or use pre-computed pairwise alignments of several vertebrate genomes available from the ECR Browser and GALA database. The rVISTA web server is closely interconnected with the TRANSFAC database, allowing users to either search for matrices present in the TRANSFAC library collection or search for user-defined consensus sequences. The rVISTA tool is publicly available at http://rvista.dcode.org/.
Figures
Figure 1
rVISTA 2.0 analysis data flow. (A) The rVISTA tool can process blastz alignments submitted at the rVISTA homepage (
), or alignments automatically forwarded from the zPicture alignment program (
), the ECR Browser (
) or the GALA database (
http://globin.cse.psu.edu/gala/
). (B) Users select the search criteria, and the results are returned in the same page as the downloadable static data files and dynamic links to visual analysis of TFBS distribution. (C) TFBSs for pre-selected TFs can be visualized above the conservation profile as tick marks, and the clustering module can detect user-specified groups of TFBSs.
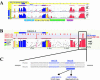
Figure 2
TFBS analysis of the NKX2.5 genomic locus. (A) The NKX2.5 genomic region was accessed in the ECR Browser. Human/mouse and human/rat alignments are displayed (7 kb in the window). (B) Coding exons are in blue, untranslated regions (UTRs) are in yellow, conserved intronic noncoding ECRs are in pink and conserved intergenic ECRs are in red. The alignment was processed for Smad4 binding sites. (C) Smad4 TFBS matches to the reference sequence (human) are in blue, aligned pairs in red and aligned-and-conserved in green. NKX2.5 cardiac enhancer harbors 4 conserved Smad4 sites; one site corresponds with a previously functionally characterized Smad4 site.
Similar articles
- Dcode.org anthology of comparative genomic tools.
Loots GG, Ovcharenko I. Loots GG, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W56-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki355. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980535 Free PMC article. - ECR Browser: a tool for visualizing and accessing data from comparisons of multiple vertebrate genomes.
Ovcharenko I, Nobrega MA, Loots GG, Stubbs L. Ovcharenko I, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jul 1;32(Web Server issue):W280-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh355. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15215395 Free PMC article. - MAPPER: a search engine for the computational identification of putative transcription factor binding sites in multiple genomes.
Marinescu VD, Kohane IS, Riva A. Marinescu VD, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Mar 30;6:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-79. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15799782 Free PMC article. - CONREAL web server: identification and visualization of conserved transcription factor binding sites.
Berezikov E, Guryev V, Cuppen E. Berezikov E, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W447-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki378. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980509 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Evolutionary history and genome organization of DUF1220 protein domains.
O'Bleness MS, Dickens CM, Dumas LJ, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Wyckoff GJ, Sikela JM. O'Bleness MS, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Sep;2(9):977-86. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.003061. Epub 2012 Sep 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 22973535 Free PMC article. - Enrichment of _Cis_-Acting Regulatory Elements in Differentially Methylated Regions Following Lipopolysaccharide Treatment of Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells.
Jhamat N, Guo Y, Han J, Humblot P, Bongcam-Rudloff E, Andersson G, Niazi A. Jhamat N, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 11;25(18):9832. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189832. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337320 Free PMC article. - Arabidopsis intragenomic conserved noncoding sequence.
Thomas BC, Rapaka L, Lyons E, Pedersen B, Freeling M. Thomas BC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 27;104(9):3348-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611574104. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17301222 Free PMC article. - Conditional HIF-1alpha expression produces a reversible cardiomyopathy.
Bekeredjian R, Walton CB, MacCannell KA, Ecker J, Kruse F, Outten JT, Sutcliffe D, Gerard RD, Bruick RK, Shohet RV. Bekeredjian R, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Jul 21;5(7):e11693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011693. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20657781 Free PMC article. - BLISS: binding site level identification of shared signal-modules in DNA regulatory sequences.
Meng H, Banerjee A, Zhou L. Meng H, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Jun 7;7:287. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-287. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16756683 Free PMC article.
References
- Venter J.C., Adams,M.D., Myers,E.W., Li,P.W., Mural,R.J., Sutton,G.G., Smith,H.O., Yandell,M., Evans,C.A., Holt,R.A. et al. (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science, 291, 1304–1351. - PubMed
- Waterston R.H., Lindblad-Toh,K., Birney,E., Rogers,J., Abril,J.F., Agarwal,P., Agarwala,R., Ainscough,R., Alexandersson,M., An,P. et al. (2002) Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature, 420, 520–562. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous