Expression Profiler: next generation--an online platform for analysis of microarray data - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2004 Jul 1;32(Web Server issue):W465-70.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh470.
Affiliations
- PMID: 15215431
- PMCID: PMC441608
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh470
Expression Profiler: next generation--an online platform for analysis of microarray data
Misha Kapushesky et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004.
Abstract
Expression Profiler (EP, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/expressionprofiler) is a web-based platform for microarray gene expression and other functional genomics-related data analysis. The new architecture, Expression Profiler: next generation (EP:NG), modularizes the original design and allows individual analysis-task-related components to be developed by different groups and yet still seamlessly to work together and share the same user interface look and feel. Data analysis components for gene expression data preprocessing, missing value imputation, filtering, clustering methods, visualization, significant gene finding, between group analysis and other statistical components are available from the EBI (European Bioinformatics Institute) web site. The web-based design of Expression Profiler supports data sharing and collaborative analysis in a secure environment. Developed tools are integrated with the microarray gene expression database ArrayExpress and form the exploratory analytical front-end to those data. EP:NG is an open-source project, encouraging broad distribution and further extensions from the scientific community.
Figures
Figure 1
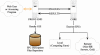
A typical analysis workflow. (A) After the user logs in, the data file is uploaded via the Data Upload component. (B) A subselection is made via the Data Selection component (the distribution histogram indicates the spread of the data and helps choose the range criteria). (C) Data Transformation is used to impute the missing values in the resulting data subset; clicking on the dataset name will return the new matrix with estimated missing values. (D) Hierarchical Clustering with tree collapsing is used to get the first overview of the data structure; (E) the hierarchical tree is displayed as an SVG image, allowing the user to zoom in on the tree in detail.
Figure 2
EP:NG system overview. All access is realized through the FRONT-END, which uses the Expression Profiler Component (EPC) description files to present a graphical user interface (GUI), and then sends the user's request to the CORE for either local execution on the Linux server farm at the EBI or remote processing on external (non-EBI) computer servers.
Figure 3
Similarity Search Visualization component. The user can select with the mouse a subset of conditions where the expression line-plot shows correlation by visual inspection. The chosen genes and conditions can be sent to other components for further analysis (e.g. to Data Selection).
Similar articles
- ArrayExpress--a public repository for microarray gene expression data at the EBI.
Parkinson H, Sarkans U, Shojatalab M, Abeygunawardena N, Contrino S, Coulson R, Farne A, Lara GG, Holloway E, Kapushesky M, Lilja P, Mukherjee G, Oezcimen A, Rayner T, Rocca-Serra P, Sharma A, Sansone S, Brazma A. Parkinson H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 1;33(Database issue):D553-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki056. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15608260 Free PMC article. - Plant-based microarray data at the European Bioinformatics Institute. Introducing AtMIAMExpress, a submission tool for Arabidopsis gene expression data to ArrayExpress.
Mukherjee G, Abeygunawardena N, Parkinson H, Contrino S, Durinck S, Farne A, Holloway E, Lilja P, Moreau Y, Oezcimen A, Rayner T, Sharma A, Brazma A, Sarkans U, Shojatalab M. Mukherjee G, et al. Plant Physiol. 2005 Oct;139(2):632-6. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.063156. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16219923 Free PMC article. - ArrayExpress--a public database of microarray experiments and gene expression profiles.
Parkinson H, Kapushesky M, Shojatalab M, Abeygunawardena N, Coulson R, Farne A, Holloway E, Kolesnykov N, Lilja P, Lukk M, Mani R, Rayner T, Sharma A, William E, Sarkans U, Brazma A. Parkinson H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D747-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl995. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17132828 Free PMC article. - MILANO--custom annotation of microarray results using automatic literature searches.
Rubinstein R, Simon I. Rubinstein R, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jan 20;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-12. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15661078 Free PMC article. - High-dimensional biology in obstetrics and gynecology: functional genomics in microarray studies.
Romero R, Tromp G. Romero R, et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006 Aug;195(2):360-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2006.06.077. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006. PMID: 16890547 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- MicroGen: a MIAME compliant web system for microarray experiment information and workflow management.
Burgarella S, Cattaneo D, Pinciroli F, Masseroli M. Burgarella S, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Dec 1;6 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-S4-S6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16351755 Free PMC article. - Bioinformatics resources for cancer research with an emphasis on gene function and structure prediction tools.
Kihara D, Yang YD, Hawkins T. Kihara D, et al. Cancer Inform. 2007 Feb 7;2:25-35. Cancer Inform. 2007. PMID: 19458756 Free PMC article. - Gitools: analysis and visualisation of genomic data using interactive heat-maps.
Perez-Llamas C, Lopez-Bigas N. Perez-Llamas C, et al. PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019541. Epub 2011 May 13. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21602921 Free PMC article. - High-throughput processing and normalization of one-color microarrays for transcriptional meta-analyses.
Dozmorov MG, Wren JD. Dozmorov MG, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Oct 18;12 Suppl 10(Suppl 10):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-S10-S2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 22166002 Free PMC article. - MAGMA: analysis of two-channel microarrays made easy.
Rehrauer H, Zoller S, Schlapbach R. Rehrauer H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W86-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm302. Epub 2007 May 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17517778 Free PMC article.
References
- Quackenbush J. (2001) Computational analysis of microarray data. Nature Rev. Genet., 2, 418–427. - PubMed
- Brazma A., Parkinson,H., Sarkans,U., Shojatalab,M., Vilo,J., Abeygunawardena,N., Holloway,E., Kapushesky,M., Kemmeren,P., Lara,G.G., Oezcimen,A., Rocca-Serra,P. and Sansone,S. (2003) ArrayExpress—a public repository for microarray gene expression data at the EBI. Nucleic Acids Res., 31, 68–71. - PMC - PubMed
- Vilo J., Kapushesky,M., Kemmeren,P., Sarkans,U. and Brazma,A. (2003) Expression Profiler. In Parmigiani,G., Garret,E.S., Irizarry,R. and Zeger,S.L. (eds), The Analysis of Gene Expression Data: Methods and Software. Springer Verlag, New York.
- Ihaka R. and Gentleman,R. (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat., 5, 299–314.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources