Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor with related factors is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor with related factors is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer
D E B Swinson et al. Br J Cancer. 2004.
Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is commonly expressed in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and promotes a host of mechanisms involved in tumorigenesis. However, EGFR expression does not reliably predict prognosis or response to EGFR-targeted therapies. The data from two previous studies of a series of 181 consecutive surgically resected stage I-IIIA NSCLC patients who had survived in excess of 60 days were explored. Of these patients, tissue was available for evaluation of EGFR in 179 patients, carbonic anhydrase (CA) IX in 177 patients and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in 169 patients. We have previously reported an association between EGFR expression and MMP-9 expression. We have also reported that MMP-9 (P=0.001) and perinuclear (p)CA IX (P=0.03) but not EGFR expression were associated with a poor prognosis. Perinuclear CA IX expression was also associated with EGFR expression (P<0.001). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that coexpression of MMP-9 with EGFR conferred a worse prognosis than the expression of MMP-9 alone (P<0.001) and coexpression of EGFR and pCA IX conferred a worse prognosis than pCA IX alone (P=0.05). A model was then developed where the study population was divided into three groups: group 1 had expression of EGFR without coexpression of MMP-9 or pCA IX (number=21); group 2 had no expression of EGFR (number=75); and group 3 had coexpression of EGFR with pCA IX or MMP-9 or both (number=70). Group 3 had a worse prognosis than either groups 1 or 2 (P=0.0003 and 0.027, respectively) and group 1 had a better prognosis than group 2 (P=0.036). These data identify two cohorts of EGFR-positive patients with diametrically opposite prognoses. The group expressing either EGFR and or both MMP-9 and pCA IX may identify a group of patients with activated EGFR, which is of clinical relevance with the advent of EGFR-targeted therapies.
Figures
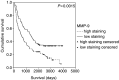
Figure 1
Kaplan–Meier survival curve and log-rank _P_-value for MMP-9 expression in NSCLC.
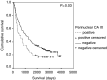
Figure 2
Kaplan–Meier survival curve and log-rank _P_-value for pCA IX expression in NSCLC.
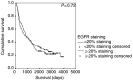
Figure 3
Kaplan–Meier survival curve and log-rank _P_-value for EGFR expression in NSCLC.
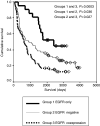
Figure 4
Survival curves for EGFR expression alone (group 1), EGFR negative (group 2) and coexpression of EGFR with either MMP-9 or CA IX or both (group 3).
Similar articles
- Carbonic anhydrase IX expression, a novel surrogate marker of tumor hypoxia, is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Swinson DE, Jones JL, Richardson D, Wykoff C, Turley H, Pastorek J, Taub N, Harris AL, O'Byrne KJ. Swinson DE, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2003 Feb 1;21(3):473-82. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.11.132. J Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12560438 - Expression of HIF-1alpha, CA IX, VEGF, and MMP-9 in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.
Kim SJ, Rabbani ZN, Dewhirst MW, Vujaskovic Z, Vollmer RT, Schreiber EG, Oosterwijk E, Kelley MJ. Kim SJ, et al. Lung Cancer. 2005 Sep;49(3):325-35. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.03.036. Lung Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15935515 - Quantitative analysis of carbonic anhydrase IX mRNA in human non-small cell lung cancer.
Simi L, Venturini G, Malentacchi F, Gelmini S, Andreani M, Janni A, Pastorekova S, Supuran CT, Pazzagli M, Orlando C. Simi L, et al. Lung Cancer. 2006 Apr;52(1):59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.11.017. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Lung Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16513206 - Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in non small cell lung cancer: relation to growth factor, protease and apoptosis pathways.
Swinson DE, Jones JL, Cox G, Richardson D, Harris AL, O'Byrne KJ. Swinson DE, et al. Int J Cancer. 2004 Aug 10;111(1):43-50. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20052. Int J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15185341 - Circulating oncoproteins HER2/neu, EGFR and CAIX (MN) as novel cancer biomarkers.
Carney WP. Carney WP. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007 May;7(3):309-19. doi: 10.1586/14737159.7.3.309. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007. PMID: 17489737 Review.
Cited by
- In Vivo Anticancer Evaluation of 6b, a Non-Covalent Imidazo[1,2-a]quinoxaline-Based Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor against Human Xenograft Tumor in Nude Mice.
Bhat ZR, Kumar M, Sharma N, Yadav UP, Singh T, Joshi G, Pujala B, Raja M, Chatterjee J, Tikoo K, Singh S, Kumar R. Bhat ZR, et al. Molecules. 2022 Aug 28;27(17):5540. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175540. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080307 Free PMC article. - The relationship between EGFR gain and VHL loss in lung adenocarcinoma and poor patient survival.
Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang S, Lu H, Chen J, Zhang Z, Jin Y, Zhu ZZ. Zhao Y, et al. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011 Dec;16(6):679-85. doi: 10.1007/s10147-011-0248-9. Epub 2011 May 11. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21556796 - Increased MET gene copy number negatively affects survival of surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients.
Cappuzzo F, Marchetti A, Skokan M, Rossi E, Gajapathy S, Felicioni L, Del Grammastro M, Sciarrotta MG, Buttitta F, Incarbone M, Toschi L, Finocchiaro G, Destro A, Terracciano L, Roncalli M, Alloisio M, Santoro A, Varella-Garcia M. Cappuzzo F, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Apr 1;27(10):1667-74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.1635. Epub 2009 Mar 2. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19255323 Free PMC article. - Oseltamivir phosphate monotherapy ablates tumor neovascularization, growth, and metastasis in mouse model of human triple-negative breast adenocarcinoma.
Haxho F, Allison S, Alghamdi F, Brodhagen L, Kuta VE, Abdulkhalek S, Neufeld RJ, Szewczuk MR. Haxho F, et al. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2014 Dec 9;6:191-203. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S74663. eCollection 2014. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2014. PMID: 25525387 Free PMC article. - PEGylated DX-1000: pharmacokinetics and antineoplastic activity of a specific plasmin inhibitor.
Devy L, Rabbani SA, Stochl M, Ruskowski M, Mackie I, Naa L, Toews M, van Gool R, Chen J, Ley A, Ladner RC, Dransfield DT, Henderikx P. Devy L, et al. Neoplasia. 2007 Nov;9(11):927-37. doi: 10.1593/neo.07544. Neoplasia. 2007. PMID: 18030361 Free PMC article.
References
- Abdollahi A, Bao R, Hamilton TC (1999) Lot1 is a growth suppressor gene down-regulated by the epidermal growth factor receptor ligands and encodes a nuclear zinc-finger protein. Oncogene 18: 6477–6487 - PubMed
- Bailey LR, Janas M, Schmidt K, Bindsley N, Wolf M, Grous J, Askaa J, Herbst R, Johnson D, Giaccone G (2004) Evaluation of epidermal growth factor receptor (egfr) as a predictive marker in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (nsclc) receiving first-line gentifinib combined with cisplatin based chemotherapy. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 23: 618
- Cohen S, Carpenter G, King Jr L (1981) Epidermal growth factor-receptor–protein kinase interactions. Prog Clin Biol Res 66: 557–567 - PubMed
- Cohen S, Carpenter G, King LJ (1980) Epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase interactions: co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem 255: 4834–4842 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous