Gene duplication: the genomic trade in spare parts - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Gene duplication: the genomic trade in spare parts
Matthew Hurles. PLoS Biol. 2004 Jul.
Abstract
The duplication of genes and their subsequent diversification has had a key role in evolution. A range of fates can befall a duplicated gene
Figures
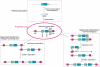
Figure 1. Mechanism of Gene Duplication
A two-exon gene is flanked by two Alu elements and a neighbouring replication termination site. Recombination between the two Alu elements leads to a tandem duplication event, as does a replication error instigated by the replication termination site. Retrotransposition of the mRNA of the gene leads to the random integration of an intron-less paralogue at a distinct genomic location.
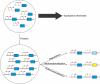
Figure 2. Fates of Duplicate Genes
A new duplication in a gene (blue) with two tissue-specific promoters (arrows) arises in a population of single copy genes. Fixation within the population results in a minority of cases. After fixation, one gene is inactivated (degradation) or assumes a new function (neofunctionalization), or the expression pattern of the original gene is partitioned between the two duplicates as one promoter is silenced in each duplicate in a complementary manner (subfunctionalization).
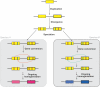
Figure 3. Concerted Evolution
Different gene conversion events homogenize minimally diverged duplicate genes in each daughter species (A and B), with the result that while paralogues are highly similar, orthologues diverge over time.
Similar articles
- All genomes great and small.
Knight J. Knight J. Nature. 2002 May 23;417(6887):374-6. doi: 10.1038/417374a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12024187 No abstract available. - Gene duplication and evolution.
Zhang L, Gaut BS, Vision TJ. Zhang L, et al. Science. 2001 Aug 31;293(5535):1551. Science. 2001. PMID: 11550701 No abstract available. - Evolution after gene duplication: models, mechanisms, sequences, systems, and organisms.
Roth C, Rastogi S, Arvestad L, Dittmar K, Light S, Ekman D, Liberles DA. Roth C, et al. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2007 Jan 15;308(1):58-73. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.21124. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2007. PMID: 16838295 - On the origin and evolution of new genes--a genomic and experimental perspective.
Zhou Q, Wang W. Zhou Q, et al. J Genet Genomics. 2008 Nov;35(11):639-48. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60085-5. J Genet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 19022197 Review. - Expression divergence between duplicate genes.
Li WH, Yang J, Gu X. Li WH, et al. Trends Genet. 2005 Nov;21(11):602-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Trends Genet. 2005. PMID: 16140417 Review.
Cited by
- Genome-Wide Characterization and Analysis of R2R3-MYB Genes Related to Fruit Ripening and Stress Response in Banana (Musa acuminata L. AAA Group, cv. 'Cavendish').
Wang Z, Yao X, Jia C, Zheng Y, Lin Q, Wang J, Liu J, Zhu Z, Peng L, Xu B, Cong X, Jin Z. Wang Z, et al. Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;12(1):152. doi: 10.3390/plants12010152. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616281 Free PMC article. - Evolutionary tinkering of the expression of PDF1s suggests their joint effect on zinc tolerance and the response to pathogen attack.
Nguyen NN, Ranwez V, Vile D, Soulié MC, Dellagi A, Expert D, Gosti F. Nguyen NN, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2014 Mar 11;5:70. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00070. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24653728 Free PMC article. - Lineage-Specific Genes and Family Expansions in Dictyostelid Genomes Display Expression Bias and Evolutionary Diversification during Development.
Luna SK, Chain FJJ. Luna SK, et al. Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 16;12(10):1628. doi: 10.3390/genes12101628. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681022 Free PMC article. - i-ADHoRe 3.0--fast and sensitive detection of genomic homology in extremely large data sets.
Proost S, Fostier J, De Witte D, Dhoedt B, Demeester P, Van de Peer Y, Vandepoele K. Proost S, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(2):e11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr955. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22102584 Free PMC article. - Restriction and recruitment-gene duplication and the origin and evolution of snake venom toxins.
Hargreaves AD, Swain MT, Hegarty MJ, Logan DW, Mulley JF. Hargreaves AD, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Aug;6(8):2088-95. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu166. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25079342 Free PMC article.
References
- Dorus S, Gilbert SL, Forster ML, Barndt RJ, Lahn BT. The CDY-related gene family: Coordinated evolution in copy number, expression profile and protein sequence. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:1643–1650. - PubMed
- Emes RD, Goodstadt L, Winter EE, Ponting CP. Comparison of the genomes of human and mouse lays the foundation of genome zoology. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:701–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources