Transcriptional regulation and binding of heat shock factor 1 and heat shock factor 2 to 32 human heat shock genes during thermal stress and differentiation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Transcriptional regulation and binding of heat shock factor 1 and heat shock factor 2 to 32 human heat shock genes during thermal stress and differentiation
Nathan D Trinklein et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004 Mar.
Abstract
Transcription of mammalian heat shock genes can be regulated by heat shock factors (HSF) 1 and 2. Although it has been shown previously that these factors respond to distinct stimuli, a broad analysis of the induction and function of these factors in living cells has not been performed. In our study, we assayed binding of human HSF1 and HSF2 at the promoters of 32 genes identified through LocusLink as heat shock genes in response to elevated temperature and hemin-induced differentiation in human K562 erythroleukemic cells using the chromatin immunoprecipitation technique. We also measured the induced expression of these genes under these 2 conditions. We found that 17 of the 32 genes were transcriptionally induced during heat shock, and HSF1 binding was detected at 15 of the 17 promoters. Nearly all the genes induced by heat shock were also induced to a lesser degree during hemin treatment. However, some genes were induced significantly more during hemin treatment than during heat shock. A new finding is that HSF1 and HSF2 bind to the same targets, but HSF1 binding is activated more by heat than by hemin treatment, and HSF2 binding is only activated by hemin treatment and not by heat. This technology also identified previously unknown HSF1 binding sites near genes that were previously shown to be heat inducible that may contribute to gene-specific regulation.
Figures
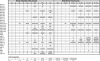
Fig 1.
Heat shock and hemin-induced gene expression patterns. The expression data for 32 genes during heat shock and hemin-induced differentiation show that many of the same genes are induced during heat shock and hemin treatment. Time points are listed at the top of the figure. The number of vertical bars in each box indicate the fold-induction of a given gene at that time point according to the key at the bottom of the figure
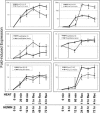
Fig 2.
Expression kinetics of 6 genes during heat shock and differentiation. Each panel displays the expression kinetics of a single gene during heat shock and hemin-induced differentiation. Fold-induction is shown in log scale on the y-axis for each panel. Time points for heat shock and differentiation are shown on the x-axis at the bottom of the graph
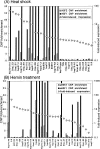
Fig 3.
HSF1 and HSF2 binding during heat shock and differentiation. (A) The bars indicate the degree of HSF1 and HSF2 binding to each promoter. Binding was quantitated by the ChIP fold-enrichment of each gene's promoter, which is shown on the scale on the left of the y-axis. Solid bars are from the heat shock HSF1 ChIP, and hatched bars are from the heat shock HSF2 ChIP. Both ChIPs were done 1 hour after heat shock. The white diamonds indicate the fold-induced expression at the 2-hour recovery time point after heat shock. Fold-induced expression values are shown on the right of the y-axis. (B) Same as panel A, except binding was assayed by ChIP 24 hours after the addition of hemin, and the diamonds indicate the fold-induced expression at the 72-hour time point of hemin treatment. HSF, heat shock factor; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation
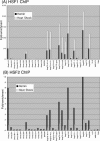
Fig 4.
Reciprocal binding of HSF1 and HSF2 during heat shock and differentiation. Binding was quantitated in both panels by the ChIP fold-enrichment of each gene's promoter. Fold-enrichment is shown on the y-axis. (A) The white and black bars show HSF1 binding during heat shock and hemin treatment, respectively. (B) The white and black bars show HSF2 binding during heat shock and hemin treatment, respectively. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation
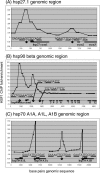
Fig 5.
HSF1 binding throughout the genomic regions of 5 heat shock genes. We assayed HSF1 binding at regularly spaced intervals throughout 3 genomic regions that contain 5 heat shock genes. Amplicons were designed to assay binding in the genomic regions of hsp27.1 (panel A), hsp90-β (panel B), and the region including hsp70-A1A, A1B, and A1L (panel C). White diamonds indicate HSE, and the sequence is shown for each. The enrichment of each amplicon is shown on the y-axis. HSF, heat shock factor; HSE, heat shock element
Similar articles
- Heat shock factor 2 (HSF2) contributes to inducible expression of hsp genes through interplay with HSF1.
Ostling P, Björk JK, Roos-Mattjus P, Mezger V, Sistonen L. Ostling P, et al. J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7077-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607556200. Epub 2007 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17213196 - Human heat shock factors 1 and 2 are differentially activated and can synergistically induce hsp70 gene transcription.
Sistonen L, Sarge KD, Morimoto RI. Sistonen L, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2087-99. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2087-2099.1994. Mol Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8114740 Free PMC article. - Activation of heat shock factor 2 during hemin-induced differentiation of human erythroleukemia cells.
Sistonen L, Sarge KD, Phillips B, Abravaya K, Morimoto RI. Sistonen L, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4104-11. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4104-4111.1992. Mol Cell Biol. 1992. PMID: 1508207 Free PMC article. - [Regulation of heat shock gene expression in response to stress].
Garbuz DG. Garbuz DG. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2017 May-Jun;51(3):400-417. doi: 10.7868/S0026898417020100. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2017. PMID: 28707656 Review. Russian. - Heat shock proteins and heat shock factor 1 in carcinogenesis and tumor development: an update.
Ciocca DR, Arrigo AP, Calderwood SK. Ciocca DR, et al. Arch Toxicol. 2013 Jan;87(1):19-48. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0918-z. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 22885793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- HSF2 binds to the Hsp90, Hsp27, and c-Fos promoters constitutively and modulates their expression.
Wilkerson DC, Skaggs HS, Sarge KD. Wilkerson DC, et al. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2007 Autumn;12(3):283-90. doi: 10.1379/csc-250.1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2007. PMID: 17915561 Free PMC article. - The Hsp70 chaperone system: distinct roles in erythrocyte formation and maintenance.
Mathangasinghe Y, Fauvet B, Jane SM, Goloubinoff P, Nillegoda NB. Mathangasinghe Y, et al. Haematologica. 2021 Jun 1;106(6):1519-1534. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.233056. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 33832207 Free PMC article. Review. - Up-regulation of Long Non-coding RNA TUG1 in Hibernating Thirteen-lined Ground Squirrels.
Frigault JJ, Lang-Ouellette D, Morin P Jr. Frigault JJ, et al. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Apr;14(2):113-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27132145 Free PMC article. - Monitoring the induction of heat shock factor 1/heat shock protein 70 expression following 17-allylamino-demethoxygeldanamycin treatment by positron emission tomography and optical reporter gene imaging.
Doubrovin M, Che JT, Serganova I, Moroz E, Solit DB, Ageyeva L, Kochetkova T, Pillarsetti N, Finn R, Rosen N, Blasberg RG. Doubrovin M, et al. Mol Imaging. 2012 Feb;11(1):67-76. Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22418029 Free PMC article. - Inducible hsp70 in the regulation of cancer cell survival: analysis of chaperone induction, expression and activity.
Zorzi E, Bonvini P. Zorzi E, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2011 Oct 21;3(4):3921-56. doi: 10.3390/cancers3043921. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24213118 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous