Effects of exogenous leptin on satiety and satiation in patients with lipodystrophy and leptin insufficiency - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effects of exogenous leptin on satiety and satiation in patients with lipodystrophy and leptin insufficiency
Jennifer R McDuffie et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Sep.
Abstract
To examine leptin's role in human appetite regulation, we studied recombinant methionyl human leptin's effects on satiation and satiety in a model of leptin insufficiency, lipodystrophy. Eight females with hypoleptinemia and lipodystrophy were given sc injections of A-100 (maximal dose, 200% of that predicted to normalize serum leptin) for 4 months. Satiation and satiety were determined before and again during leptin treatment. Satiation was measured as the time to voluntary cessation of eating from a standardized food array after a 12-h fast. Satiety was determined as the time to hunger sufficient to consume a full meal after consumption of a standardized preload. During leptin treatment, satiation time decreased (41.2 +/- 18.2 to 19.5 +/- 10.6 min; P = 0.01), satiety time increased (62.9 +/- 64.8 to 137.8 +/- 91.6 min; P = 0.04), energy consumed to produce satiation decreased (2034 +/- 405 to 1135 +/- 432 kcal or 8.5 +/- 1.7 to 4.7 +/- 1.8 MJ; P < 0.01), and the amount of food desired in the postabsorptive state decreased (P < 0.02). Ghrelin concentrations also decreased during leptin administration (284.3 +/- 127.9 to 140.6 +/- 104.5 pmol/liter; P < 0.002). We conclude that increased leptin in patients with lipodystrophy results in less caloric, shorter, more satiating meals and longer-lived satiety. These data support the hypothesis that leptin plays an important, permissive role in human appetite regulation.
Figures
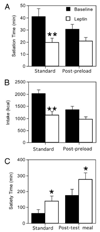
FIG. 1
Changes in indicators of appetite before and after leptin therapy. A, Satiation time; B, intake; C, satiety. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01.
Comment in
- Leptin and appetite control in lipodystrophy.
Ahima R, Osei SY. Ahima R, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Sep;89(9):4254-7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-1232. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15356017 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- The clinical efficacy of the adipocyte-derived hormone leptin in metabolic dysfunction.
Gorden P, Park JY. Gorden P, et al. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2006 Apr;112(2):114-8. doi: 10.1080/13813450600736117. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16931453 Review. - Leptin and appetite control in lipodystrophy.
Ahima R, Osei SY. Ahima R, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Sep;89(9):4254-7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-1232. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15356017 No abstract available. - Effect of leptin replacement on pituitary hormone regulation in patients with severe lipodystrophy.
Oral EA, Ruiz E, Andewelt A, Sebring N, Wagner AJ, Depaoli AM, Gorden P. Oral EA, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jul;87(7):3110-7. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.7.8591. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12107209 Clinical Trial. - Leptin Substitution in Patients With Lipodystrophy: Neural Correlates for Long-term Success in the Normalization of Eating Behavior.
Schlögl H, Müller K, Horstmann A, Miehle K, Püschel J, Villringer A, Pleger B, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M. Schlögl H, et al. Diabetes. 2016 Aug;65(8):2179-86. doi: 10.2337/db15-1550. Epub 2016 May 10. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27207511 Clinical Trial. - The clinical uses of leptin.
Gorden P, Gavrilova O. Gorden P, et al. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;3(6):655-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2003.06.006. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14644019 Review.
Cited by
- Low-affinity CCK-A receptors are coexpressed with leptin receptors in rat nodose ganglia: implications for leptin as a regulator of short-term satiety.
Li Y, Wu X, Zhou S, Owyang C. Li Y, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):G217-27. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00356.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21109591 Free PMC article. Retracted. - Partial and generalized lipodystrophy: comparison of baseline characteristics and response to metreleptin.
Diker-Cohen T, Cochran E, Gorden P, Brown RJ. Diker-Cohen T, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 May;100(5):1802-10. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4491. Epub 2015 Mar 3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25734254 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A rapid action plan to improve diagnosis and management of lipodystrophy syndromes.
Fourman LT, Lima JG, Simha V, Cappa M, Alyaarubi S, Montenegro R Jr, Akinci B, Santini F. Fourman LT, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 4;15:1383318. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1383318. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38952397 Free PMC article. Review. - Adipokines as Clinically Relevant Therapeutic Targets in Obesity.
Würfel M, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Ebert T, Kovacs P, Tönjes A, Breitfeld J. Würfel M, et al. Biomedicines. 2023 May 11;11(5):1427. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051427. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239098 Free PMC article. Review. - Metreleptin for injection to treat the complications of leptin deficiency in patients with congenital or acquired generalized lipodystrophy.
Meehan CA, Cochran E, Kassai A, Brown RJ, Gorden P. Meehan CA, et al. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016;9(1):59-68. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2016.1096772. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26465174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Havel PJ. Control of energy homeostasis and insulin action by adipocyte hormones: leptin, acylation stimulating protein, and adiponectin. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002;13:51–59. - PubMed
- Havel PJ, Townsend R, Chaump L, Teff K. High-fat meals reduce 24-h circulating leptin concentrations in women. Diabetes. 1999;48:334–341. - PubMed
- Weigle DS, Cummings DE, Newby PD, Breen PA, Frayo RS, Matthys CC, Callahan HS, Purnell JQ. Roles of leptin and ghrelin in the loss of body weight caused by a low fat, high carbohydrate diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:1577–1586. - PubMed
- Schwartz MW. Brain pathways controlling food intake and body weight. Exp Biol Med. 2001;226:978–981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Z01 HD000641/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-54387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 HD999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ZO1-HD-00641/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 HD000641-12/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources