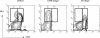Pre-B cell receptor expression is necessary for thymic stromal lymphopoietin responsiveness in the bone marrow but not in the liver environment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Pre-B cell receptor expression is necessary for thymic stromal lymphopoietin responsiveness in the bone marrow but not in the liver environment
Christian A J Vosshenrich et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004.
Abstract
IL-7 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) are two major cytokines controlling murine B cell development. IL-7 has been studied extensively, but only recently has it become possible to unravel the role of TSLP in detail. We studied the biological activities of TSLP in B cell development at distinct ages in the mouse. On the one hand, TSLP is able to give rise to a measurable B1 cell compartment derived from fetal liver pro-B cells, although, as is the case for B2 cells, it does not play a prevalent role in the development of this subset. On the other hand, TSLP drives the proliferation of pro-B cells from the fetal and neonatal liver, but in the bone marrow environment, B cell precursors require pre-B cell receptor expression for TSLP responsiveness.
Figures
Fig. 1.
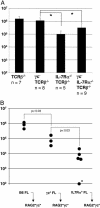
TSLP supports the generation of B1 cells. (A) Number of B1 cells in the peritoneal cavity of control, γc°, IL-7Rα°, and γc°IL-7Rα° mice. The number of CD5+IgM+ cells found in the peritoneal cavity of the indicated mouse strains at 12 weeks of age is shown. n, number of mice analyzed; *, P < 0.01. (B) Fetal liver precursors from γc° and IL7Rα° mice have a 10- and 100-fold reduced capacity, respectively, to generate B1 cells upon transfer into alymphoid recipient mice. The number of B220+IgM+ cells found in the peritoneal cavity of Rag2°γc° mice 5 weeks after reconstitution with 105 sorted, day-15 FL precursors from donor mice of the indicated genotypes is shown. *, below detection limit.
Fig. 2.
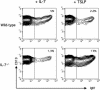
TSLP and IL-7 drive the generation of IgM+ cells. Phenotypic analysis of BM-derived C57BL/6(Upper) and C57BL/6.IL-7° (Lower) pro-B cells from 1- to 2-week-old mice cultured for 7 days in the presence of NIH 3T3 feeder cells supplemented with IL-7 (Left) or TSLP (Right). Cultures with IL-7 typically yield 100 times, and TSLP cultures 30 times, more cells than at the start of the culture (not shown). Numbers indicate the percentage of IgM+ cells among CD19+ cells.
Fig. 3.
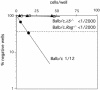
TSLP does not support the growth of BM B cell precursors from adult λ5° mice. Shown is a limiting dilution analysis of pro-B cells, isolated from adult BM of λ5° (▴), BALB/c.Rag2° (○), and BALB/c mice (•) in the presence of TSLP. The best-fit line crossing the origin is plotted. The dashed line intercepts the vertical axis at 37%. Data are representative of two experiments. No growth was observed in cultures not supplemented with either IL-7 or TSLP (not shown).
Fig. 4.
Expression of TSLP-R on BM precursor B cells from C57BL/6 and C57BL/6.Rag2° mice. BM cells from 8-week-old mice were stained for CD19, CD43, CD25, and TSLP-R. Shown are living (propidium iodide-negative) CD19+ BM cells from C57BL/6(Left) and C57BL/6.Rag2° (Right) mice. The expression of TSLP-R on pro-B cells (CD43+CD25–)(Upper) and pre-B cells (CD25+)(Lower) are shown as histograms. Gray shading indicates isotype control antibody.
Fig. 5.
The BM pro-B cell compartment in C57BL/6, C57BL/6.Rag2°, and H3 × Rag2° mice. BM cells from the indicated mice were stained for B220, CD43, HSA (30F1), and BP-1. Shown are the profiles of HSA versus BP-1 expression on gated B220+CD43+ BM cells. Cells of Hardy's fraction C (pro-B cells) and C′ (large pre-B cells) are boxed. Note the reduced level of expression of BP-1 on cells from fraction C′ in the BM of H3 × Rag2° mice.
Similar articles
- Characterization of thymic stromal-derived lymphopoietin (TSLP) in murine B cell development in vitro.
Ray RJ, Furlonger C, Williams DE, Paige CJ. Ray RJ, et al. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Jan;26(1):10-6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260103. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8566050 - Development of B cells in aged mice: decline in the ability of pro-B cells to respond to IL-7 but not to other growth factors.
Stephan RP, Lill-Elghanian DA, Witte PL. Stephan RP, et al. J Immunol. 1997 Feb 15;158(4):1598-609. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9029095 - Interleukin-7 contributes to human pro-B-cell development in a mouse stromal cell-dependent culture system.
Taguchi T, Takenouchi H, Shiozawa Y, Matsui J, Kitamura N, Miyagawa Y, Katagiri YU, Takahashi T, Okita H, Fujimoto J, Kiyokawa N. Taguchi T, et al. Exp Hematol. 2007 Sep;35(9):1398-407. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.05.019. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17656007 - Apoptosis and its modulation during B lymphopoiesis in mouse bone marrow.
Lu L, Osmond DG. Lu L, et al. Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:158-74. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933601 Review. - B-cell commitment, development and selection.
Hardy RR, Li YS, Allman D, Asano M, Gui M, Hayakawa K. Hardy RR, et al. Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:23-32. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933588 Review.
Cited by
- Human lymphoid development in the absence of common γ-chain receptor signaling.
Kohn LA, Seet CS, Scholes J, Codrea F, Chan R, Zaidi-Merchant S, Zhu Y, De Oliveira S, Kapoor N, Shah A, Abdel-Azim H, Kohn DB, Crooks GM. Kohn LA, et al. J Immunol. 2014 Jun 1;192(11):5050-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303496. Epub 2014 Apr 25. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24771849 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The Fetal-to-Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transition and its Role in Childhood Hematopoietic Malignancies.
Mack R, Zhang L, Breslin Sj P, Zhang J. Mack R, et al. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Dec;17(6):2059-2080. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10230-x. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 34424480 Free PMC article. Review. - B-1 B cell development in the fetus and adult.
Montecino-Rodriguez E, Dorshkind K. Montecino-Rodriguez E, et al. Immunity. 2012 Jan 27;36(1):13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.017. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22284417 Free PMC article. Review. - The absence of a microbiota enhances TSLP expression in mice with defective skin barrier but does not affect the severity of their allergic inflammation.
Yockey LJ, Demehri S, Turkoz M, Turkoz A, Ahern PP, Jassim O, Manivasagam S, Kearney JF, Gordon JI, Kopan R. Yockey LJ, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Dec;133(12):2714-2721. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.228. Epub 2013 May 22. J Invest Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23698100 Free PMC article. - Type I interferons protect neonates from acute inflammation through interleukin 10-producing B cells.
Zhang X, Deriaud E, Jiao X, Braun D, Leclerc C, Lo-Man R. Zhang X, et al. J Exp Med. 2007 May 14;204(5):1107-18. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062013. Epub 2007 May 7. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17485512 Free PMC article.
References
- Osmond, D. G. & Nossal, G. J. (1974) Cell Immunol. 13, 132–145. - PubMed
- Ehlich, A., Schaal, S., Gu, H., Kitamura, D., Muller, W. & Rajewsky, K. (1993) Cell 72, 695–704. - PubMed
- Coffman, R. L. & Weissman, I. L. (1983) J. Mol. Cell. Immunol. 1, 31–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases